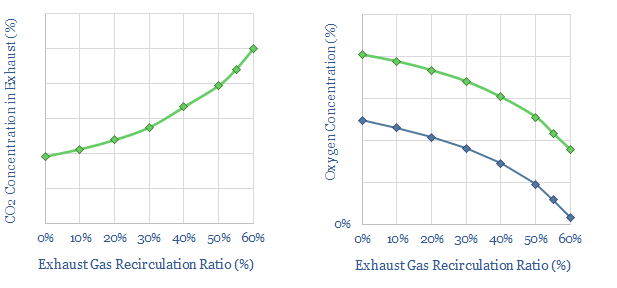
This data-file explores an alternative design for a combined cycle gas turbine, re-circulating exhaust gases (including CO2) after the combustion stage, back into the turbine’s compressor and combustion zones. The result is to increase the concentration of CO2 and thus improve the economics of carbon capture (chart below).
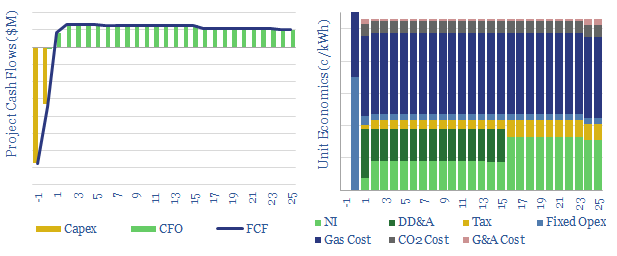
The data-file draws on costs data and operating parameters from several detailed technical papers, and model the economics. Even with EGR technology, it will still be challenging to decarbonize a conventional gas turbine for less than $100/ton (at which point blue hydrogen becomes competitive).
A short note is presented on the first tab, explaining the background, the theory and our main conclusions. You can stress-test the numbers and input assumptions in the model.