Digital
-
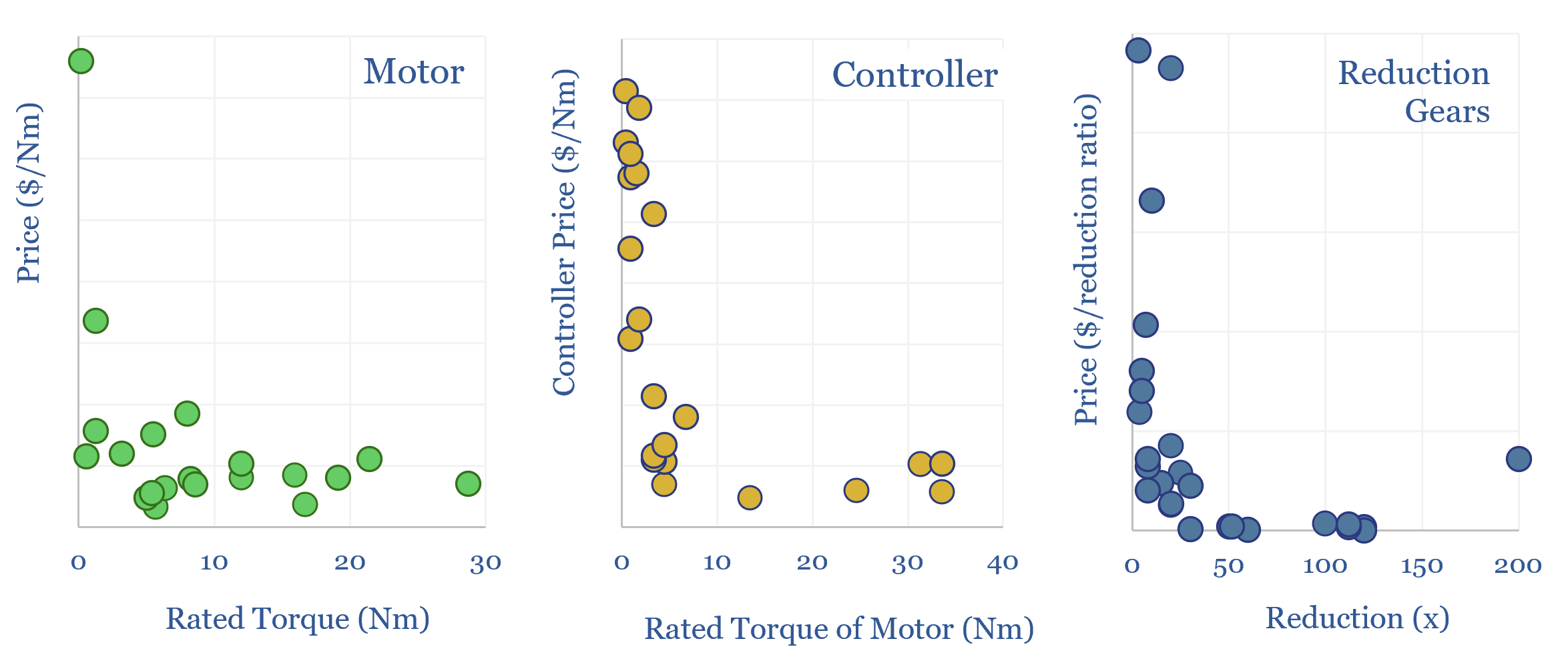
Servo motors: cost calculator?
Servo motors form a $16bn pa market, used in robotics, precision manufacturing equipment, CNC machines, aerospace and med-tech. This data-file estimates the costs of servo-motors, based on underlying controller costs, motor costs and reduction gear costs. Hence we have attempted a simple servo motor cost calculator.
-
Cognex: machine vision technology?
Cognex machine vision technology is used to ID products, inspect products, guide robotics and gauge sizes. This data-file reviews 20 case studies, with payback periods typically below 1-year. Increasing capabilities of AI are already extending use cases for these systems. We conclude this trend will continue, and also unlock more demand for industrial robots.
-
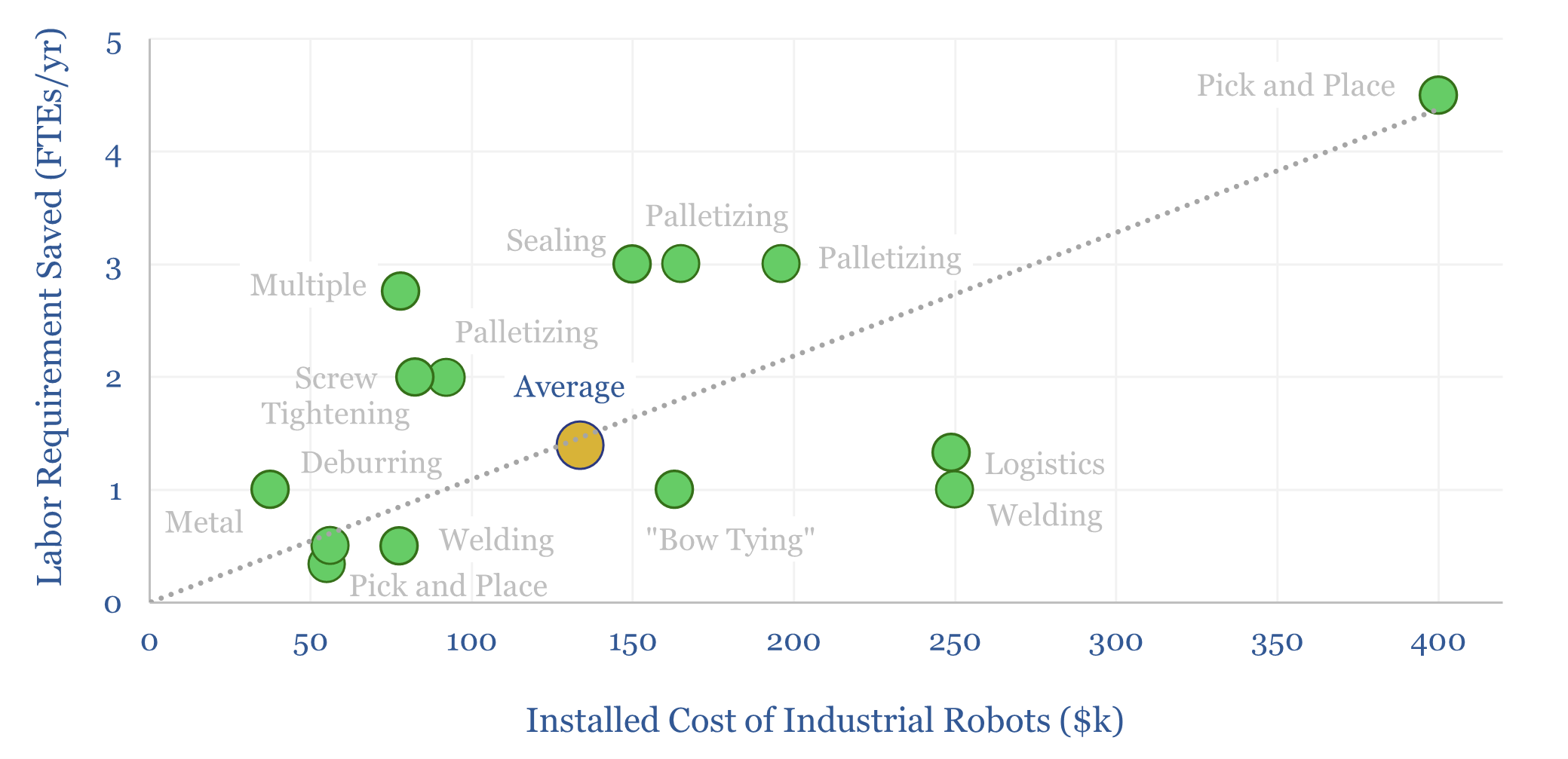
Industrial robots: arm’s reach?
5 million industrial robots have now been deployed globally, in an $18bn pa market. But growth could inflect, with the rise of AI, and to solve labor bottlenecks, as strategic value chains are re-shored. Robotics effectively substitute labor inputs for electricity inputs. Hence today’s 18-page report compiles 25 case studies, explores the theme and who…
-
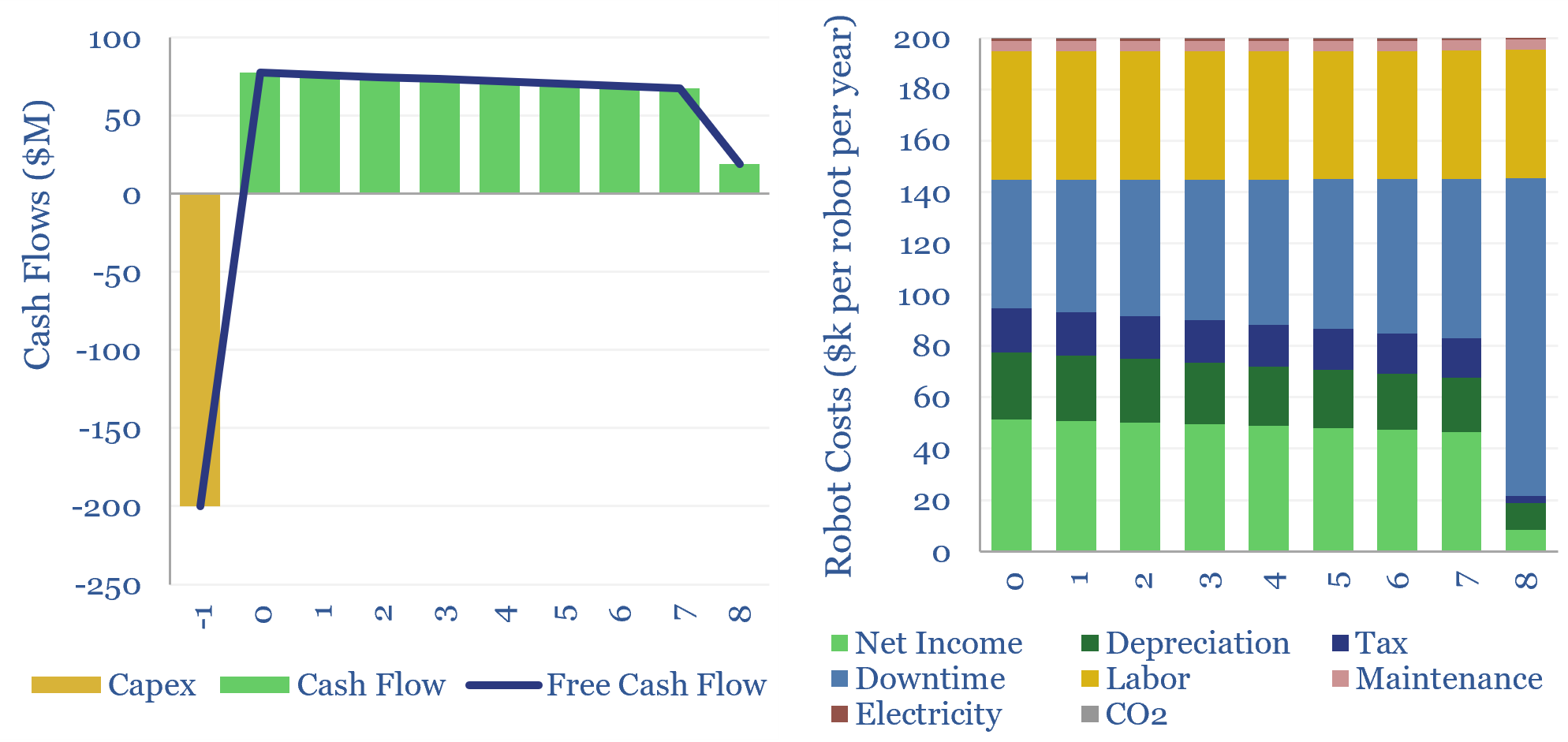
Industrial robot costs: robotic economics?
There are 5M industrial robots deployed globally. A typical example costs $130k to install, does incur costs to run, but displaces 1.3 FTE jobs, saves 50% total costs, and thus achieves a payback of 1.5-years and a project-level IRR of 65%. This data-file captures the economics of deploying industrial robots.
-
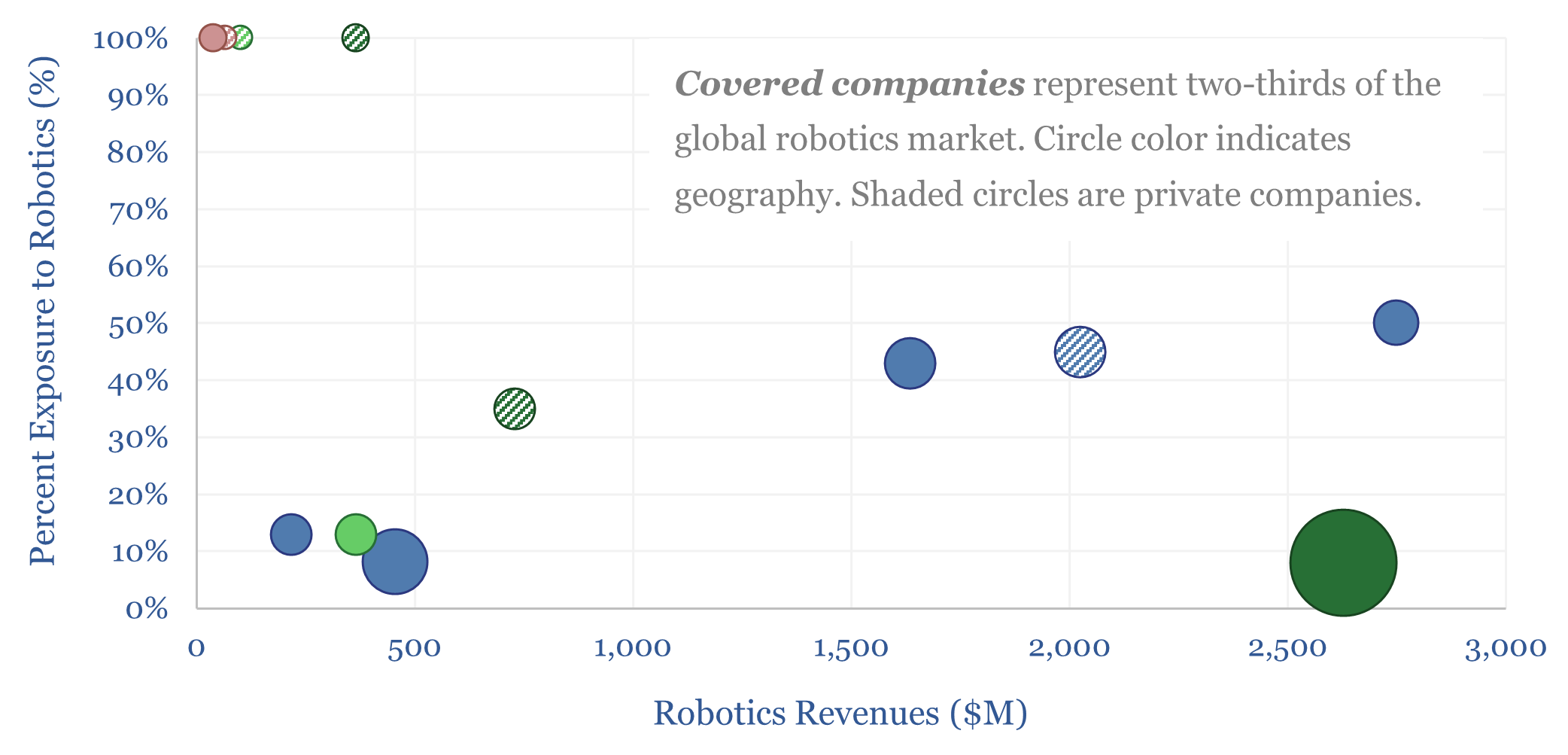
Industrial robotics companies screen?
This data-file profiles a dozen leading industrial robotics companies. The top five producers account for 60% of the global market, led by companies in Japan and Europe. Although China now comprises half of all industrial robot deployments, and thus Chinese companies are entering the robotics space.
-
Exail: inertial navigation technology?
Exail Technologies is listed in Paris and focuses on navigational and maritime robotics. It has a range of maritime drones, with applications from mine-sweeping to assisting with offshore wind, offshore oil and gas and civil infrastructure projects in coastal waters. A key to these drones is incorporating Exail’s Inertial Navigation Systems. We have reviewed the…
-
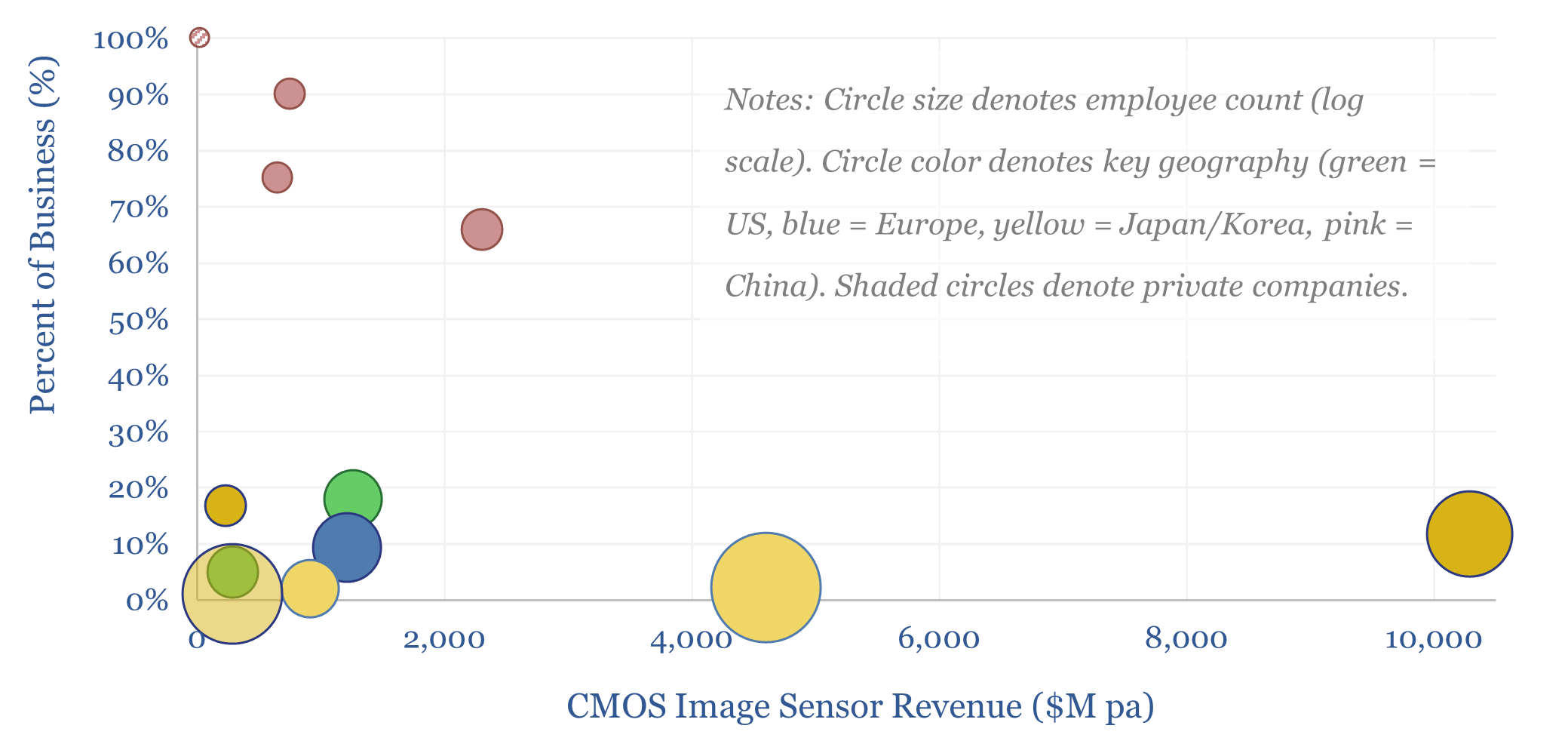
CMOS image sensors: leading companies?
This screen captures a dozen leading companies in CMOS image sensors, which underpin modern digital imagery, from cell-phone cameras to vehicle applications to industrial robots with “machine vision”. It is a concentrated landscape, with incumbents in Japan, Korea, the US and Europe, and fast-growing Chinese competitors. What upside here amidst the rise of AI?
-
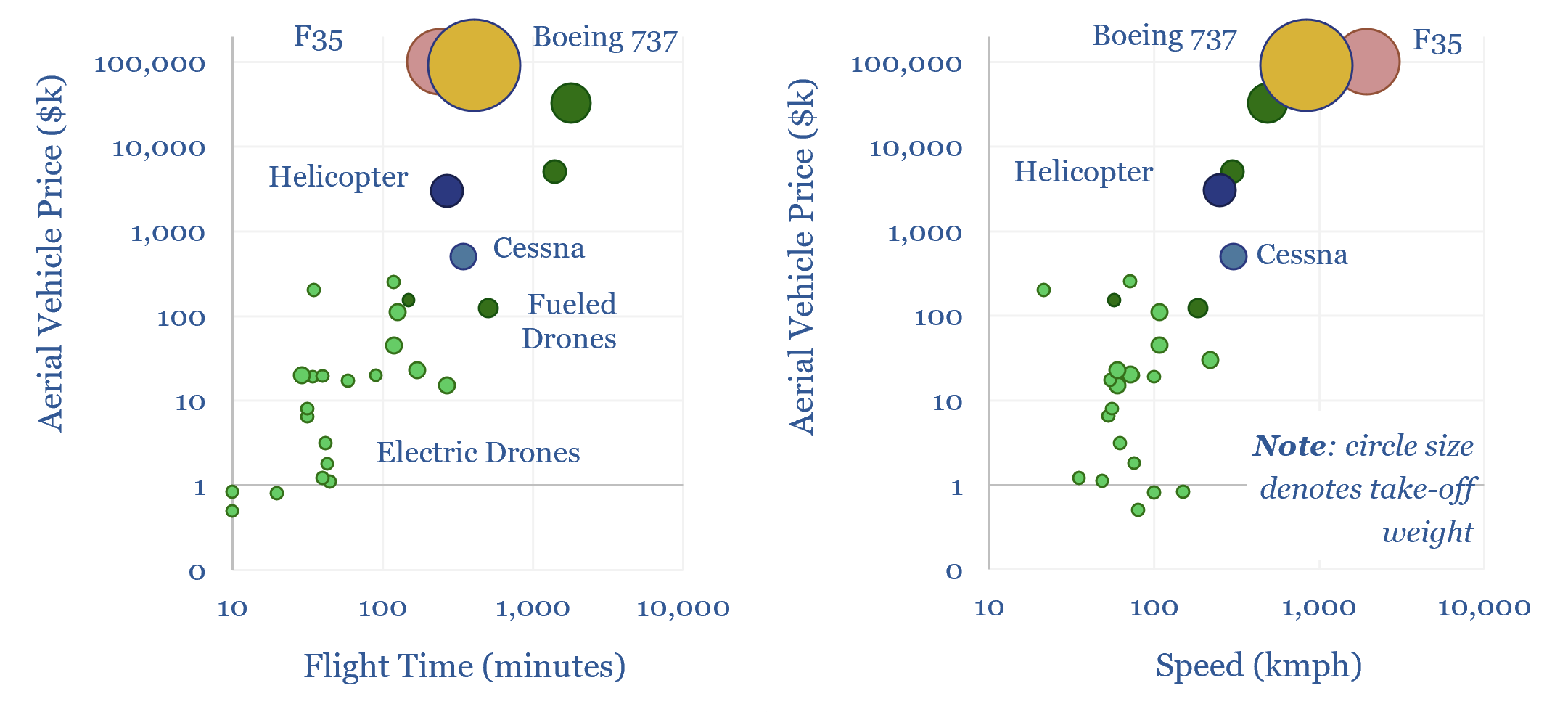
Drone deployment: vertical take-off?
Drones cost just $1k-100k each. They may use 95-99% less energy than traditional vehicles. Their ascent is being helped by battery technology and AI. Hence this 14-page report reviews recent progress from 40 leading drone companies. What stood out most was a re-shaping of the defense industry, plus helpful deflation across power grids, renewables, agriculture,…
-
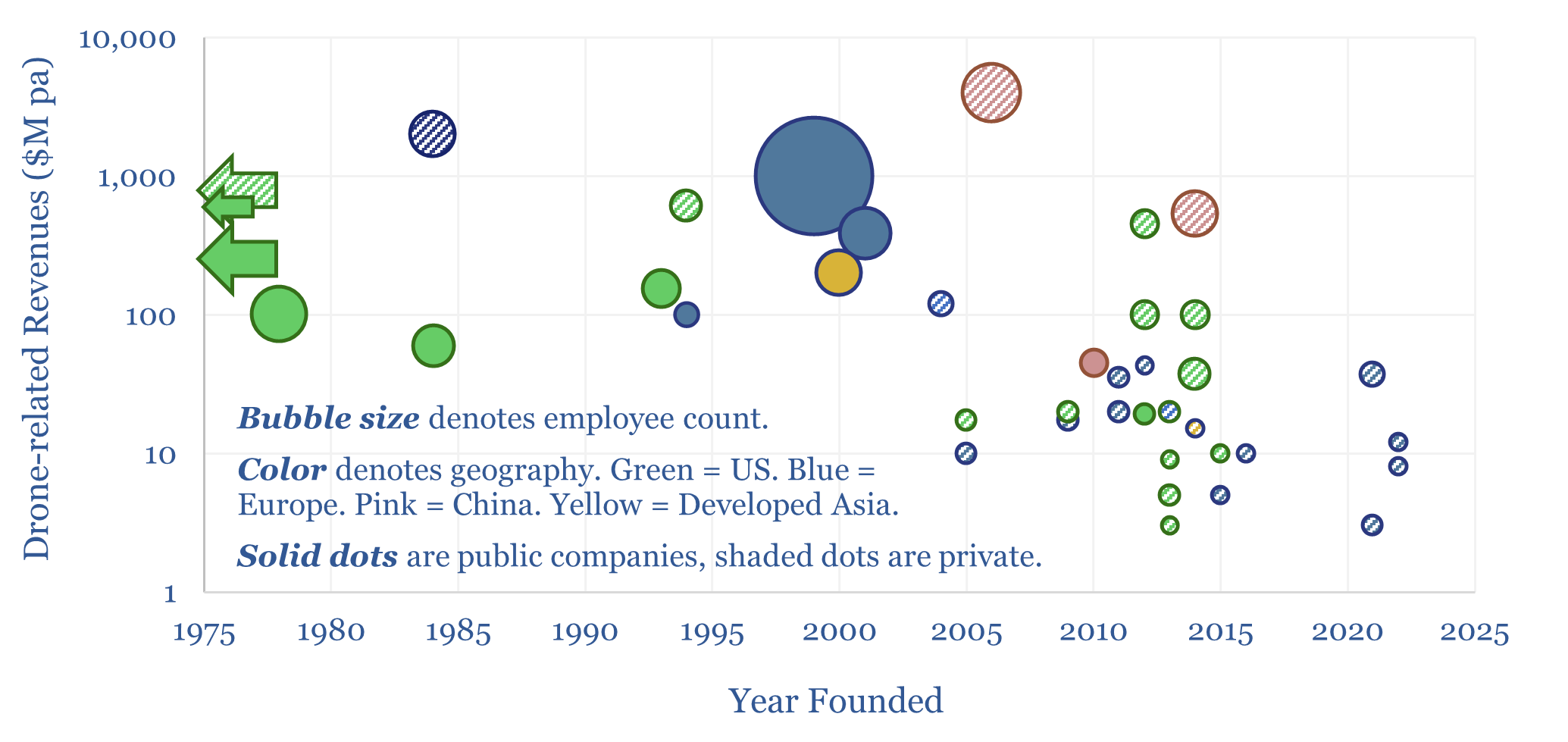
Drone companies: OEMs, inspection, defense and delivery?
This data-file is a screen of 40 leading drone companies, which either manufacturing drones for consumer, commercial and defense purposes; offer drone inspection services; or offer drone delivery services. It is a vibrant landscape, with over half of the companies founded after 2010, worth c$40bn pa, and creating c$120bn pa of economic benefits.
-
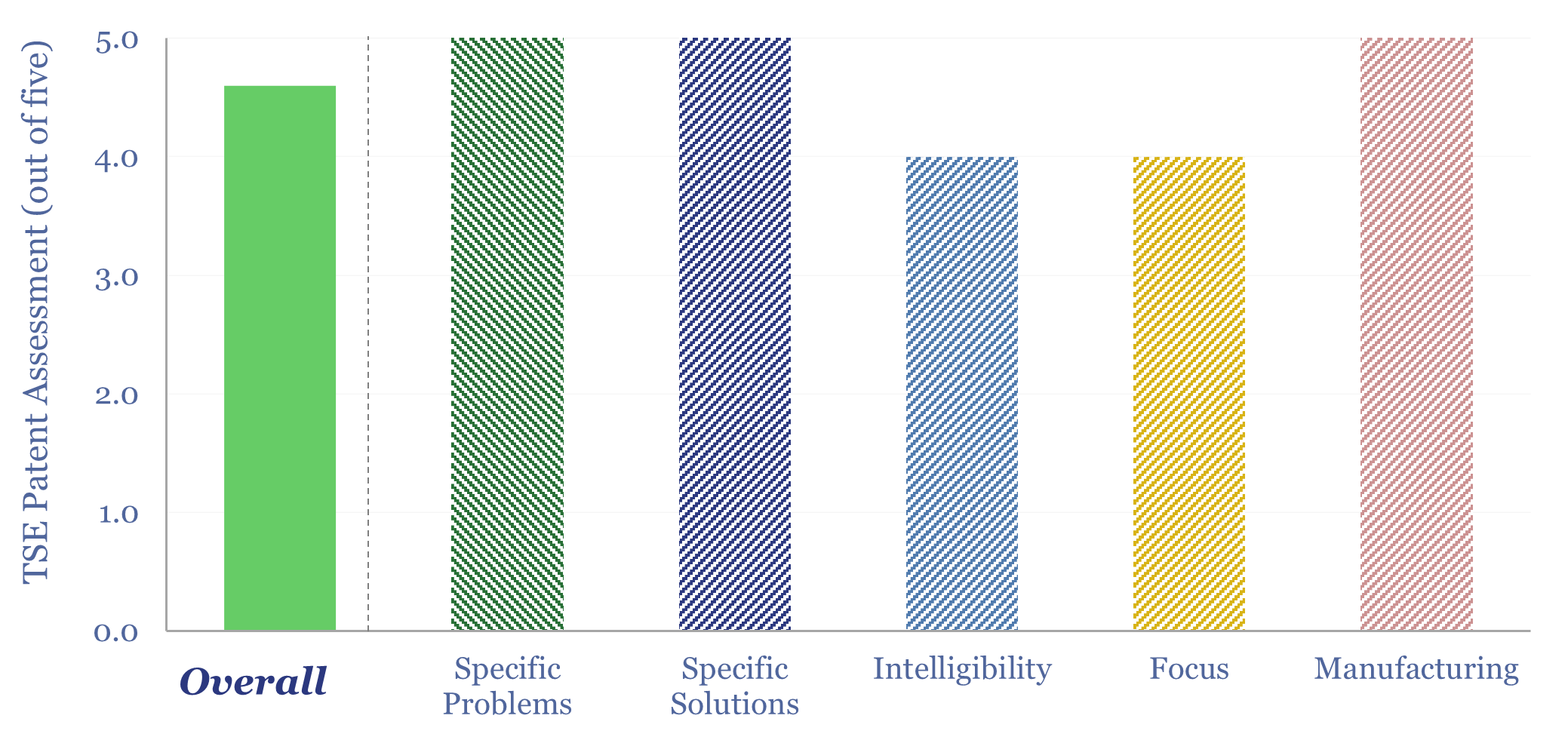
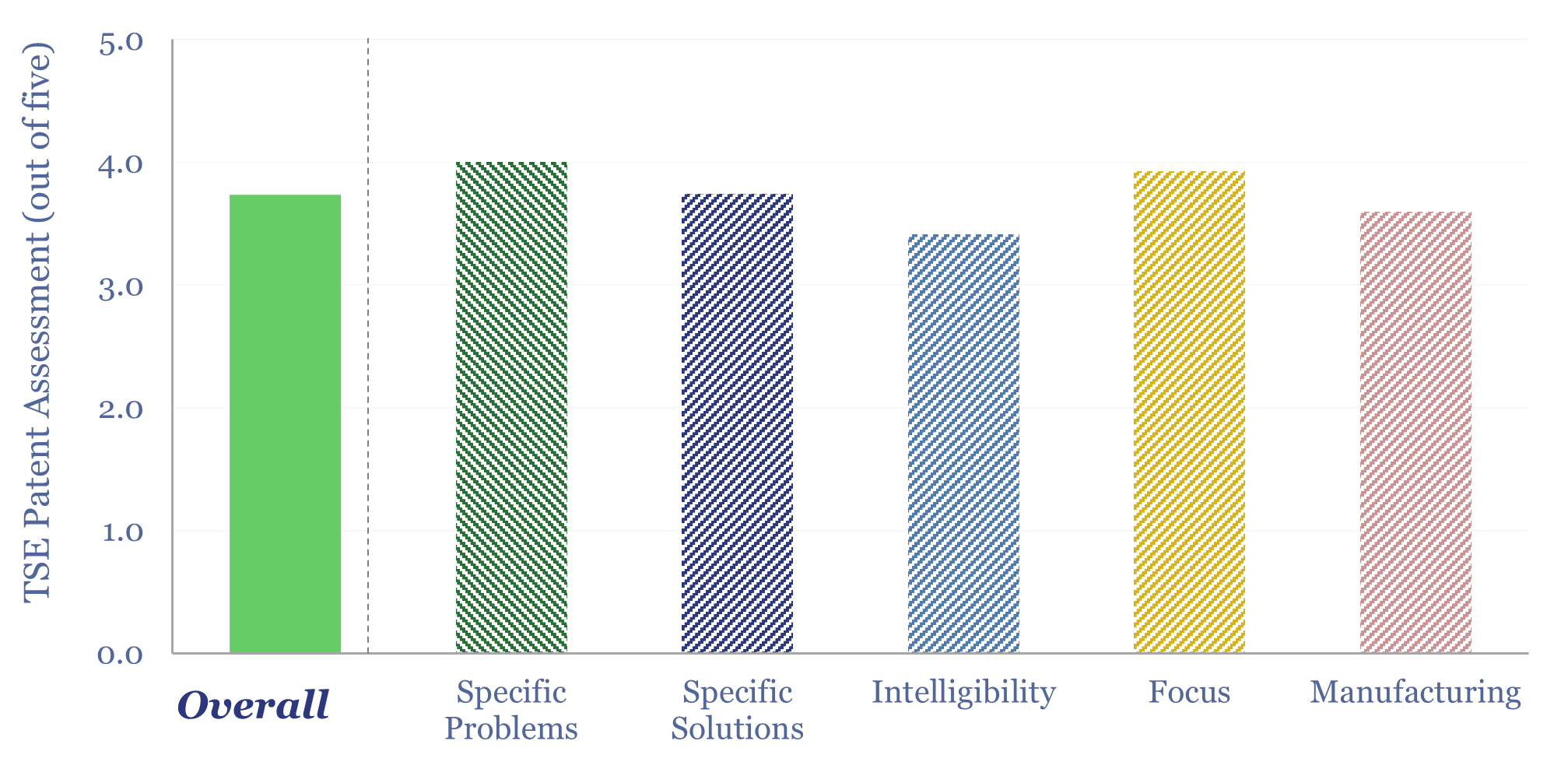
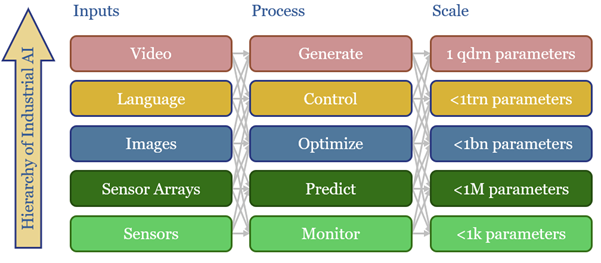
AI energy: industrial demand and the Jevons effect?
Increasingly efficient AI should unlock ever more widespread and more sophisticated uses of AI. This is shown by reviewing 40,000 patents from 200 industrial companies. This 15-page report summarizes notable companies, patent filings, and updates our 2030 forecasts for AI energy.
Content by Category
- Batteries (88)
- Biofuels (44)
- Carbon Intensity (49)
- CCS (63)
- CO2 Removals (9)
- Coal (38)
- Company Diligence (93)
- Data Models (833)
- Decarbonization (159)
- Demand (110)
- Digital (58)
- Downstream (44)
- Economic Model (203)
- Energy Efficiency (75)
- Hydrogen (63)
- Industry Data (278)
- LNG (48)
- Materials (82)
- Metals (79)
- Midstream (43)
- Natural Gas (148)
- Nature (76)
- Nuclear (23)
- Oil (164)
- Patents (38)
- Plastics (44)
- Power Grids (127)
- Renewables (149)
- Screen (116)
- Semiconductors (30)
- Shale (51)
- Solar (67)
- Supply-Demand (45)
- Vehicles (90)
- Wind (43)
- Written Research (351)