Economic Model
-
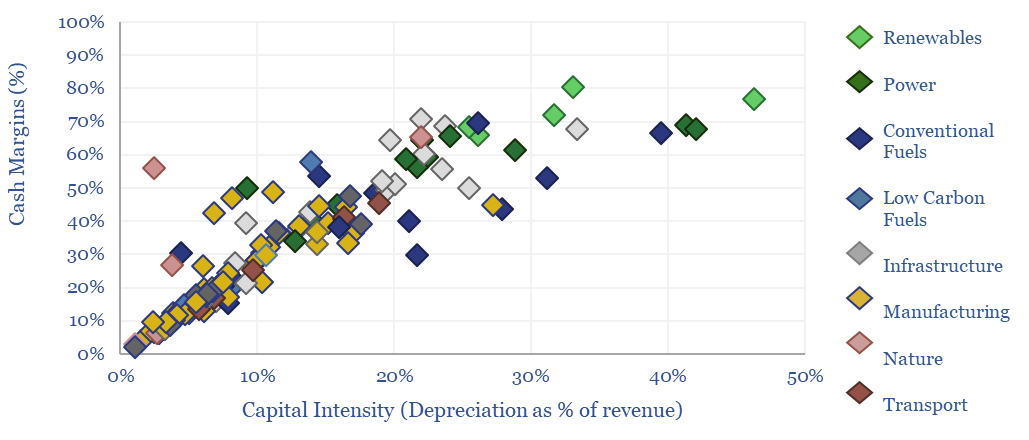
Energy economics: an overview?
This data-file provides an overview of energy economics, across 175 different economic models constructed by Thunder Said Energy, in order to put numbers in context. This helps to compare marginal costs, capex costs, energy intensity, interest rate sensitivity, and other key parameters that matter in the energy transition.
-
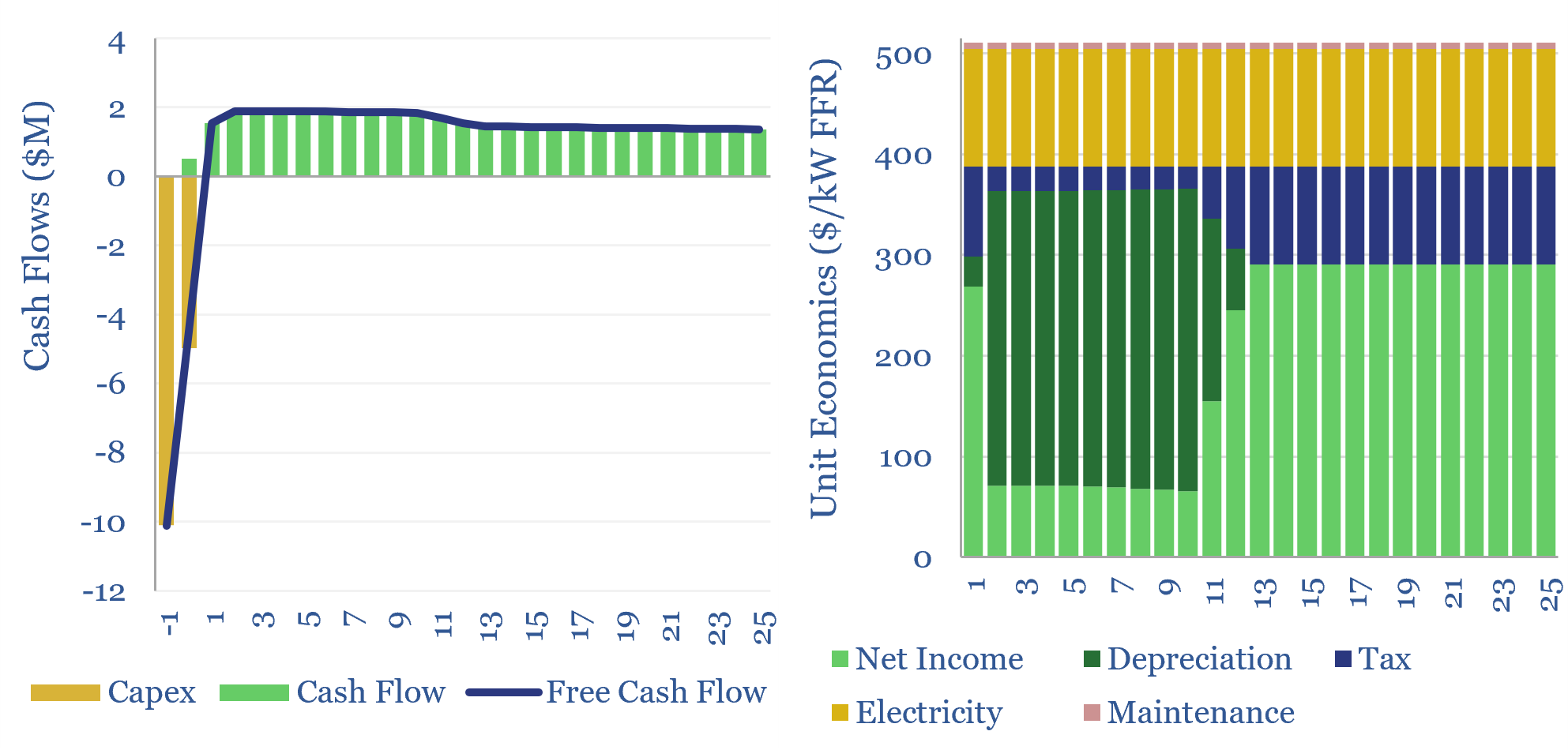
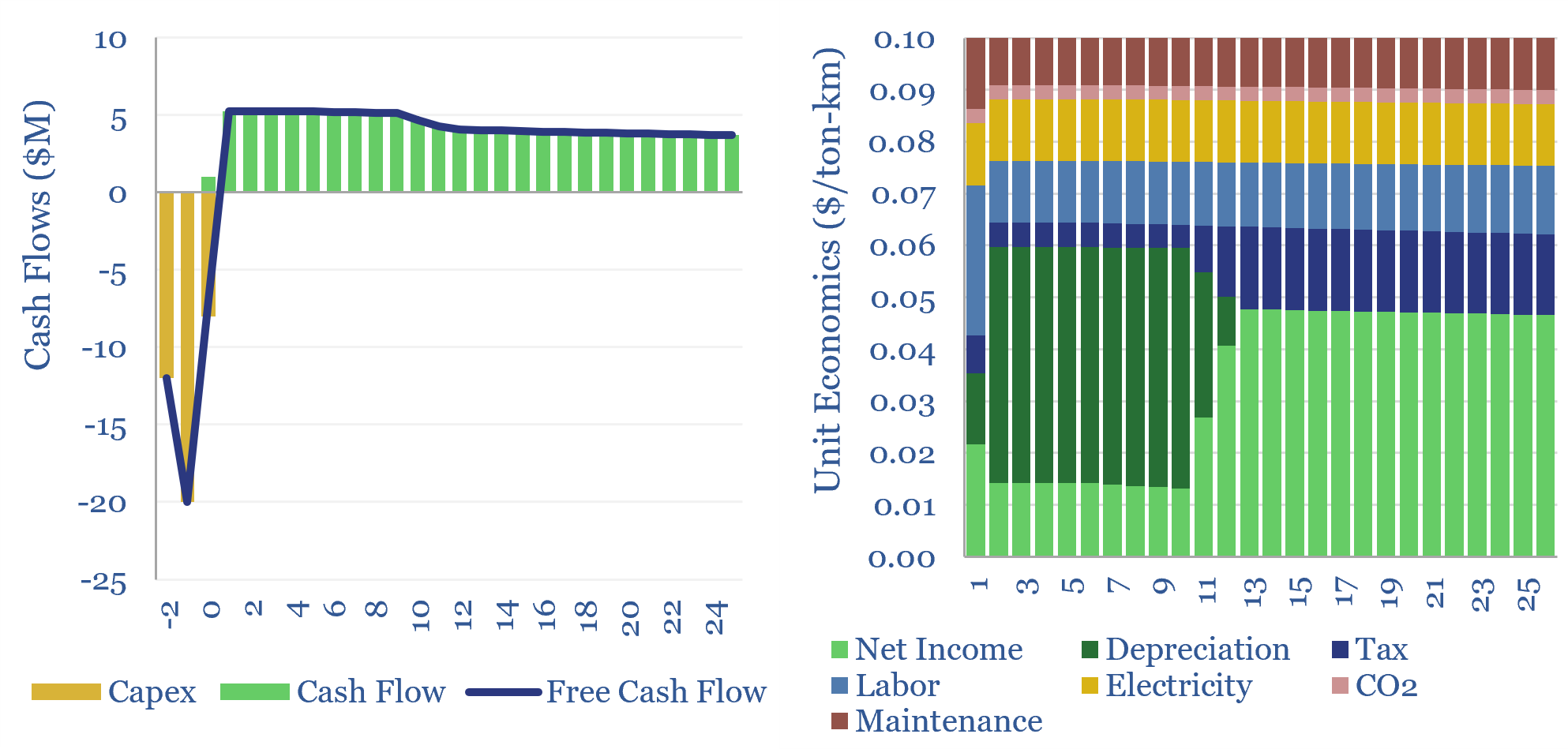
Economics of flywheels: fast frequency response?
The economics of flywheels can be stress-tested in this data-file, requiring a $500/kW fee for fast-frequency response, to generate a 10% IRR on c$10,000/kWh of capex costs, on a typical flywheel plant with around 15-minutes of energy storage. The rise of renewables and AI increasingly requires adding inertia to power grids. Flywheels may be one…
-
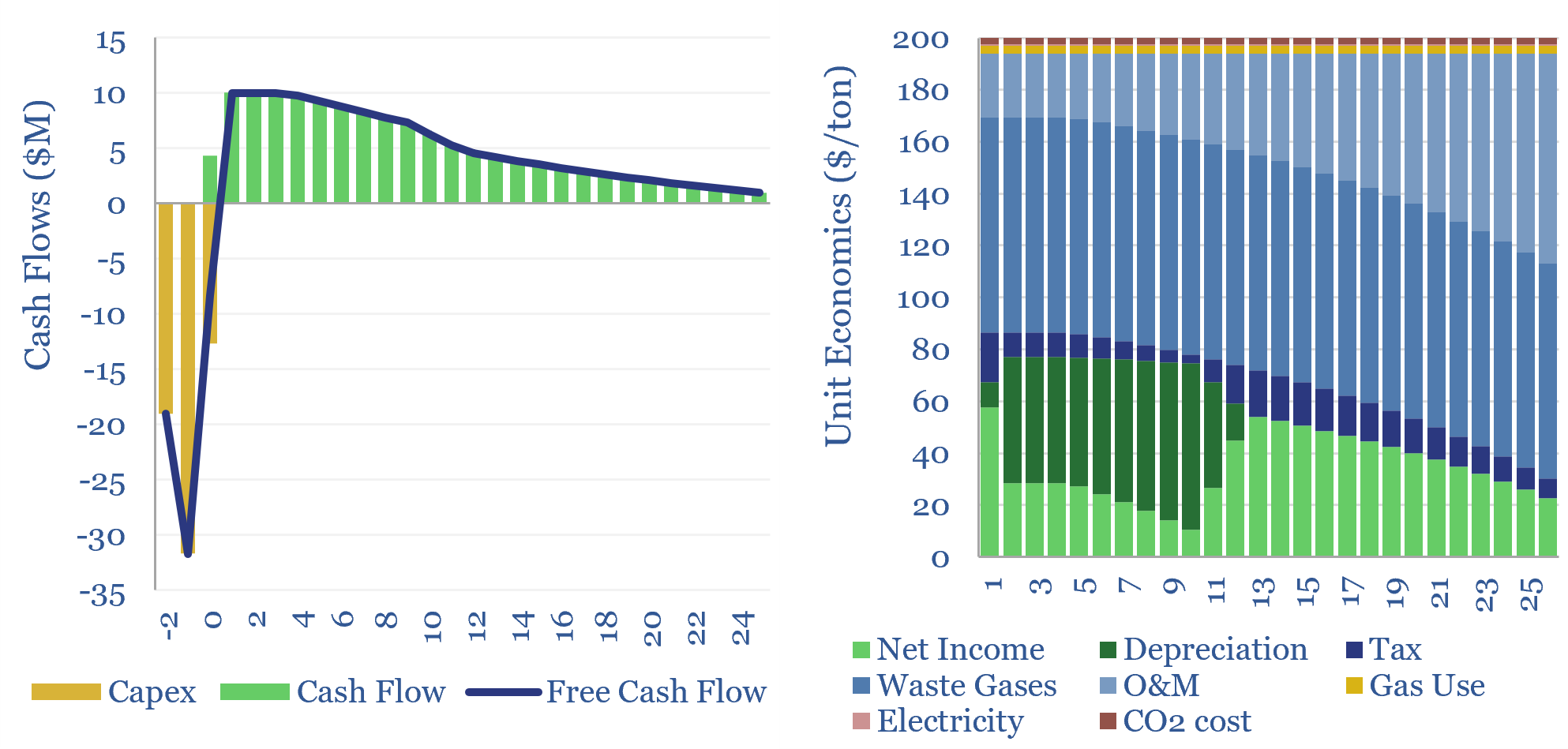
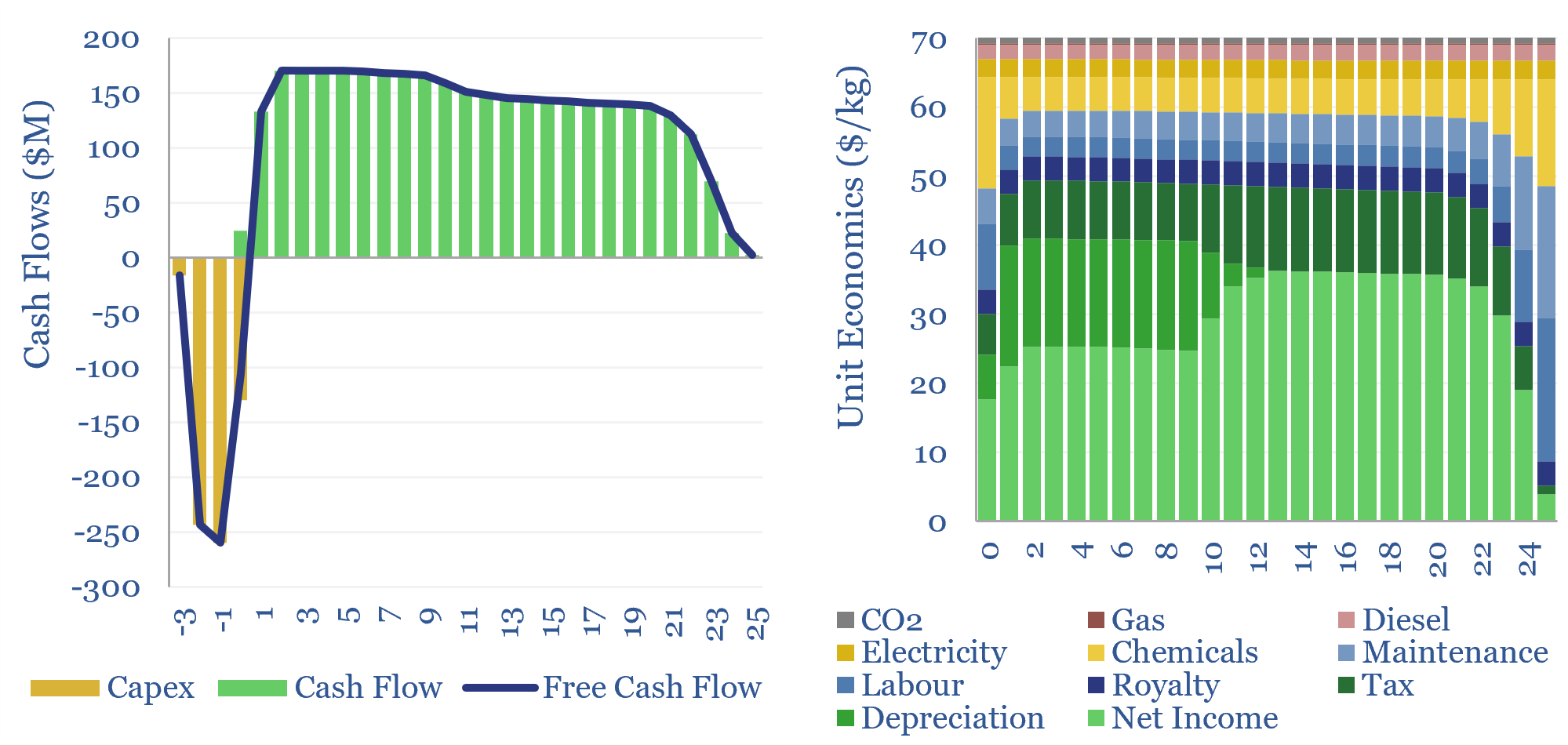
Helium production: the economics?
This economic model captures the production costs of helium, which is cryogenically extracted from low concentrations in natural gas. $200/mcf helium prices can support 10% IRRs on a resource with 2% helium content. $400-1,000/mcf spot prices can unlock 50-100% IRRs and trigger a capex boom. Economics can be stress-tested in this data-file.
-
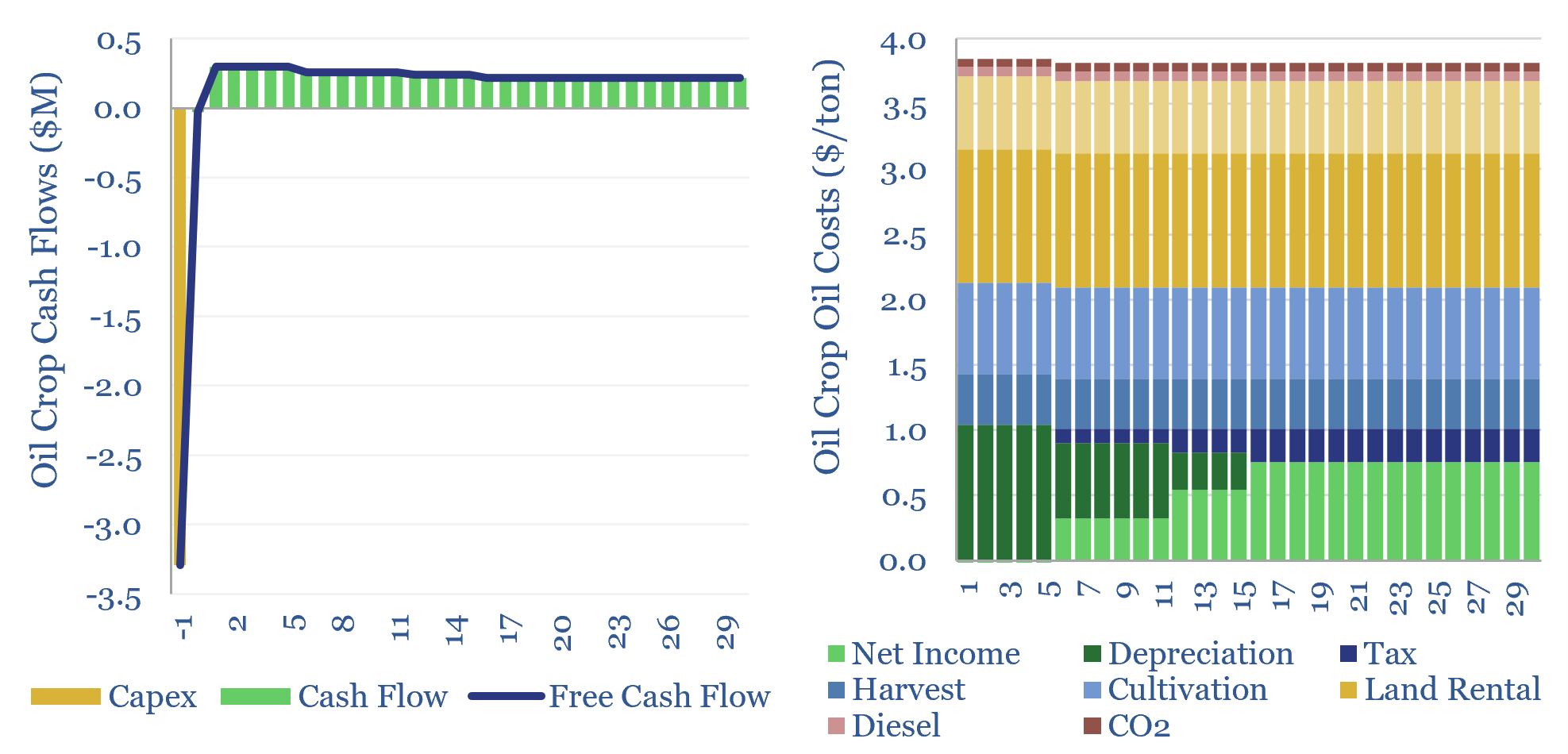
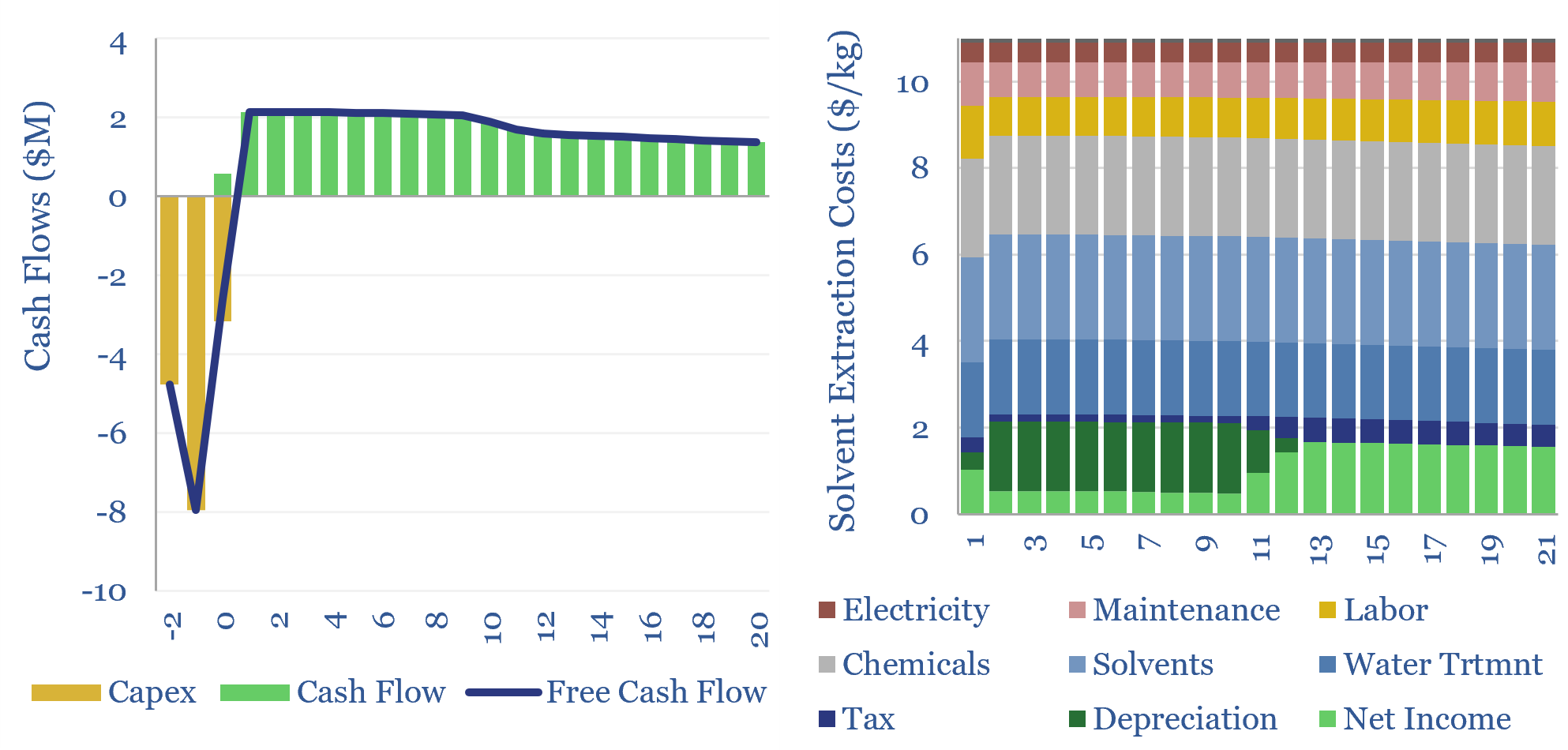
Oil crops: the economics?
The costs of oil crops, a crucial input for bio-diesel and SAF, will usually range from $900-1,200/ton, in order to generate acceptable 6-15% IRRs for producers. This translates into $3-4/gallon in feedstock costs. These oil crops also likely embed over 2 kg/gallon of CO2 intensity. The economics of oil crops can be stress-tested in this…
-
Investment casting: the economics?
Investment casting is fast and scalable, especially when producing hundreds-thousands of metal parts. $5/kg unlocks a 10% IRR on a 70% utilized metal-casting plant with $2,000/Tpa of capex, producing a typical 10kg aluminium product. This data-file captures the costs of investment-cast products, which can be stress-tested. 115MTpa of metals are cast every year, of which…
-
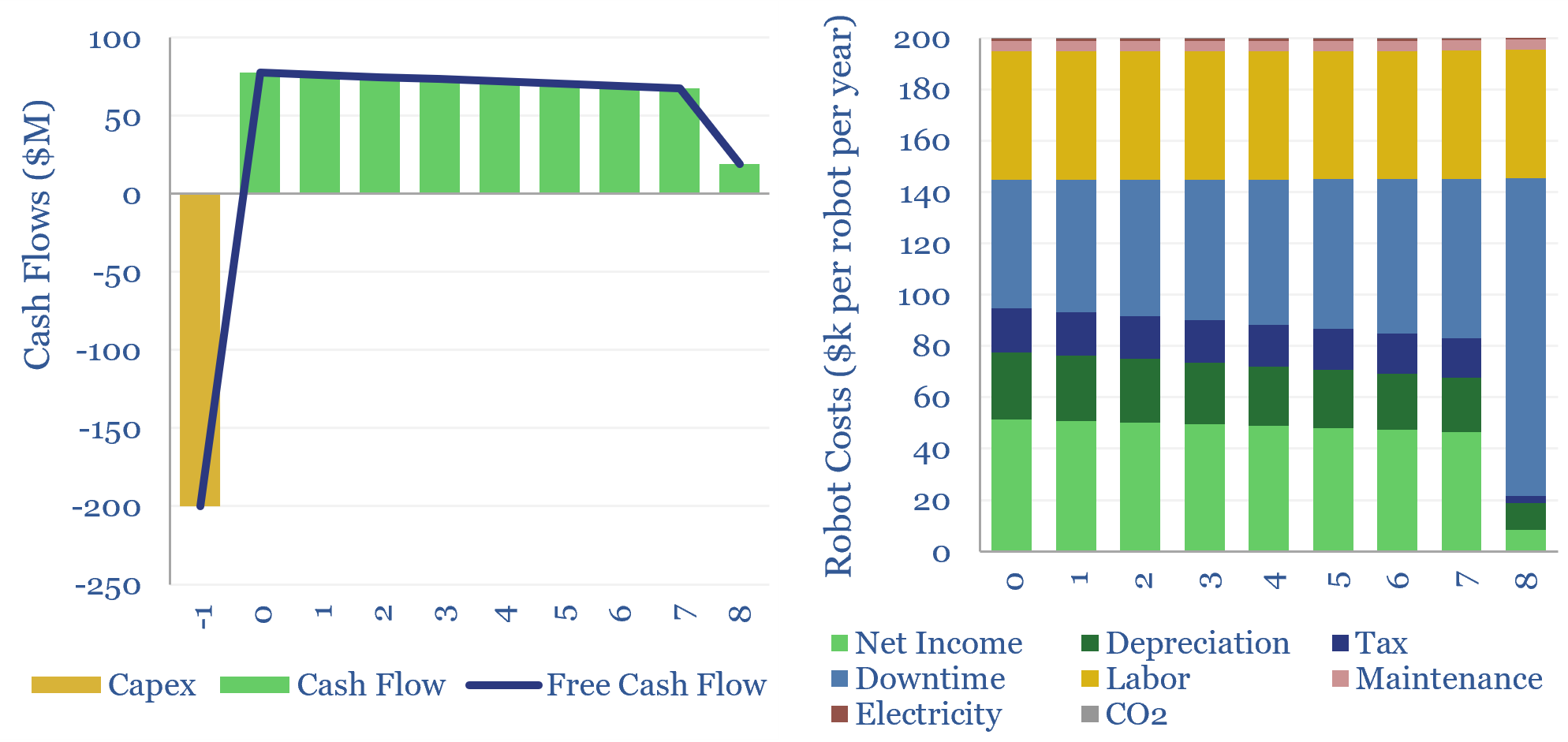
Industrial robot costs: robotic economics?
There are 5M industrial robots deployed globally. A typical example costs $130k to install, does incur costs to run, but displaces 1.3 FTE jobs, saves 50% total costs, and thus achieves a payback of 1.5-years and a project-level IRR of 65%. This data-file captures the economics of deploying industrial robots.
-
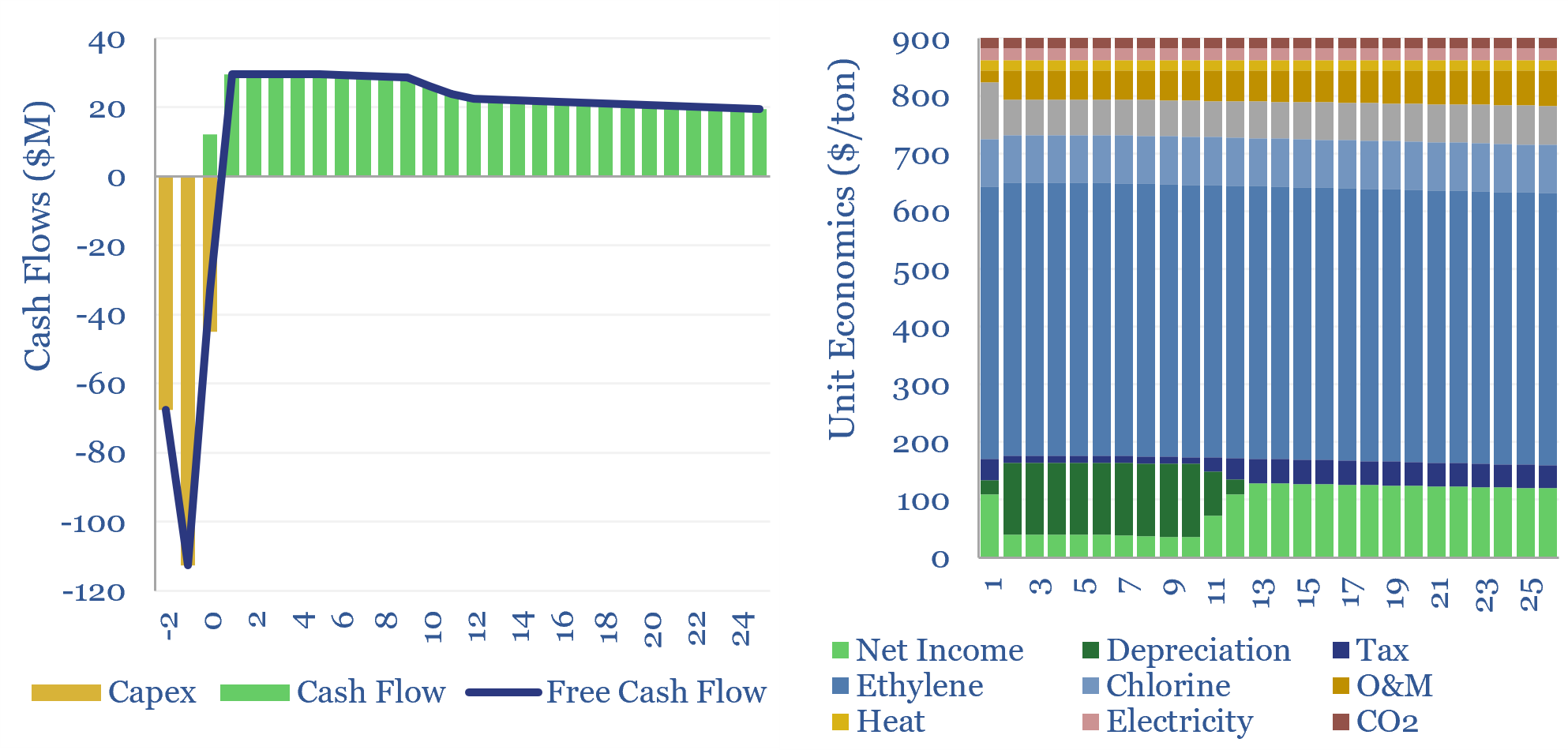
Poly Vinyl Chloride: the economics?
This data-file estimates the cost of PVC production and the cost of VCM production, from first principles, based on capex, input materials, heat, electricity, labor and other opex. As a rule of thumb, 10% IRRs require c$900/ton PVC and c$750/ton VCM, and PVC will embed around 2 tons of CO2 per ton of PVC. Numbers…
Content by Category
- Batteries (89)
- Biofuels (44)
- Carbon Intensity (49)
- CCS (63)
- CO2 Removals (9)
- Coal (38)
- Company Diligence (94)
- Data Models (838)
- Decarbonization (160)
- Demand (110)
- Digital (59)
- Downstream (44)
- Economic Model (204)
- Energy Efficiency (75)
- Hydrogen (63)
- Industry Data (279)
- LNG (48)
- Materials (82)
- Metals (80)
- Midstream (43)
- Natural Gas (148)
- Nature (76)
- Nuclear (23)
- Oil (164)
- Patents (38)
- Plastics (44)
- Power Grids (130)
- Renewables (149)
- Screen (117)
- Semiconductors (32)
- Shale (51)
- Solar (68)
- Supply-Demand (45)
- Vehicles (90)
- Wind (44)
- Written Research (354)