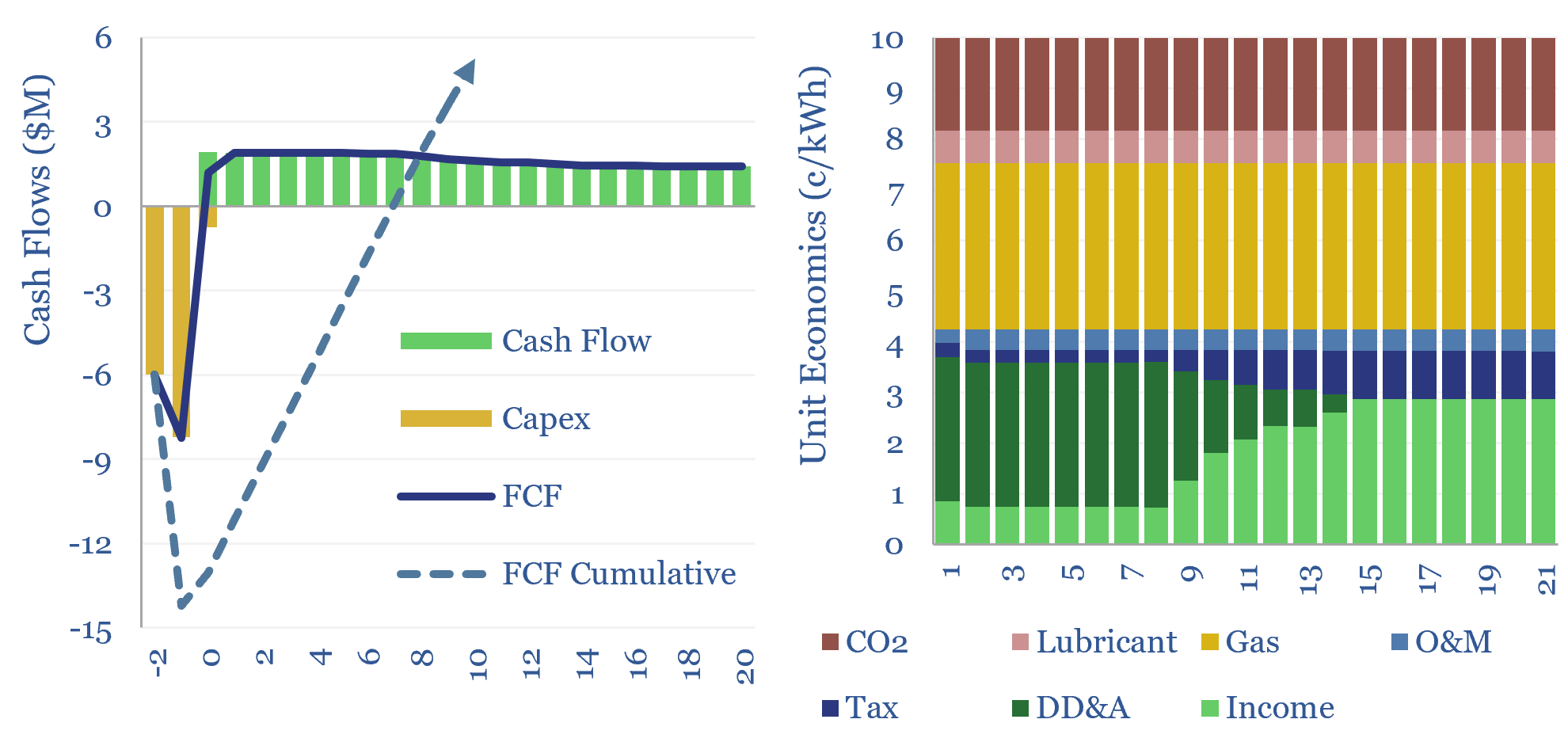
The economics costs of reciprocating gas engines are captured in this data-file. As a rule of thumb, a 5MW recip that costs $1,500/kW, runs with 60% utilization, and 40% efficiency, requires a 8-10c/kWh power price (or levelized cost) to generate a 10% IRR, depending on the CO2 price. Capex costs are derived from prior case studies in a backup tab of the model.
Reciprocating gas engines generate electricity as the combustion of natural gas pushes a piston through a cylinder, which is then connected to a crankshaft. The advantages and challenges of reciprocating gas engines are covered in our recent research report into different forms of gas generation.
In this data-file, the levelized cost of electricity from reciprocating gas engines are quantified, based on past projects, and economic modeling, similar to our work into CCGTs and gas peakers.
A typical gas engine is around 5MW in size, within a range of 0.3MW to 18MW. Capex costs of reciprocating gas engines decrease for larger units (chart below).
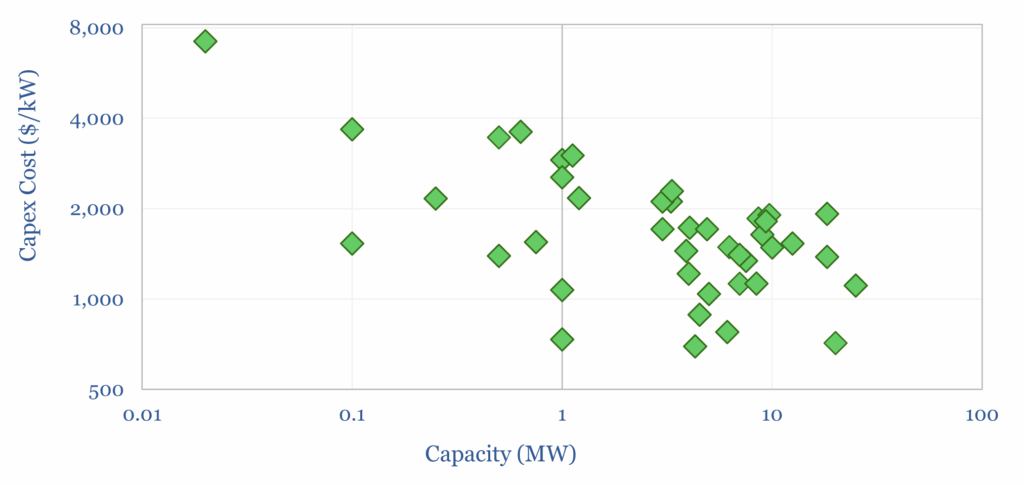
Note the capex costs in the chart above have all been translated in 2025$, using standard inflation assumptions, so we can derive a best-fir formula for how larger units achieve lower $/kW costs.
Multiple units can also be combined for a plant with larger capacity, and higher availability.
Examples and case studies of recip deployments are shown in the data-file, especially for peaker facilities (including in wind-heavy grids) and for reliable power-generation in smaller grids that require reliable backup generation.
Three companies stood out in particular in the case studies: Jenbacher, Wärtsilä and Caterpillar. Further details are in the data-file.
As a rule of thumb, a reciprocating gas engine that costs $1,500/kW, runs with 60% utilization and 40% efficiency factor, requires a levelized cost of 8-10 c/kWh to generate a 10% IRR, depending on whether a price is placed on CO2 emissions.
Please download the data-file to stress-test the economics of reciprocating gas engine power generation.