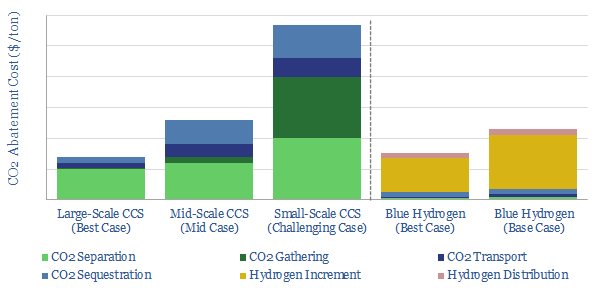-
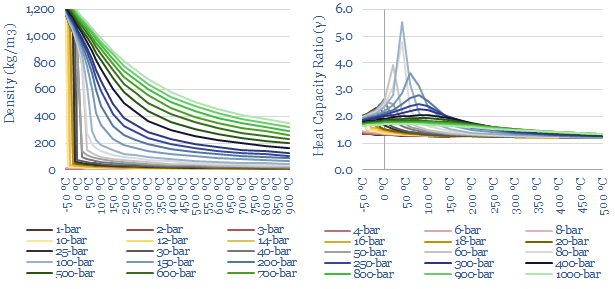
CO2 compression: stranger things?
CO2 is a strange gas. This matters as energy transition will require over 120 GW of compressors for 6GTpa of CCUS. This 13-page note explains CO2’s strange properties, which helps to fine-tune appropriate risking factors for vanilla CCS, blue hydrogen, CO2-EOR, CO2 shipping, super-critical CO2 power cycles. There is also a wide moat around leading…
-
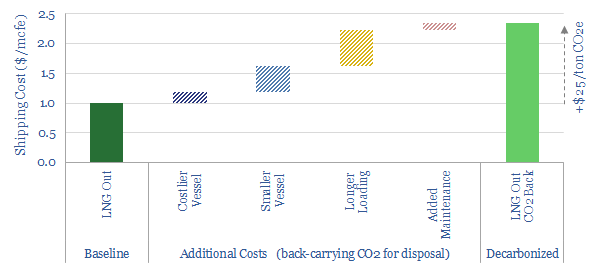
Decarbonized gas: ship LNG out, take CO2 back?
This note explores an option to decarbonize global LNG: (i) capture the CO2 from combusting natural gas (ii) liquefy it, including heat exchange with the LNG regas stream, then (iii) send the liquid CO2 back for disposal in the return journey of the LNG tanker. There are some logistical headaches, but no technical show-stoppers. Abatement…
-
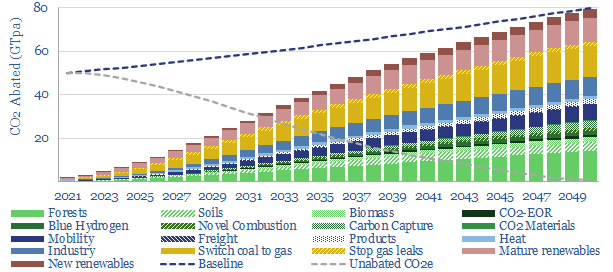
Decarbonizing global energy: the route to net zero?
This 18-page report revises our roadmap for the world to reach ‘net zero’ by 2050. The average cost is still $40/ton of CO2, with an upper bound of $120/ton, but this masks material mix-shifts. New opportunities are largest in efficiency gains, under-supplied commodities, power-electronics, conventional CCUS and nature-based CO2 removals.
-
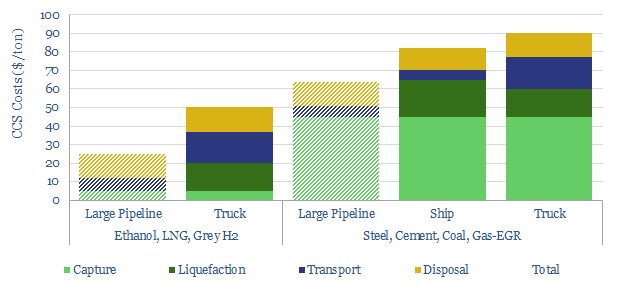
Small-scale CCS: transport liquid CO2?
CO2 has unusual physical properties, which make small-scale liquefaction and transport much more viable than we had expected. The energy burden is 70% less than other industrial gases. Total CCS costs are $50-90/ton for leading examples. This 15-page note outlines the opportunity.
-
Carbon capture: how big is the opportunity?
This 13-page note quantifies the upside case for CCS in the United States, using top-down and bottom-up calculations. Our conclusion is that a clear, $100/ton incentive could help CCS scale by c25x, accelerating over 500MTpa of projects in the next decade, cutting US CO2 by 10%.
-
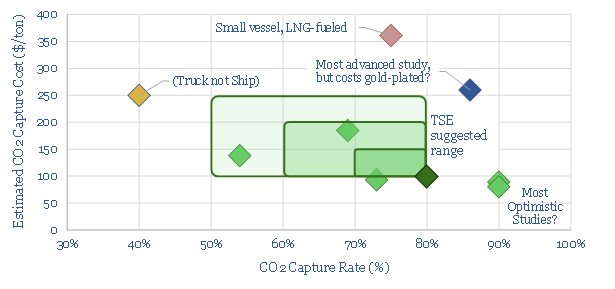
Carbon capture on ships: raising a sail?
CCS is adapting to go to sea. 80% of some ships’ CO2 emissions could be captured for c$100/ton and an energy penalty of just 5%, albeit this is the best case within a broad range. This 15-page note explores the opportunity, challenges, progress and who might benefit.
-
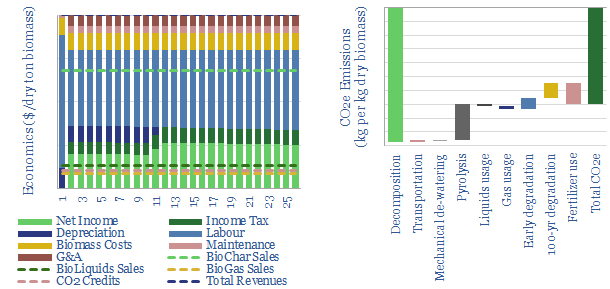
Biochar: burnt offerings?
Biochar is a miraculous material, improving soils, enhancing agricultural yields and avoiding 1.4kg of net CO2 emissions per kg of waste biomass. IRRs surpass 20% without CO2 prices or policy support. Hence this 18-page note outlines the opportunity.
-
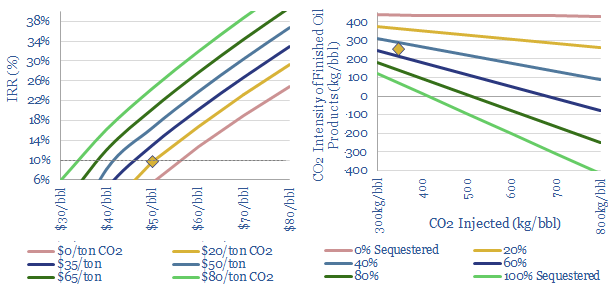
CO2-EOR: well disposed?
CO2-EOR is the most attractive option for large-scale CO2 disposal. Unlike CCS, which costs over $70/ton, additional oil revenues cover the costs of sequestration. And the resultant oil is 50-100% lower carbon than usual. The technology is mature. Potential exceeds 2GTpa. This 23-page report outlines the opportunity.
-
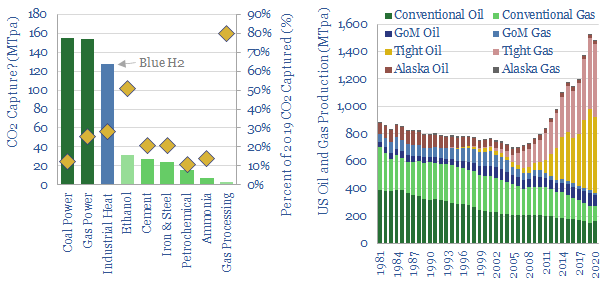
Deep blue: cracking the code of carbon capture?
Carbon capture is cursed by colossal costs at small scale. But blue hydrogen may be its saviour. Crucial economies of scale are guaranteed by deploying both technologies together. The combination is a dream scenario for gas producers. This 22-page note outlines the opportunity and costs.
-
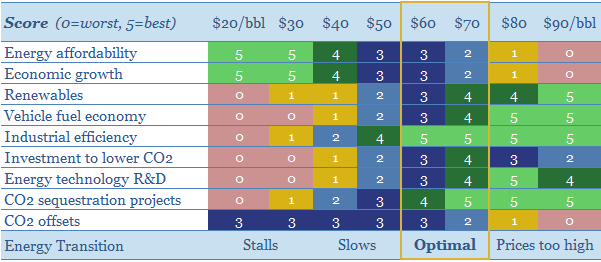
What oil price is best for energy transition?
$30/bbl oil prices stall the energy transition. They kill the relative economics of electric vehicles, renewables, industrial efficiency, flaring reductions, CO2 sequestration and new energy R&D. This 15-page note finds $60/bbl oil is ‘best’ for decarbonization. Policymakers should target $60 oil.
Content by Category
- Batteries (87)
- Biofuels (42)
- Carbon Intensity (49)
- CCS (63)
- CO2 Removals (9)
- Coal (38)
- Company Diligence (91)
- Data Models (821)
- Decarbonization (159)
- Demand (110)
- Digital (58)
- Downstream (44)
- Economic Model (200)
- Energy Efficiency (75)
- Hydrogen (63)
- Industry Data (275)
- LNG (48)
- Materials (81)
- Metals (74)
- Midstream (43)
- Natural Gas (146)
- Nature (76)
- Nuclear (23)
- Oil (162)
- Patents (38)
- Plastics (44)
- Power Grids (123)
- Renewables (149)
- Screen (112)
- Semiconductors (30)
- Shale (51)
- Solar (67)
- Supply-Demand (45)
- Vehicles (90)
- Wind (43)
- Written Research (347)