Offshore developments will change dramatically in the 2020s, eliminating new production platforms in favour of fully subsea solutions. The opportunity can increase a typical project’s NPV by 50%, reduce its breakeven by one-third and effectively eliminate upstream CO2 emissions. We have reviewed 1,850 patents to find the best-placed operators and service providers, versus others that will be disrupted. Overall, the theme supports the ascent of low-carbon natural gas, which should treble in the energy mix by 2050. This 22-page note presents the opportunity.
The offshore oil and gas industry’s progress towards ‘fully subsea’ developments, without any platforms or surface infrastructure being necessary, is reviewed in detail in pages 2-5, covering key projects and milestones from 1985-2000.
30% economic savings in both capex and opex are quantified line-by-line, across c50 cost lines, in pages 6-9.
1.5x NPV uplifts and 4pp IRR uplifts are quantified by modelling a representative fully greenfield gas-condensate project on pages 11-12.
CO2 emissions can be virtually eliminated by a fully subsea development solution. Pages 12-13 add up the impacts of higher efficiency, power from shore, fewer materials and the elimination of PSV/helicopter trips.
The key engineering challenges for fully subsea systems, which remain to be resolved, are summarized on page 14.
Who benefits from the trend toward fully subsea systems, is described from page 15 onwards after reviewing 1,850 patents around the industry. This includes both the leading service companies and operators (primarily Equinor, but also TOTAL, Shell).
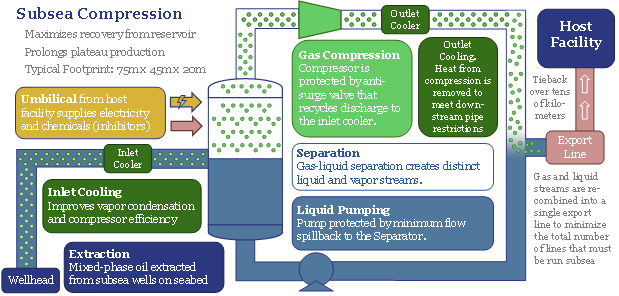
The leaders in subsea compression technology are assessed on pages 16-17.
The leaders in subsea power systems are described on pages 18-19.
The leaders in next-generation subsea robotics are assessed on pages 20-21.
Others are disrupted, as is described in detail in page 22.
Covered service companies in the report include ABB, Aker, Eelume, GE, Kraken, Oceaneering, OneSubsea, Saipem, Siemens, Technip-FMC, Wood Group, the PSV and helicopter sector, and c20 early stage companies in next-generating subsea robotics.