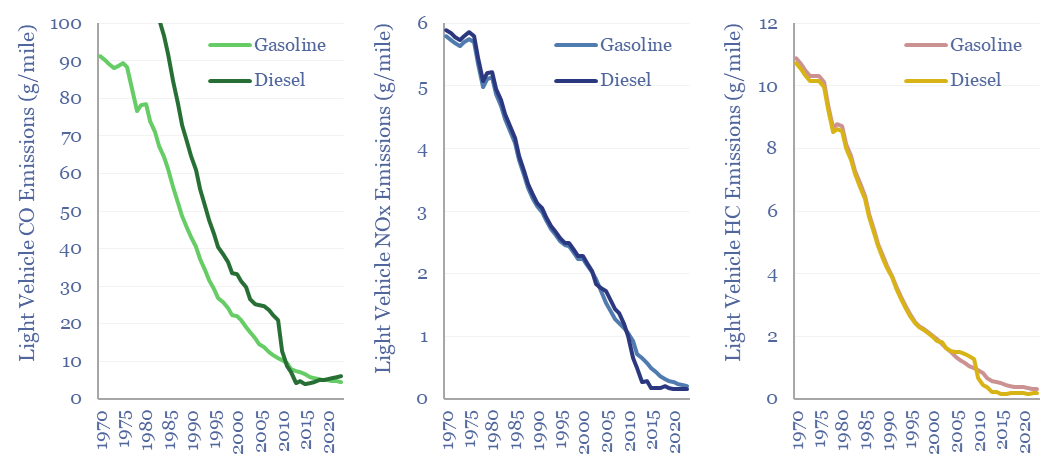
There has been a remarkable reduction in the negative air quality impacts of combustion vehicles since 1970, as quantified in this data-file and over time. Vehicle emissions of CO, NOx and HCs have all fallen by 20-60x over the past 50-years, to 5 grams/mile, 0.2 grams/mile and 0.3 grams per mile, respectively.
This data-file quantifies vehicle emissions of CO, NOx and HCs across the active US fleet, using data reported by the BTS. The reported BTS data series go back to 1990, however, we have been able to take the data-series back to 1970, by interpolating between other data-sets, such as the total miles driven across the US since 1970.
Vehicle emissions of CO. The average modern ICE vehicle emits 4 grams of carbon monoxide (CO) per mile, while comparable vehicles 50-years ago emitted 20x more CO.
Vehicle emissions of NOx. The average modern ICE vehicle emits 0.2 grams of NOx per mile, while comparable gasoline vehicles 50-years ago emitted 30x more NOx, and comparable diesel vehicles emitted 40x more.
Gasoline vehicle emissions of HCs. The average modern gasoline vehicle emits 0.3 grams of uncombusted hydrocarbons per mile, while a comparable vehicle 50-years ago emitted 35x more.
Diesel vehicle emissions of HCs. The average modern diesel vehicle emits 0.2 grams of uncombusted hydrocarbons per mile, while a comparable vehicle 50-years ago emitted 60x more.
The main reason for these reductions in air emissions has been improving engine technology and the use of PGMs within catalytic converters, as mandated by emissions standards.
Continued improvements will come from electric vehicles which do not have any tailpipe emissions at all. Please see our broader vehicles research.