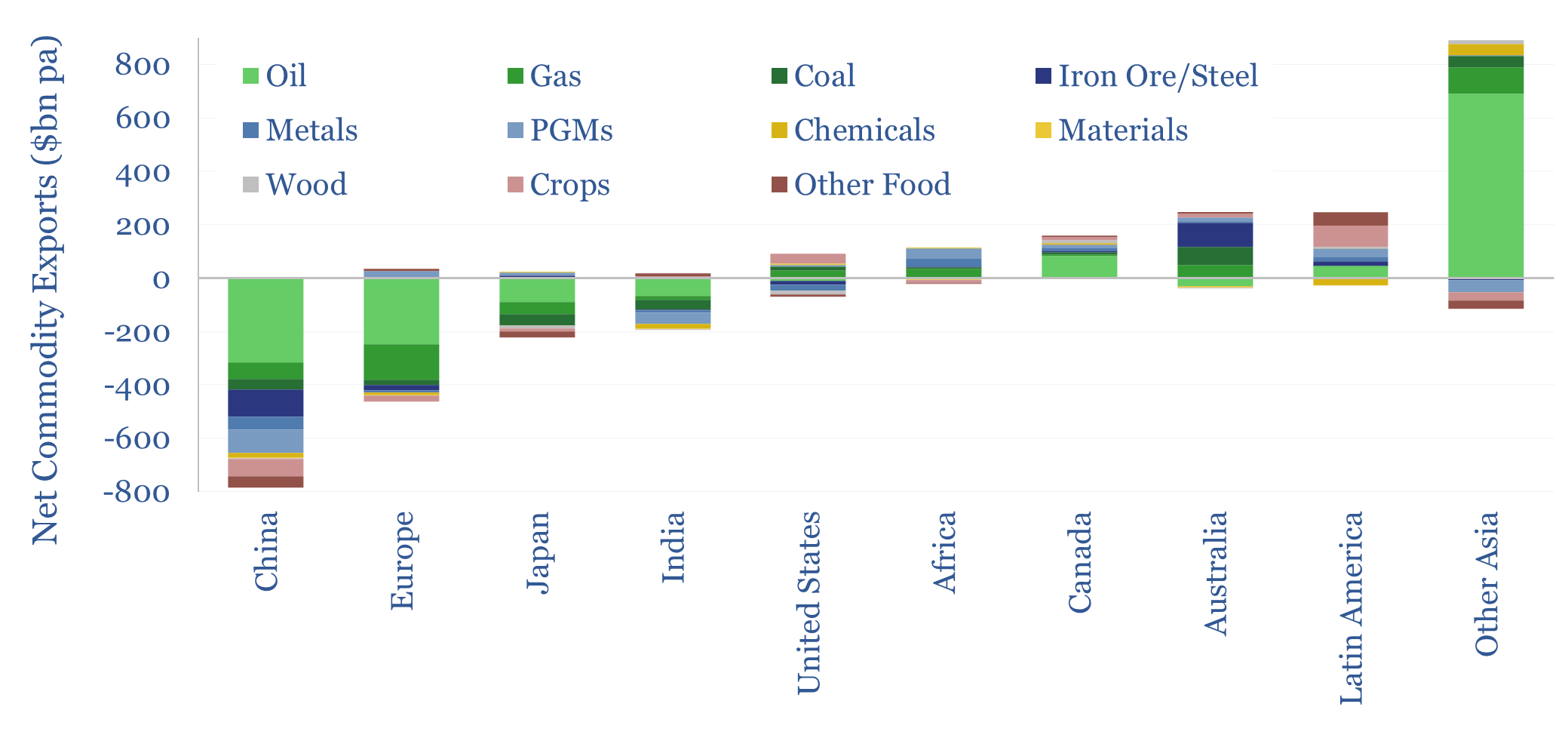
Search results for: “corn”
-
Ethanol from corn: the economics?
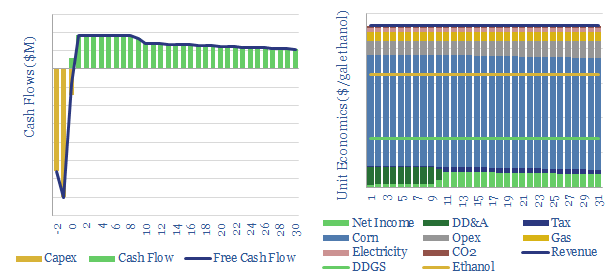
This data-file captures the economics of producing ethanol from corn. Our base case requires a price of $1.6/gallon of ethanol for a 10% IRR on a new greenfield plant, equivalent to $2.4/gallon gasoline. 40% of the US corn crop is diverted into biofuels, but the rationale is marginal.
-
Crop production: what CO2 intensity?
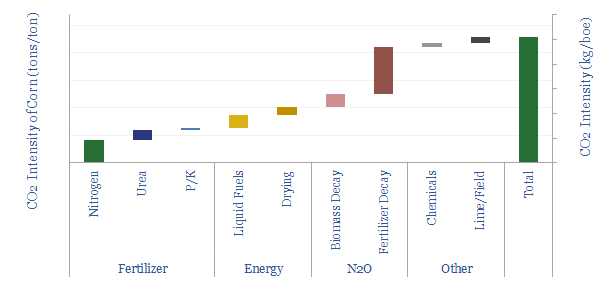
The CO2 intensity of producing corn averages 0.23 tons/ton, or 75kg/boe. 50% is from N2O emissions, a powerful greenhouse gas, from the breakdown of nitrogen fertilizer. Producing 1 kWh of food energy requires 9 kWh of fossil energy.
-
Crop production: how much does nitrogen fertilizer increase yields?
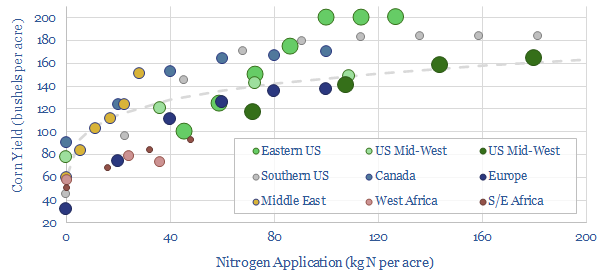
How much does fertilizer increase crop yields? Aggregating all of the global data, a good rule of thumb is that up to 200kg of nitrogen can be applied per acre, increasing corn crop yields from 60 bushels per acre (with no fertilizer) to 160 bushels per acre (at 200 kg/acre). But the relationship is logarithmic,…
-
Biomass accumulation: CO2 fixed by trees and energy crops?
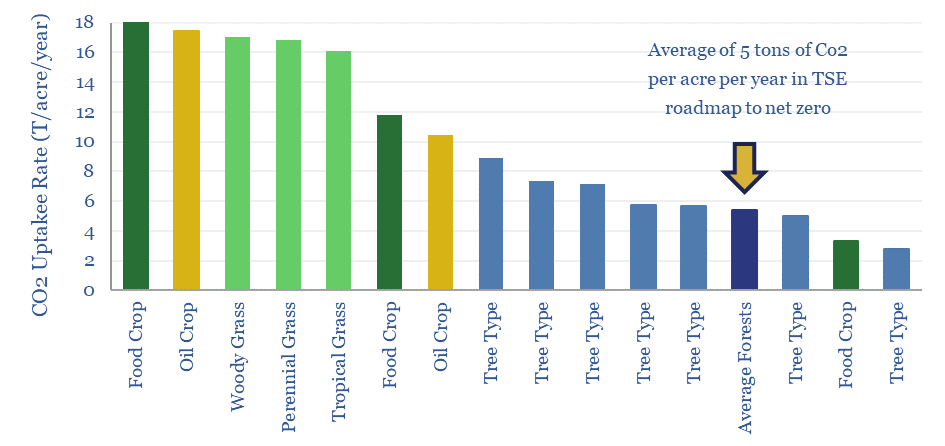
Different plant species fix 3-30 tons of CO2 per acre per year, as they accumulate biomass at 2-40 tons per hectare per year. The numbers matter for biofuels and for nature-based solutions. Hence this data-file compiles technical data into CO2 and biomass accumulation by plant species and by tree species, in different regions globally.
-
US ethanol plants: what CO2 intensity?
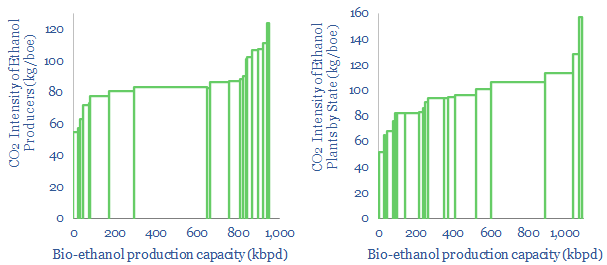
US bioethanol plants produce 1Mbpd of liquid fuels, with an average CO2 intensity of 85kg/boe. Overall, corn-based bioethanol has c40% lower CO2 than oil products. We screened the leaders and laggards by CO2-intensity, covering Poet, Valero, Great Plains, Koch, Marathon and White Energy.
-
Sugar to ethanol: the economics?
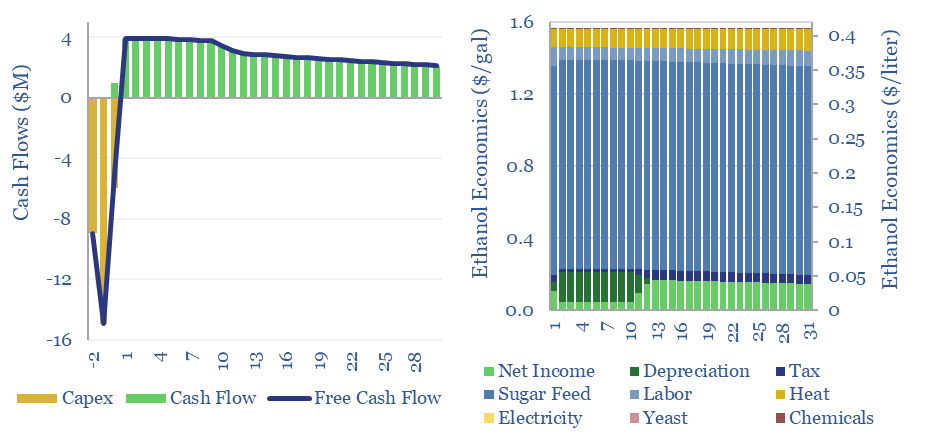
This data-file captures the economics of ethanol production, as a biofuel derived from sugar. A 10% IRR requires $1-4/gallon ethanol, equivalent to $0.25-1/liter, or $60-250/boe. Economics are most sensitive to input sugar prices. Net CO2 intensity is at least 50% lower than hydrocarbons.
-
Biofuel technologies: an overview?
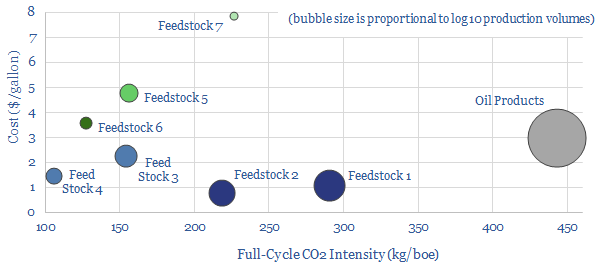
Biofuels are currently displacing 3.5Mboed of oil and gas. But they are not carbon-free, and their weighted average CO2 emissions are only c50% lower. This data-file breaks down the biofuels market across seven key feedstocks, to help identify which opportunities can scale for the lowest costs and CO2, versus others that require further technical progress.
-
Restoring soil carbon: the economics?
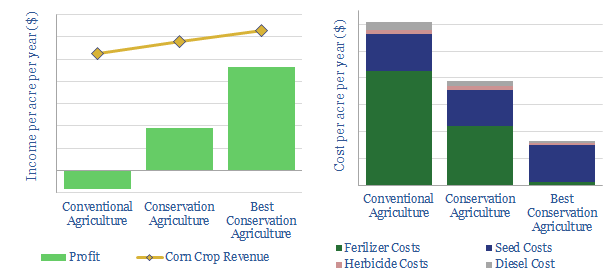
We model the economics for conservation agriculture to restore soil carbon. 5-30T of CO2 can be sequestered per acre per year, while deflating farm costs by 36-73% and raising yields 10-20%. This would transform crop-growing economics from marginal to material.
-
Biomass to biofuel, or biomass for burial?
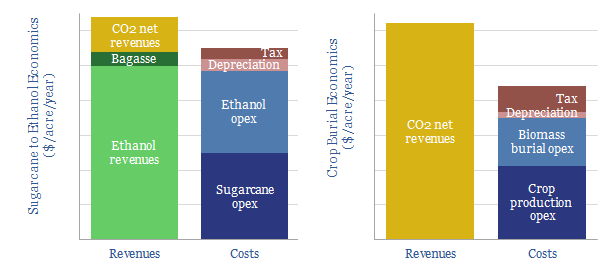
Greater decarbonization at a lower cost is achievable by burying biomass (such as corn or sugarcane) rather than converting it into bio-ethanol. This model captures the economics. Detailed costs and CO2 comparisons are shown under different iterations.
Content by Category
- Batteries (89)
- Biofuels (44)
- Carbon Intensity (49)
- CCS (63)
- CO2 Removals (9)
- Coal (38)
- Company Diligence (95)
- Data Models (840)
- Decarbonization (160)
- Demand (110)
- Digital (60)
- Downstream (44)
- Economic Model (205)
- Energy Efficiency (75)
- Hydrogen (63)
- Industry Data (279)
- LNG (48)
- Materials (82)
- Metals (80)
- Midstream (43)
- Natural Gas (149)
- Nature (76)
- Nuclear (23)
- Oil (164)
- Patents (38)
- Plastics (44)
- Power Grids (131)
- Renewables (149)
- Screen (117)
- Semiconductors (32)
- Shale (51)
- Solar (68)
- Supply-Demand (45)
- Vehicles (90)
- Wind (44)
- Written Research (356)