Nuclear
-
US nuclear generation by company?
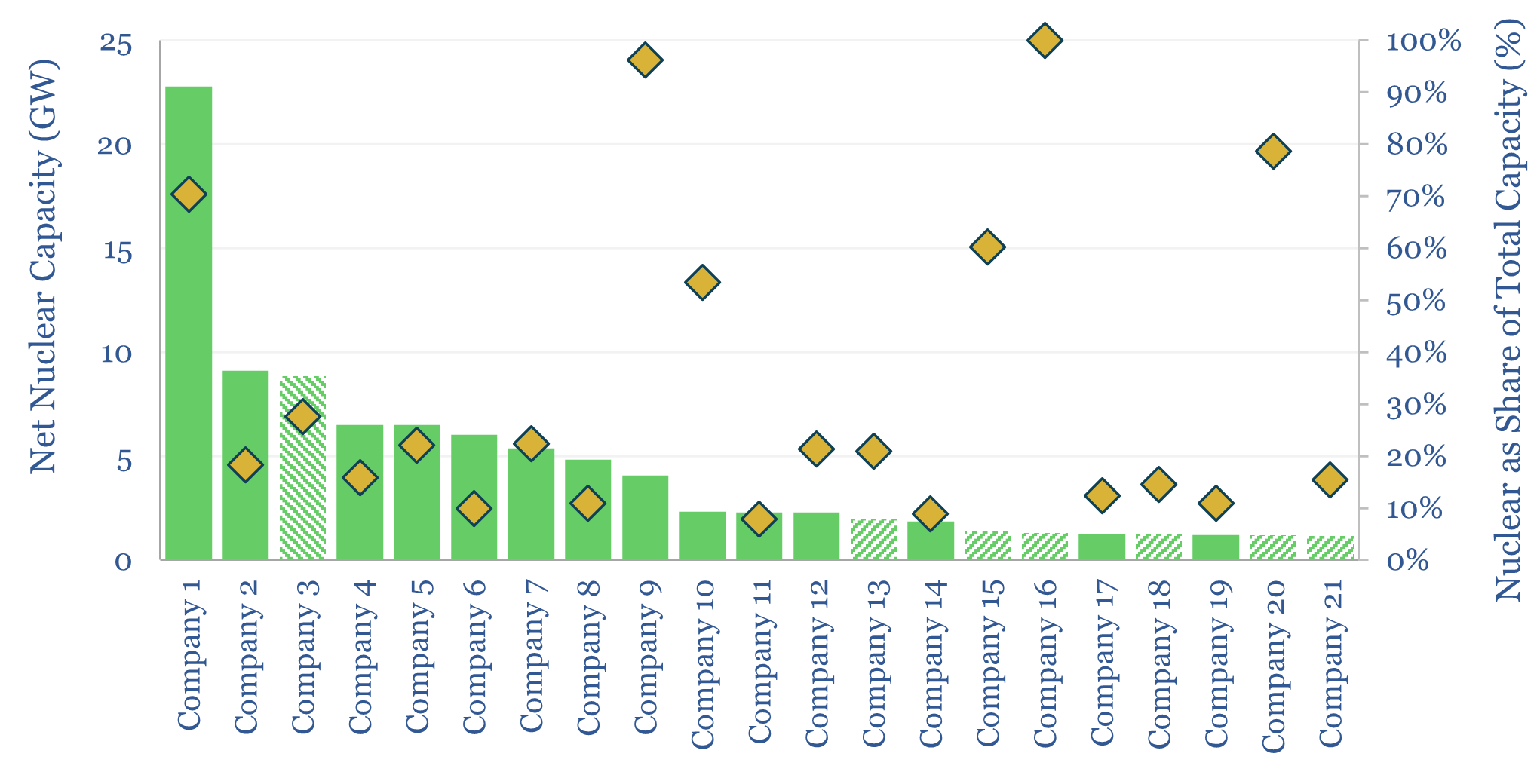
US nuclear generation of 800 TWH pa has come from 94 reactors, at 65 nuclear plants, owned by c50 companies, with 102 GW of current capacity. This data-file breaks down the industry by plant and by owner/operator, and assesses the restart potential of shuttered nuclear plants.
-
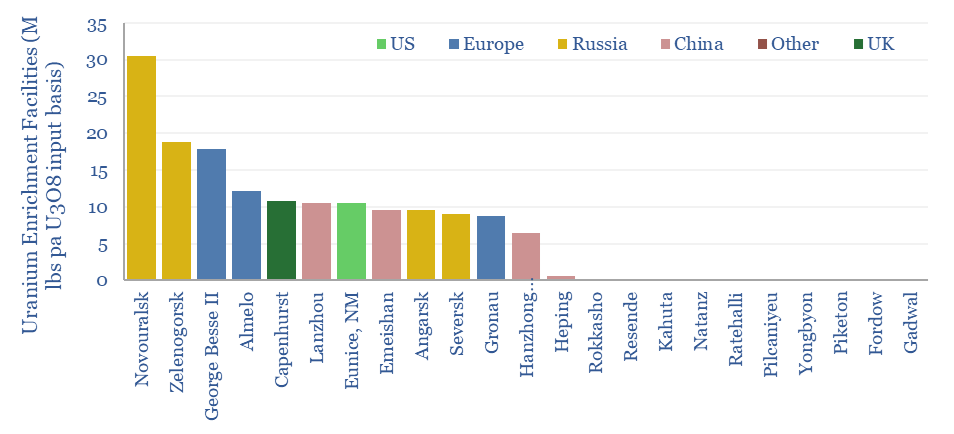
Uranium enrichment: by country, by company, by facility?
Global uranium enrichment by country, by company and by facility are estimated in this data-file, covering the 155M lbs pa uranium market. The data-file includes a build-up of enrichment facilities (ranked by SWU capacity), notes on each enrichment company and an attempt to map the world’s uranium production to where it is enriched and ultimately…
-
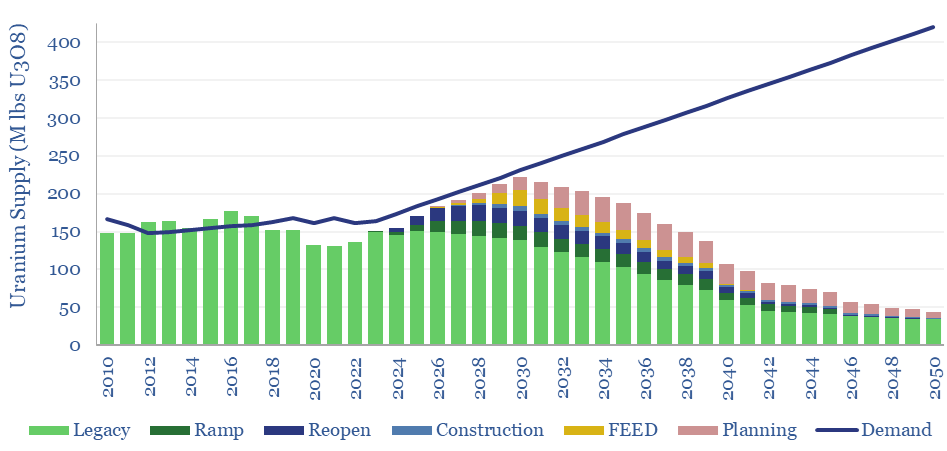
Global uranium supply-demand?
Our global uranium supply-demand model sees the market 5% under-supplied through 2030, including 7% market deficits at peak in 2025, as demand ramps from 165M lbs pa to 230M lbs pa in 2030. This is even after generous risking and no room for disruptions. What implications for broader power markets, decarbonization ambitions, and uranium prices?
-
Oklo: fast reactor technology?
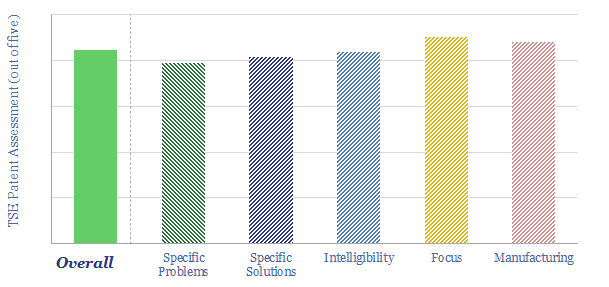
Oklo is a next-generation nuclear company, based in California, recently going public via SPAC at a $850M valuation, backed by Sam Altman, of Y-Combinator and OpenAI fame. Oklo’s fast reactor technology absorbs high energy neutrons in liquid metal and targets ultimate costs of 4c/kWh. What details can we infer from assessing Oklo’s patents, and can…
-
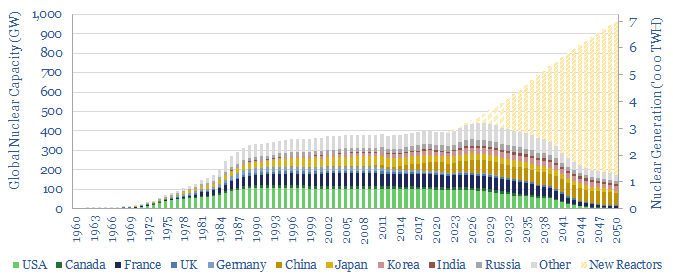
Reaching criticality: nuclear re-accelerates?
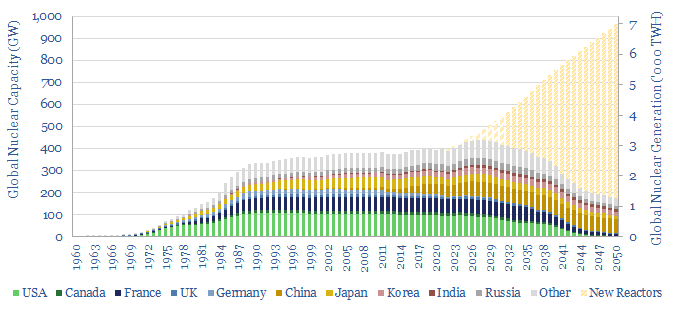
400 GW of nuclear reactors produce 2,800TWH of zero carbon electricity globally each year. But the numbers have been stagnant for two decades. This is now changing. This 14-page note explains why. We expect a >3% CAGR through 2030, and hope for a 2.5x ramp through 2050. A ‘nuclear renaissance’ helps the energy transition.
-
Nuclear capacity: forecasts, construction times, operating lives?
How much nuclear capacity would need to be constructed in our roadmap to net zero? This breakdown of global nuclear capacity forecasts that 30 GW of new reactors must be brought online each year through 2050, if the nuclear industry was to ramp up to 7,000 TWH of generation by 2050, which would be 6%…
-
X Energy: nuclear fuel breakthrough?
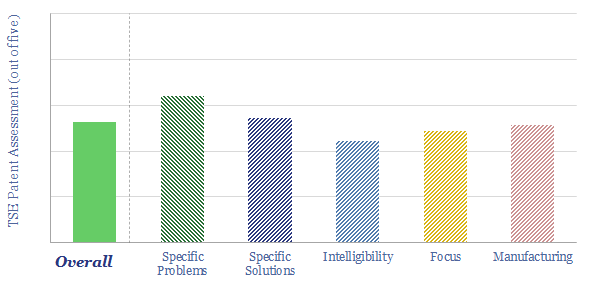
X-Energy is a next-generation nuclear company, progressing a demonstration project in Washington State, due to start up in 2027. The key innovation is using TRISO fuels, whose manufacturing is locked up with a concentrated patent library. Long-term costs are suggested at 6c/kWh.
-
TerraPower: nuclear breakthrough?
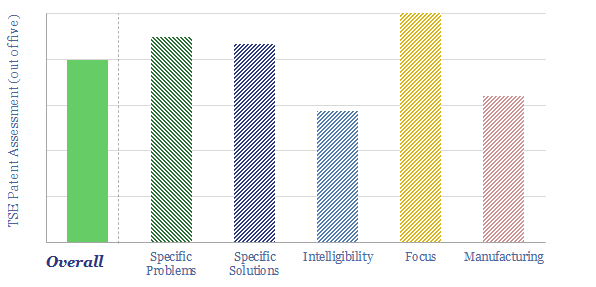
TerraPower is one of the most active next-generation nuclear companies, with funding from Bill Gates, and 600 engineers working towards the first, 345MWe Natrium reactor before 2030. We could not entirely de-risk a “breakthrough” due to the breadth and novelty of its patents.
-
Terrestrial Energy: small modular reactor breakthrough?
Terrestrial Energy is a next-generation nuclear fission company, aiming to build a small modular reactor: specifically a 2 x 195MWe Integral Molten Salt Reactor with ultimate costs below $3,000/kWe, yielding levelized costs of 5-7c/kWh. 80 patents lock up 8 core innovations in a high-quality library that helps de-risk the potential.
Content by Category
- Batteries (89)
- Biofuels (44)
- Carbon Intensity (49)
- CCS (63)
- CO2 Removals (9)
- Coal (38)
- Company Diligence (94)
- Data Models (838)
- Decarbonization (160)
- Demand (110)
- Digital (59)
- Downstream (44)
- Economic Model (204)
- Energy Efficiency (75)
- Hydrogen (63)
- Industry Data (279)
- LNG (48)
- Materials (82)
- Metals (80)
- Midstream (43)
- Natural Gas (148)
- Nature (76)
- Nuclear (23)
- Oil (164)
- Patents (38)
- Plastics (44)
- Power Grids (130)
- Renewables (149)
- Screen (117)
- Semiconductors (32)
- Shale (51)
- Solar (68)
- Supply-Demand (45)
- Vehicles (90)
- Wind (44)
- Written Research (354)