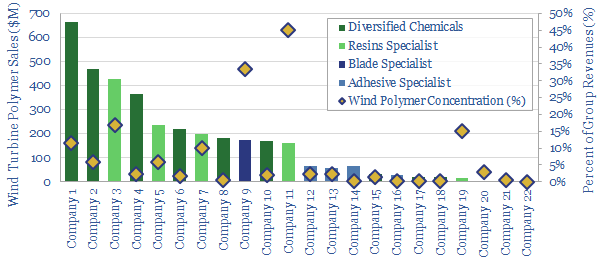
This data-file tabulates details for 20 wind turbine resin companies, i.e., specialty chemicals companies that make epoxy- or polyurethane resins and adhesives, especially those that feed into the construction of wind turbines.
Resins mind together with glass fibers or carbon fibers in a wind turbine blade, and thus these epoxies, harneers and adhesives will tend to comprise around 25-35% of a modern wind turbine blade by mass.
There are 5 public companies ex-China with 5-35% proportionate exposure to this sub-segment of the wind industry, which could therefore be exposed to an acceleration of wind capacity-building.
For example, Olin Epoxy is US listed and claims to be the #1 epoxy materials supplier in the world, after acquiring Dow’s epoxy business in 2015, sold into “wind energy, electronics, transportation, consumer goods, civil engineering and infrastructure”.
But three epoxy companies stood out particlarly in the data-file, because their products are relatively more concentrated or specialized for wind turbine applications. Two of these wind turbine resin companies were US-listed.
For each example, we have tabulated their approximate size, geography, patent filings, employee-county and estimated their exposure to wind turbine polymers.
Our outlook for wind in the energy transition sees captures wind turbine capex costs, wind opex costs, wind EROEI, materials intensity, upscaling towards larger turbines, downstream implications for power grids, and other companies across the supply chain.