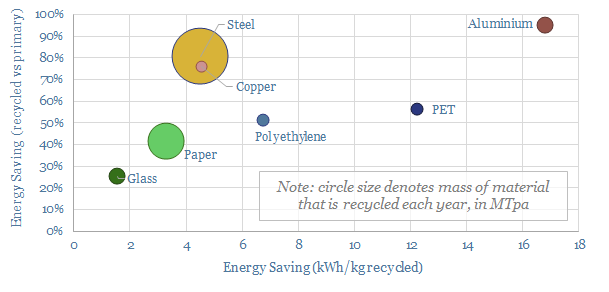
Search results for: “paper timber”
-
Cross laminated timber: costs and economics?
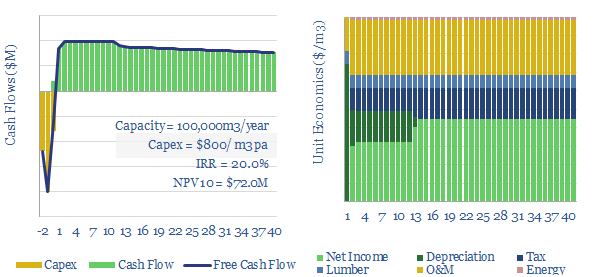
Cross laminated timber costs $1,200/ton, or $500/m3 pa, in order to derive 10-20% IRRs at a production facility costing $2,000/Tpa in capex. Cost lines include input costs of timber, polyurethane resins, labor, electricity, O&M, and capital costs. This data file is our economic model for mass timber production.
-
Paper production: energy economics?
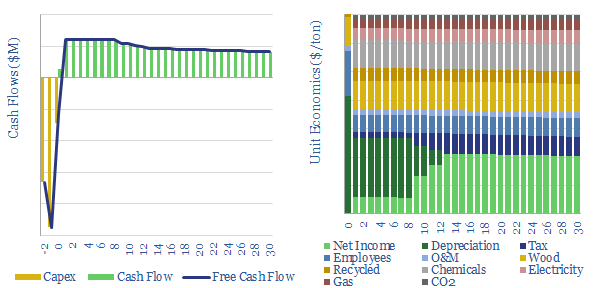
Costs of paper production are estimated at $700/ton, at a $2,000/Tpa paper mill, requiring 5,000 kWh/ton of useful energy, and emitting 2.6 tons/ton of CO2, of which 2.2 tons/ton is likely sourced from burning organic material such as waste wood and black liquor. This data-file captures the energy economics of paper production.
-
Wood products: typical pricing?
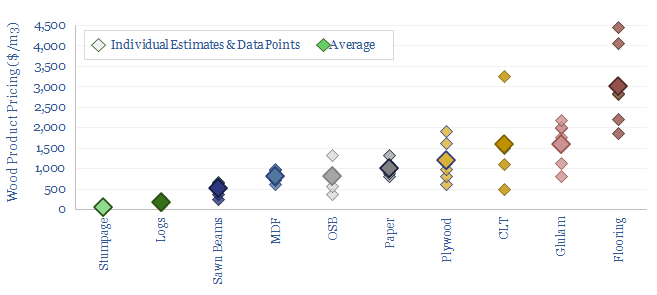
This data-file aggregates the pricing of different wood products, as storing carbon in long-lived materials matters amidst the energy transition. It can also add economic value. While upgrading raw timber into high value materials can uplift realized pricing in reforestation projects by 20-60x, which improves the permanence of nature-based CO2 removal credits.
-
Tigercat: forestry and timber innovations?
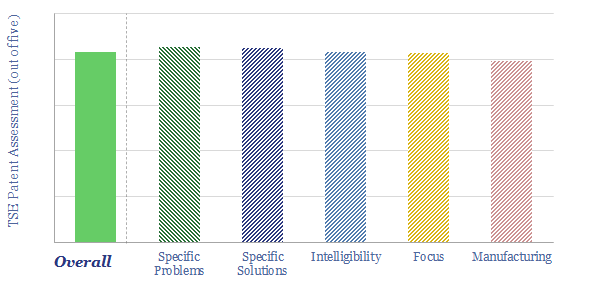
Tigercat is a private company, founded in 1992, headquartered in Ontario, Canada, with c2,000 employees. The company produces specialized machinery for forestry, logging, materials processing and off-road equipment. Our patent review has found a moat around reliable, easy-to-maintain, mobile and efficient forestry equipment.
-
Carbon negative construction: the case for mass timber?
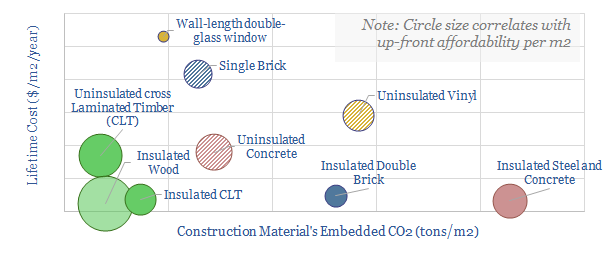
Construction accounts for 10% of global CO2, mainly due to cement and steel. But mass timber could become a dominant new material for the 21st century, lowering emissions 15-80% at no incremental cost. Debatably mass timber is carbon negative if combined with sustainable forestry. We outline the opportunity.
-
Nature based solutions to climate change?
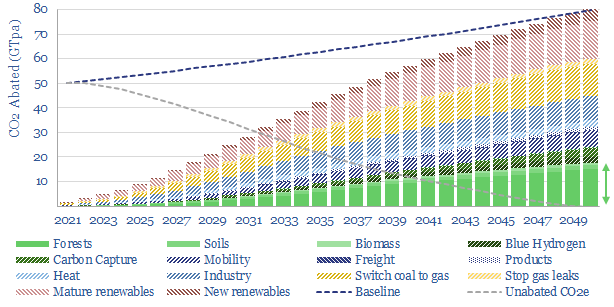
Nature based solutions are likely to deliver c20-25% of the decarbonization in a realistic roadmap to net zero. Reforestation is low-cost (c$50/ton), technically ready, convenient and helps nature. Key challenges are improving the quality of nature-based CO2 removals and accelerating momentum. We see upside for companies that can clear these hurdles. Our top ten conclusions…
-
Reforestation: costs of CO2 removals?
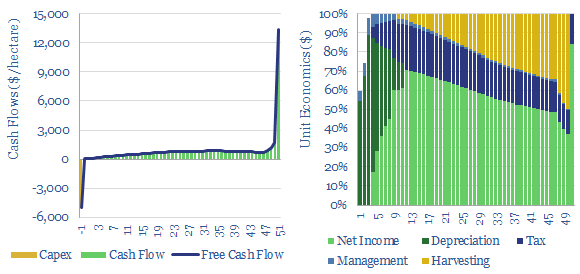
Reforestation costs are modelled in this data-file, acquiring pastureland, planting new forests to absorb CO2, over a 50-year cycle. As a good rule of thumb, we think $50/ton CO2 prices, $50/m3 timber, and 3% pa land appreciation will unlock an 8% unlevered IRR at Yield Class 16 (5 tons of CO2 per acre per year).…
-
Demand shifting: electrical flexibility by industry?
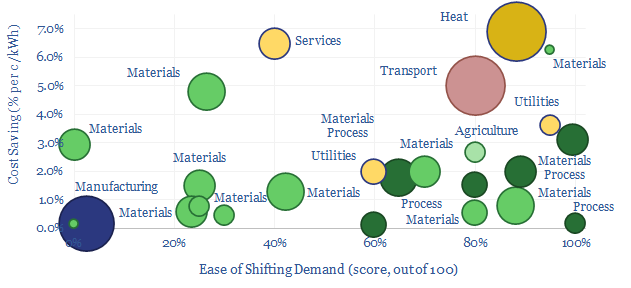
Demand shifting flexes electrical loads in a power grid, to smooth volatility and absorb more renewables. This database scores technical potential and economical potential of different electricity-consuming processes to shift demand, across materials, manufacturing, industrial heat, transportation, utilities, residential HVAC and commercial loads.
-
Reforestation: what planting density for seedlings?
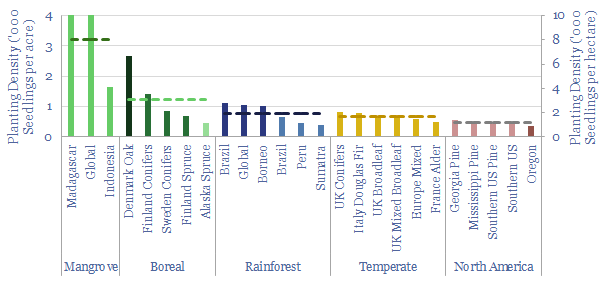
What is the typical planting density for reforestation projects globally? This matters as it can determine the costs of reforestation. Hence in this data-file we have collated data from 25 different case studies globally, which have tended to plant a median of 670 seedlings per acre (1,650 per hectare).
Content by Category
- Batteries (87)
- Biofuels (42)
- Carbon Intensity (49)
- CCS (63)
- CO2 Removals (9)
- Coal (38)
- Company Diligence (90)
- Data Models (816)
- Decarbonization (159)
- Demand (108)
- Digital (56)
- Downstream (44)
- Economic Model (197)
- Energy Efficiency (75)
- Hydrogen (63)
- Industry Data (273)
- LNG (48)
- Materials (79)
- Metals (71)
- Midstream (43)
- Natural Gas (146)
- Nature (76)
- Nuclear (22)
- Oil (162)
- Patents (38)
- Plastics (44)
- Power Grids (123)
- Renewables (149)
- Screen (112)
- Semiconductors (30)
- Shale (51)
- Solar (67)
- Supply-Demand (45)
- Vehicles (90)
- Wind (43)
- Written Research (345)