Search results for: “"gas turbine" "gas turbines"”
-
Gas power generation across five-minute intervals?
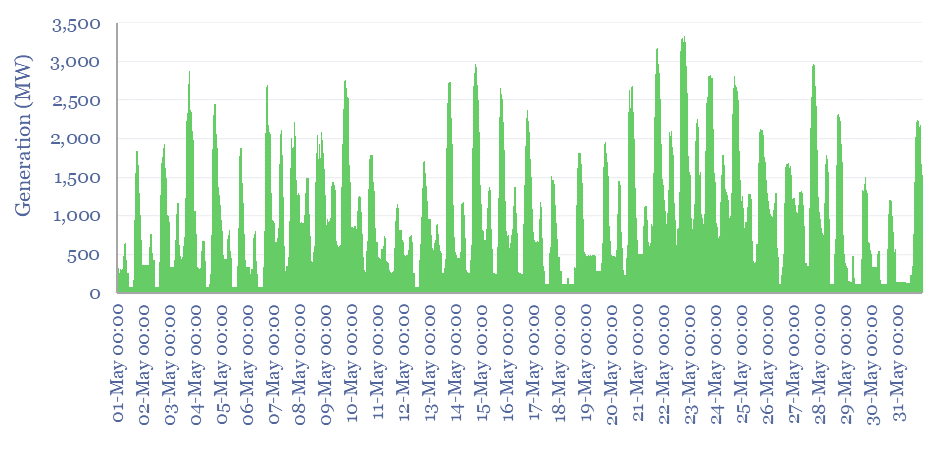
Power generation data are aggregated for ten of the largest CCGTs and gas peaker plants in Australia, across five-minute intervals, May-2024 and May-2014. This makes for a fascinating case study into how gas turbines are used to stabilize power grids, backstop renewables, and how this has changed over time.
-
Gas peaker plants: the economics?
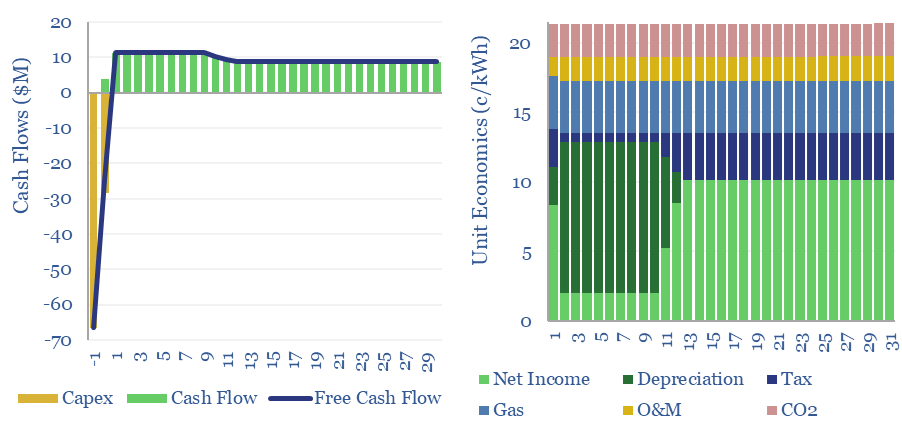
Gas peaker plants run at low utilizations of 2-20%, during times of peak demand in power grids. A typical peaker costing $950/kW and running at 10% utilization has a levelized cost of electricity around 20c/kWh, to generate a 10% IRR with 0.5 kg/kWh of CO2 intensity. This data-file shows the economic sensitivities to volatility and…
-
LNG plant compression: gas drives vs electric motors?
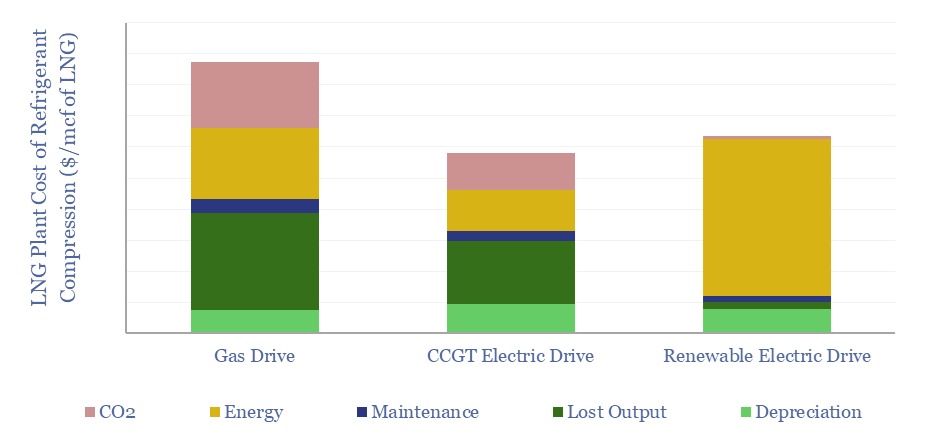
This data-file compares the costs of refrigerant compression at LNG plants, using gas turbines, electric motors powered by on-site CCGTs, or electric motors powered by renewable electricity. eLNG has higher capex costs, but higher efficiency, lower opex, and short payback times. Numbers in $/mcf and $/MTpa can be stress-tested in the data-file.
-
Adiabatic flame temperature: hydrogen, methane and oil products?
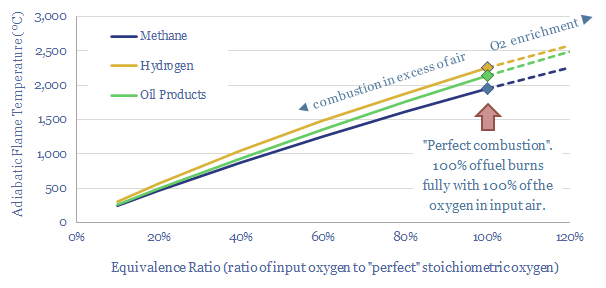
At an idealized, 100% stoichiometric ratio, the adiabatic flame temperature for natural gas is 1,960ºC, hydrogen burns 300ºC hotter at 2,250ºC and oil products burn somewhere in between, at around 2,150ºC. The calculations show why hydrogen cannot always be dropped into an existing turbine or heat engine.
-
Exhaust gas recirculation in gas power: the economics?
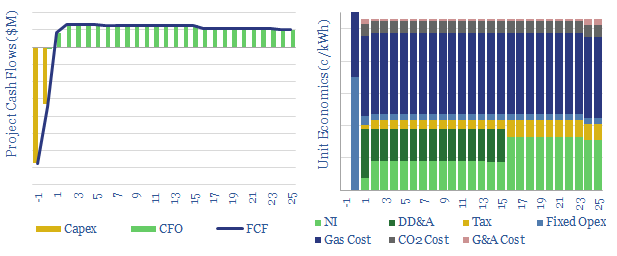
This data-file explores an alternative design for a combined cycle gas turbine, re-circulating exhaust gases after combustion, in order to facilitate CO2 capture. Costs and operating parameters are summarized from recent technical papers. Even with EGR, it will be challenging to decarbonize a gas turbine for less than $100/ton.
-
Gas power: does low utilization entail spare capacity?
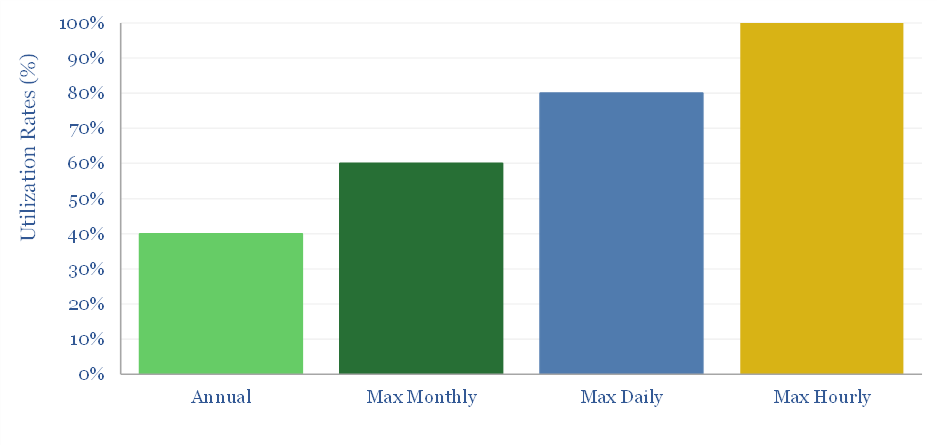
The US has >400GW of large gas-fired power plants running at 40% average annual utilization. Could they help power new loads, e.g., 60GW of AI data-centers by 2030? This 5-page note shows why low utilization does not entail spare capacity, and in turn, estimates the true spare capacity for loads such as data-centers.
-
Gas turbines: what outlook in energy transition?
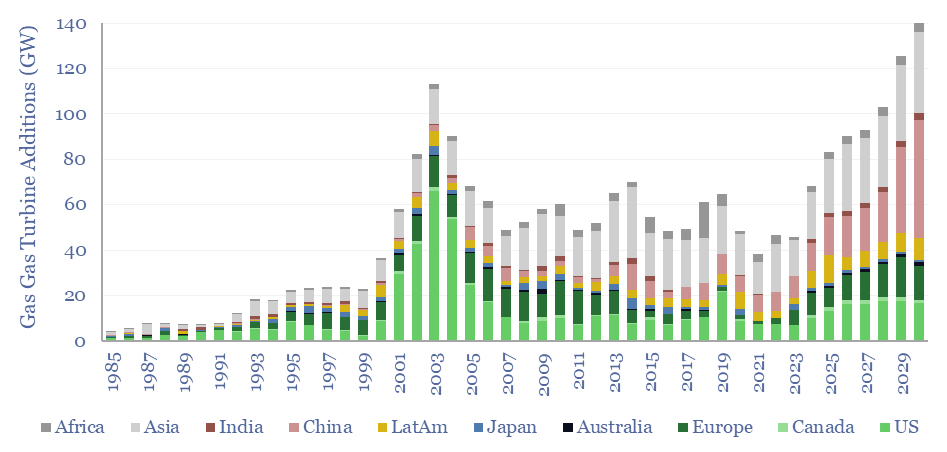
Gas turbines should be considered a key workhorse for a cleaner and more efficient global energy system. Installations will double to 100GW pa in 2024-30, and reach 140GW in 2030, surpassing their prior peak from 2003. This 16-page report outlines four key drivers in our outlook for gas turbines, and their implications.
-
Turbo-charge gas turbines: the economics?
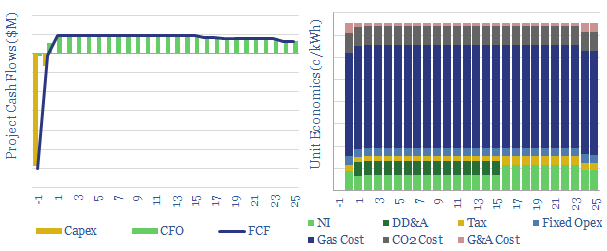
This data-file models the economics of turbo-charging gas turbines, which increases the mass flow of combustion air, to improve their power ratings by c10-20%. IRRs are solid. Turbo-charged gas turbines could thus gain greater share as grids become saturated with renewables
-
Peak loads: can batteries displace gas peakers?
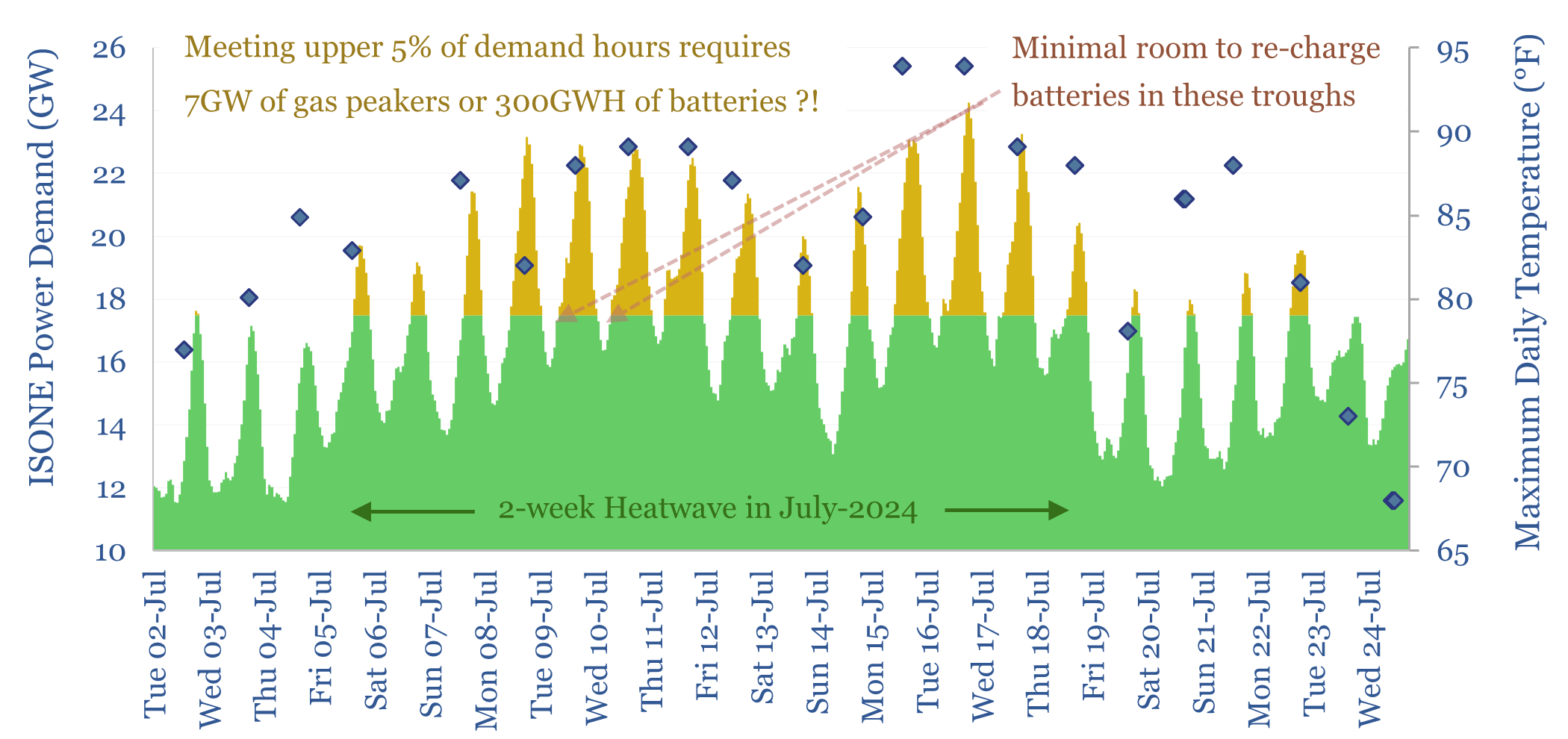
Peak loads in power grids are caused by heatwaves (in the US) and cold snaps (in Europe), which last 2-14 days. This 16-page report finds that very large batteries would be needed to ride through these episodes, costing 2-20x more than gas peakers. But the outlook differs interestingly between the US vs Europe.
Content by Category
- Batteries (87)
- Biofuels (44)
- Carbon Intensity (49)
- CCS (63)
- CO2 Removals (9)
- Coal (38)
- Company Diligence (92)
- Data Models (829)
- Decarbonization (159)
- Demand (110)
- Digital (58)
- Downstream (44)
- Economic Model (203)
- Energy Efficiency (75)
- Hydrogen (63)
- Industry Data (277)
- LNG (48)
- Materials (82)
- Metals (77)
- Midstream (43)
- Natural Gas (146)
- Nature (76)
- Nuclear (23)
- Oil (164)
- Patents (38)
- Plastics (44)
- Power Grids (126)
- Renewables (149)
- Screen (114)
- Semiconductors (30)
- Shale (51)
- Solar (67)
- Supply-Demand (45)
- Vehicles (90)
- Wind (43)
- Written Research (350)