Search results for: “climate model”
-
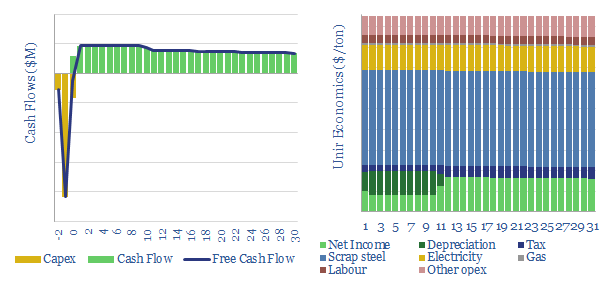
Biomass power: costs, levelized costs and BECCS?
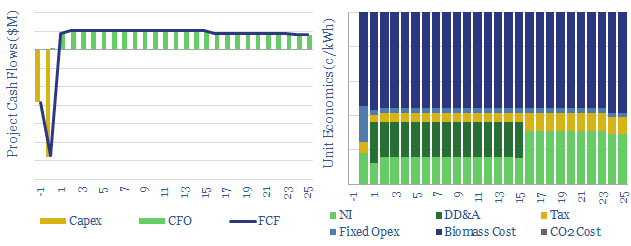
This data-file captures the economics of producing wood pellets, generating electricity from biomass, and potentially also building a further CCS facility to yield ‘carbon negative power’ (which is nevertheless more CO2 intensive than burning gas!). Our numbers are backstopped by industry data, including 340 US biomass plants.
-
Geothermal energy: costs and economics?
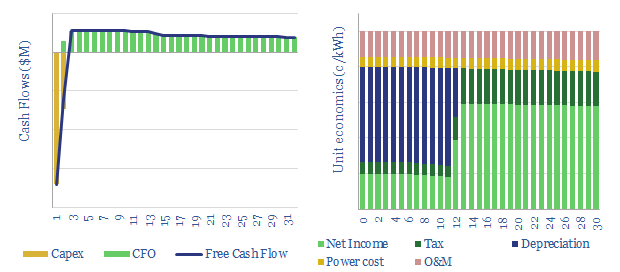
Geothermal energy costs are modelled from first principles in this data-file. LCOEs of 6c/kWh are available in geothermal hotspots. Outside of the hotspots, enhanced geothermal heat can cost 2-14c/kWh-th for a 10% IRR on $500-5,000/kW-th capex, while a rule of thumb is that geothermal electricity costs 5x geothermal heat.
-
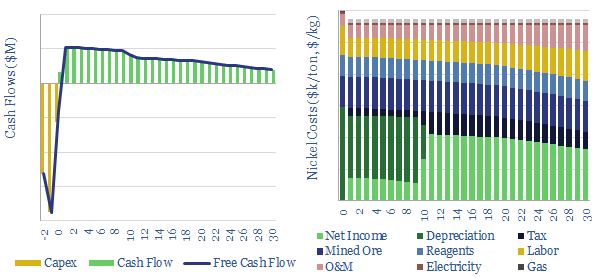
Room for reforestation: a database of global land use?
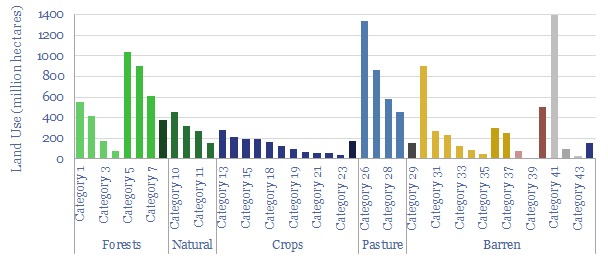
The purpose of this data-file is to provide helpful data on how land is used globally, and thus to quantify how much land is available for nature based solutions such as reforestation. Deep-dive details are provided on degraded land, agricultural land, natural ecosystems and reforestable lands.
-
Photovoltaic silicon: the economics?
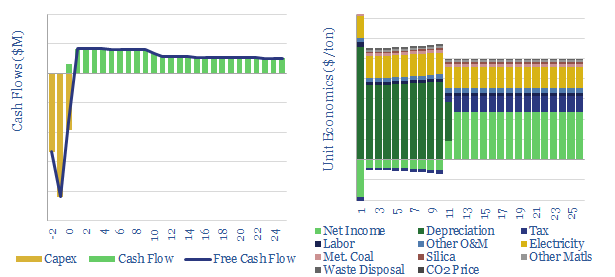
This model breaks down the costs of photovoltaic silicon, which explains $0.1/W of a $0.3/W solar panel. There is no way silicon producers are making economic returns below $12.5/kg mono-crystalline polysilicon prices. The average kg of PV silicon in a solar panel is also most likely associated with 140kg of direct CO2.
-
Landfill gas: the economics?
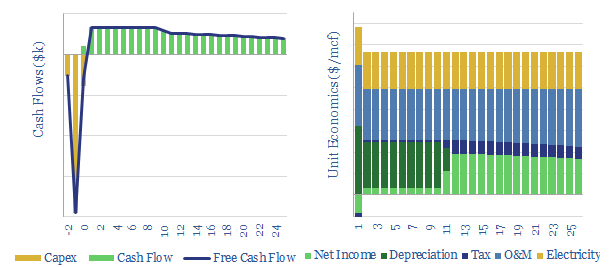
We estimate that a typical landfill facility may be able to capture and abate 70% of its methane leaks for a CO2-equivalent cost of $5/ton. Other landfill gas pathways get more complex and expensive. Raw and unprocessed landfill gas can be economical to commercialize at a cost of $2-4/mcfe.
-
Turquoise hydrogen from methane pyrolysis: economics?
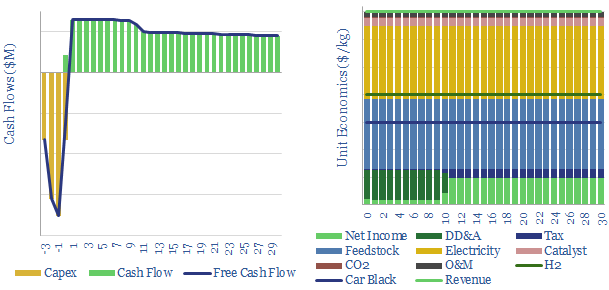
Turquoise hydrogen is produced by thermal decomposition of methane at high temperatures, from 600-1,200◦C. Costs can beat green hydrogen. This data-file quantifies the economics (in $/kg), how to generate 10% IRRs, possible capex costs, and remaining challenges for commercialization.
-
Transformer costs: the economics?
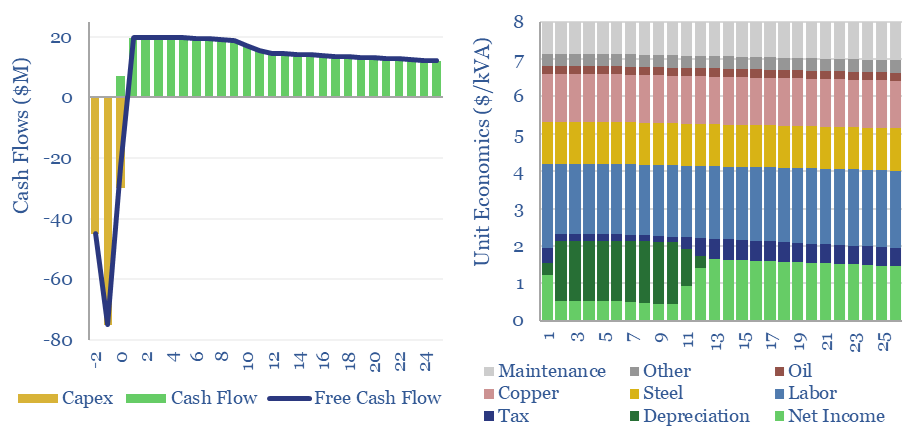
Transformer costs must typically run at $8/kVA to earn a 10% IRR constructing a new transformer manufacturing facility, across capex costs, materials costs, specialized labor costs, and all built-up from first principles in this economic model. We have also screened 25 leading companies in transformer manufacturing.
-
Global coal supply-demand: outlook in energy transition?
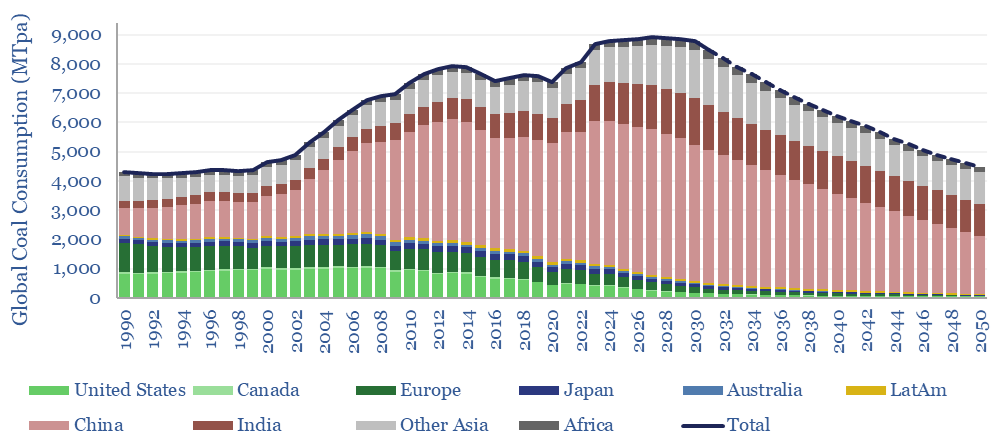
Global coal use likely hit a new all-time peak of 8.8GTpa in 2024, of which 7.6GTpa is thermal coal and 1.1GTpa is metallurgical. The largest consumers are China (5GTpa), India (1.3GTpa), other Asia (1.2GTpa), Europe (0.4GTpa) and the US (0.4GTpa). This model presents our forecasts for global coal supply-demand from 1990 to 2050.
Content by Category
- Batteries (87)
- Biofuels (42)
- Carbon Intensity (49)
- CCS (63)
- CO2 Removals (9)
- Coal (38)
- Company Diligence (92)
- Data Models (824)
- Decarbonization (159)
- Demand (110)
- Digital (58)
- Downstream (44)
- Economic Model (201)
- Energy Efficiency (75)
- Hydrogen (63)
- Industry Data (276)
- LNG (48)
- Materials (81)
- Metals (76)
- Midstream (43)
- Natural Gas (146)
- Nature (76)
- Nuclear (23)
- Oil (164)
- Patents (38)
- Plastics (44)
- Power Grids (124)
- Renewables (149)
- Screen (112)
- Semiconductors (30)
- Shale (51)
- Solar (67)
- Supply-Demand (45)
- Vehicles (90)
- Wind (43)
- Written Research (348)