Search results for: “climate model”
-
Coal-to-Power Project Economics
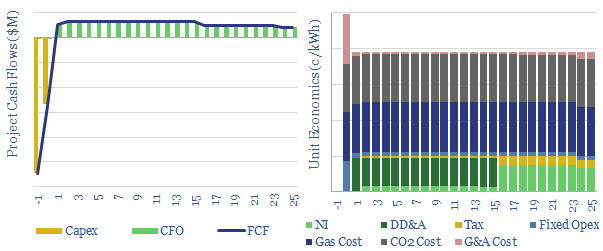
Greenfield coal-to-power economics vary markedly by region. IRRs can reach 30% in emerging markets with low capex costs, high utilization and no carbon prices. But they fail to return their capital costs under developed world air standards and $25/ton CO2 pricing. Please download the model to stress-test the economics.
-
Flare gas capture: the economics?
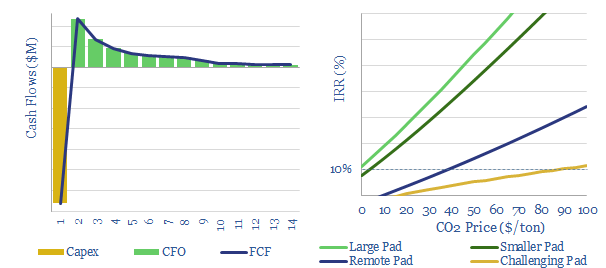
c150bcm of gas was flared globally in 2019. This data-file simplifies the economics of capturing flare gas. Generally, double-digit IRRs are achievable at large new shale pads. But costs are more challenging at smaller sites, remote pads or for contaminated gas. Carbon prices would dramatically improve economics. A $100/ton CO2 price could potentially eliminate US…
-
Levelized cost of electricity: stress-testing LCOE?
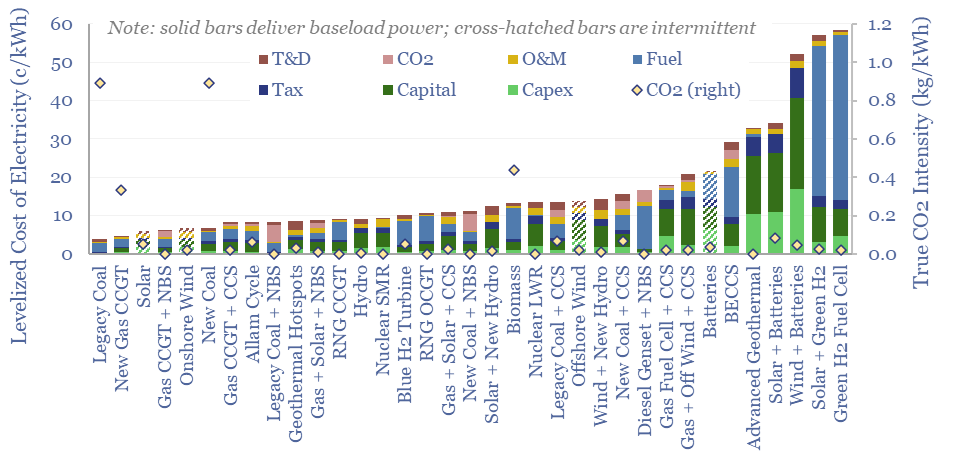
This data-file summarizes the levelized cost of electricity, across 35 different generation sources, covering 20 different data-fields for each source. Costs of generating electricity can vary from 2-200 c/kWh. The is more variability within categories than between them. Numbers can readily be stress-tested in the data-file.
-
Afforesting deserts: energy economics?
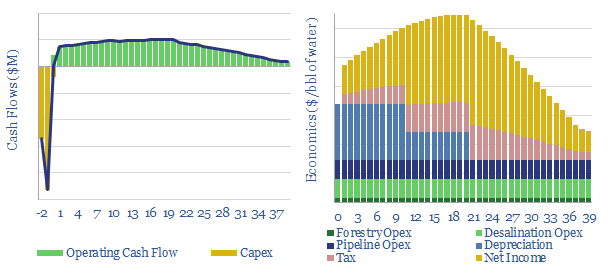
We model the economics of afforesting deserts by desalinating and distributing sufficient water for trees to grow. The best economics are achievable in the Permian, with 10% IRRs at $30/ton CO2 prices. But the energy economics cannot work to green the world’s most hyper-arid deserts, such as the Sahara.
-
Organic Rankine Cycles: the energy economics?
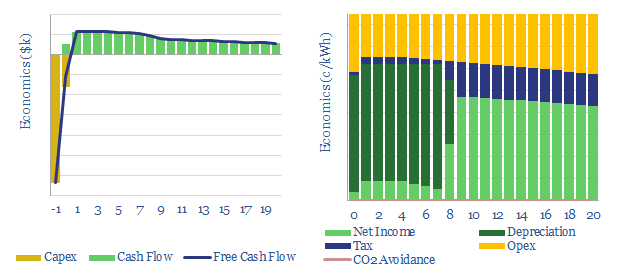
This data-file captures the energy economics of an Organic Rankine Cycle to recover low-grade waste heat (at 70-200C) from an industrial facility, or in the geothermal industry. A CO2 price of $50-75/ton could greatly accelerate adoption and improve the efficiency of industrial facilities.
-
Combined heat and power: the economics?
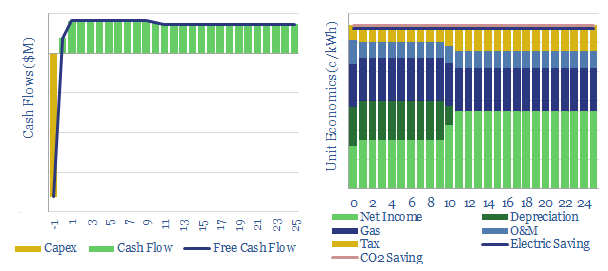
This data-file models the energy economics of a combined heat and power installation, to provide electricity and heating behind the meter, in lieu of purchasing electricity from the grid. Economics are strong, especially for larger units. CO2 emissions can also be reduced by 5-30% due to high efficiency.
-
Costs of CCS with the amine process?
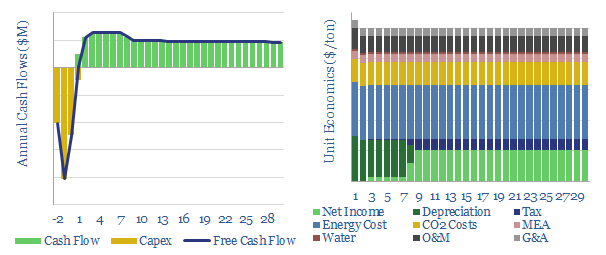
This data-file models the economics of capturing CO2 from exhaust flues using the amine process. Our base case estimate is informed by five tabs of cost data and technical papers, but all of the input assumptions can be flexed to stress-test costs. Total costs rise exponentially if it is necessary to capture CO2 from more…
-
HVDC power transmission: the economics?
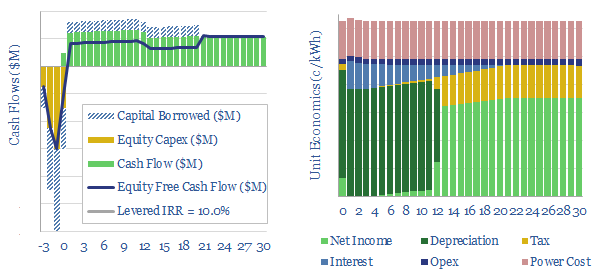
This model captures the economics of transporting electricity (e.g., wind and solar), over vast distances, using high voltage direct current power cables (HVDCs). Our base case shows a 3-10c/kWh transportation spread is required to earn a 10% levered IRR on 1,000-mile cable.
-
Ground source heat pumps: the economics?
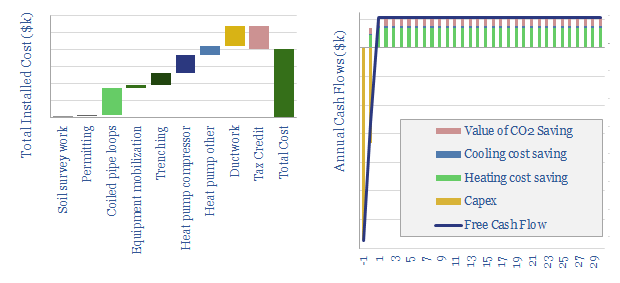
A ground source heat pump approximately doubles the efficiency of home heating and cooling, through heat-exchange with the shallow earth, which remains at 10-15°C temperatures year-round. This data-file captures the cost and CO2 savings.
-
US shale sand mines: simple economics?
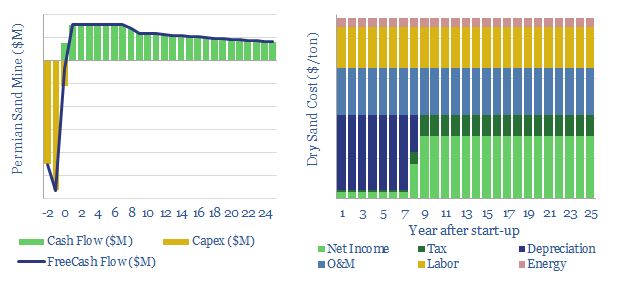
This model is a very simple breakdown of economics for in-basin sand production, around the US shale industry. The model can also be used to quantify the potential savings from shifting from dry sand to wet sand, estimated at c25% of total costs.
Content by Category
- Batteries (87)
- Biofuels (42)
- Carbon Intensity (49)
- CCS (63)
- CO2 Removals (9)
- Coal (38)
- Company Diligence (92)
- Data Models (823)
- Decarbonization (159)
- Demand (110)
- Digital (58)
- Downstream (44)
- Economic Model (200)
- Energy Efficiency (75)
- Hydrogen (63)
- Industry Data (276)
- LNG (48)
- Materials (81)
- Metals (75)
- Midstream (43)
- Natural Gas (146)
- Nature (76)
- Nuclear (23)
- Oil (163)
- Patents (38)
- Plastics (44)
- Power Grids (124)
- Renewables (149)
- Screen (112)
- Semiconductors (30)
- Shale (51)
- Solar (67)
- Supply-Demand (45)
- Vehicles (90)
- Wind (43)
- Written Research (347)