Search results for: “climate model”
-
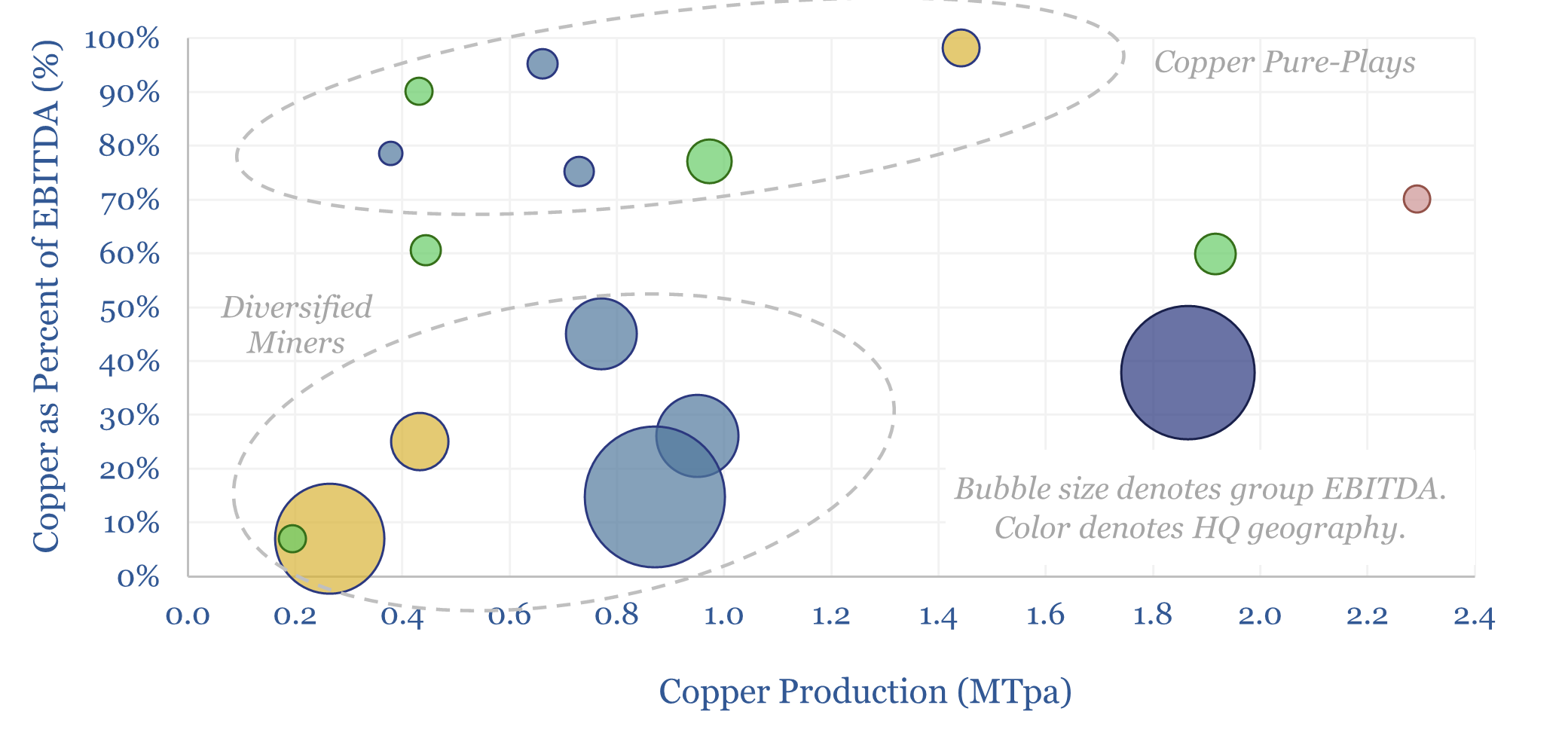
Synchronous condensers: the economics?
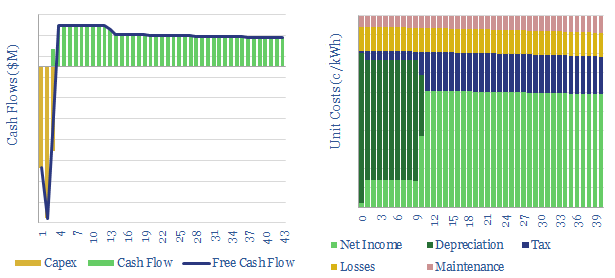
This data-file captures the costs of installing a synchronous condenser, downstream of a renewable power facility, to emulate the inertia, reactive power and short circuit power from conventional generators. 1.0 – 2.5 c/kWh of costs may be added to the power supplies flowing out of the SC.
-
Carbon neutral investing: hedge funds, forest funds?
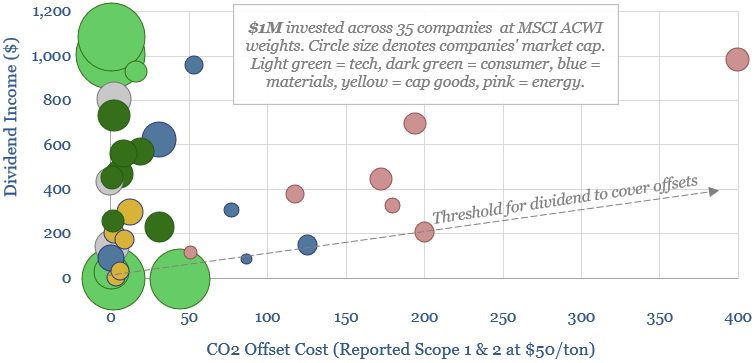
This 11-page note considers a new model of ‘carbon neutral’ investing. Look-through emissions of a portfolio are quantified (Scope 1 & 2 basis). Then accordingly, an allocation is made to high-quality, nature-based CO2 removals. Advantages and practicalities are discussed.
-
Variable frequency drives: the economics?
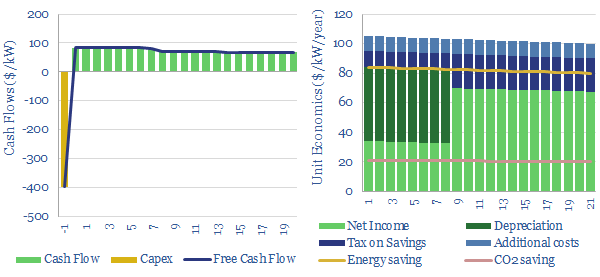
Variable frequency drives optimize the operating speeds of electric motors. Average energy saving are 34% and average costs are $250/kW. Hence our modelling calculates >15% IRRs installing a VFD at a typical industrial motor. This data-file captures the economics.
-
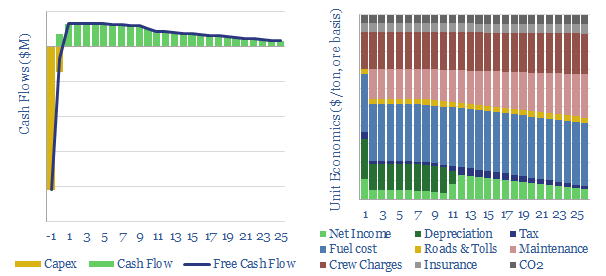
Glass fiber: the economics?
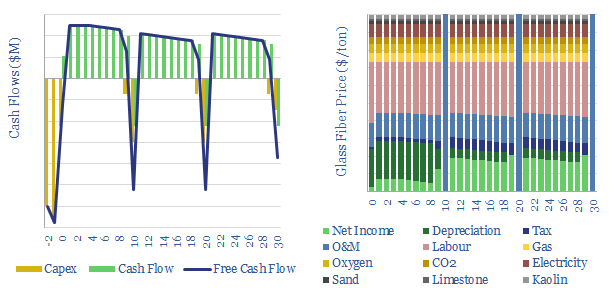
This data-file models the economics of producing glass fiber, the key component in fiberglass for wind turbines; but also a light-weight insulating material. Marginal cost is likely $2,000/ton, with a CO2 intensity of 1.5 tons/ton. Some Chinese product is 50% cheaper but 2x more CO2 intensive.
-
LNG regasification: the economics?
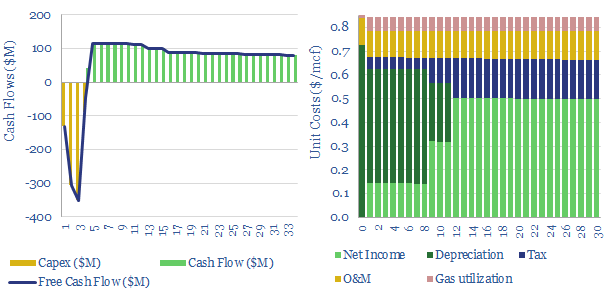
This data-file captures the economics for a typical LNG regas facility. We estimate that a fixed plant with 75-80% utilization requires a spread near to $0.5-0.8/mcf on its gas imports, in order to earn a 5-10% IRR. But there is asymmetric upside amidst gas shortages.
-
Fuel retail: economics of a petrol station?
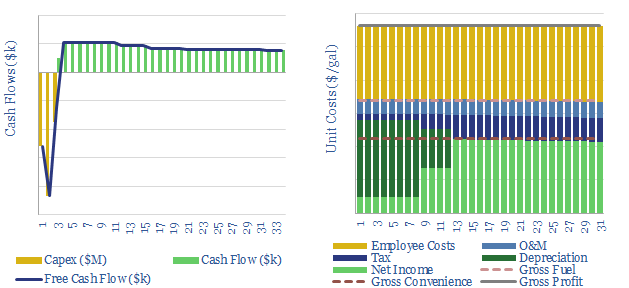
This data-file captures the economics for a fuel-retailing “petrol station” to earn a 10% IRR. A typical EBIT margin is 17c/gallon; with a c6% margin on direct fuel sales; plus 10-20% of revenues from convenience retail at a higher, c25-30% margin.
-
Japan: nuclear restart tracker?
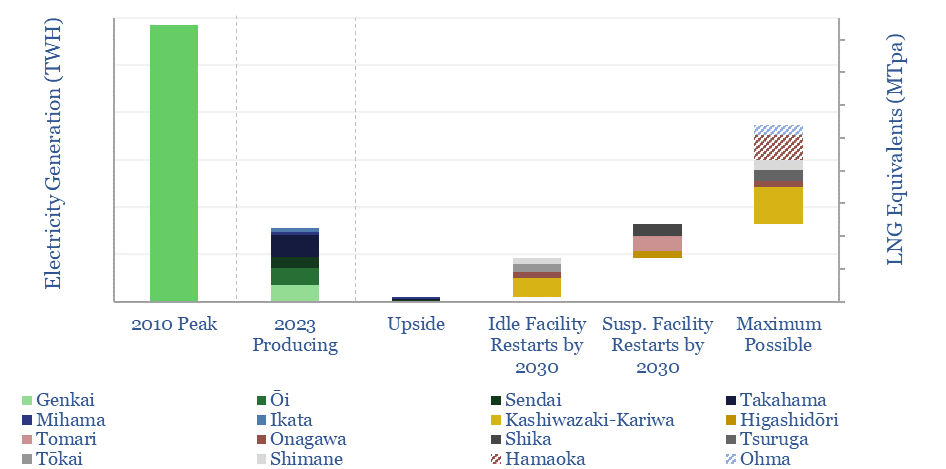
This data-file on looks through 17 major nuclear plants in Japan with 45GW of operable capacity, covering the key parameters and re-start news on each facility. Japan’s nuclear restart had ramped output back to 78TWH pa by 2023, and may rise by a further 100 TWH by 2030, to meet targets for 20% nuclear in…
-
Oil storage terminals: the economics?
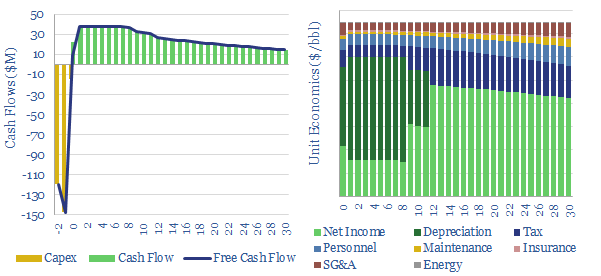
This data-file captures the economics of constructing an oil storage terminal (aka a “tank farm”). A typical facility needs to charge a $1.5/bbl storage spread to earn a 10% IRR over a 30-year life. Capex costs per kWh of energy are 97% lower than grid-scale batteries. It may become more challenging to finance new facilities…
Content by Category
- Batteries (89)
- Biofuels (44)
- Carbon Intensity (49)
- CCS (63)
- CO2 Removals (9)
- Coal (38)
- Company Diligence (95)
- Data Models (840)
- Decarbonization (160)
- Demand (110)
- Digital (60)
- Downstream (44)
- Economic Model (205)
- Energy Efficiency (75)
- Hydrogen (63)
- Industry Data (279)
- LNG (48)
- Materials (82)
- Metals (80)
- Midstream (43)
- Natural Gas (149)
- Nature (76)
- Nuclear (23)
- Oil (164)
- Patents (38)
- Plastics (44)
- Power Grids (131)
- Renewables (149)
- Screen (117)
- Semiconductors (32)
- Shale (51)
- Solar (68)
- Supply-Demand (45)
- Vehicles (90)
- Wind (44)
- Written Research (356)