Search results for: “direct air capture”
-
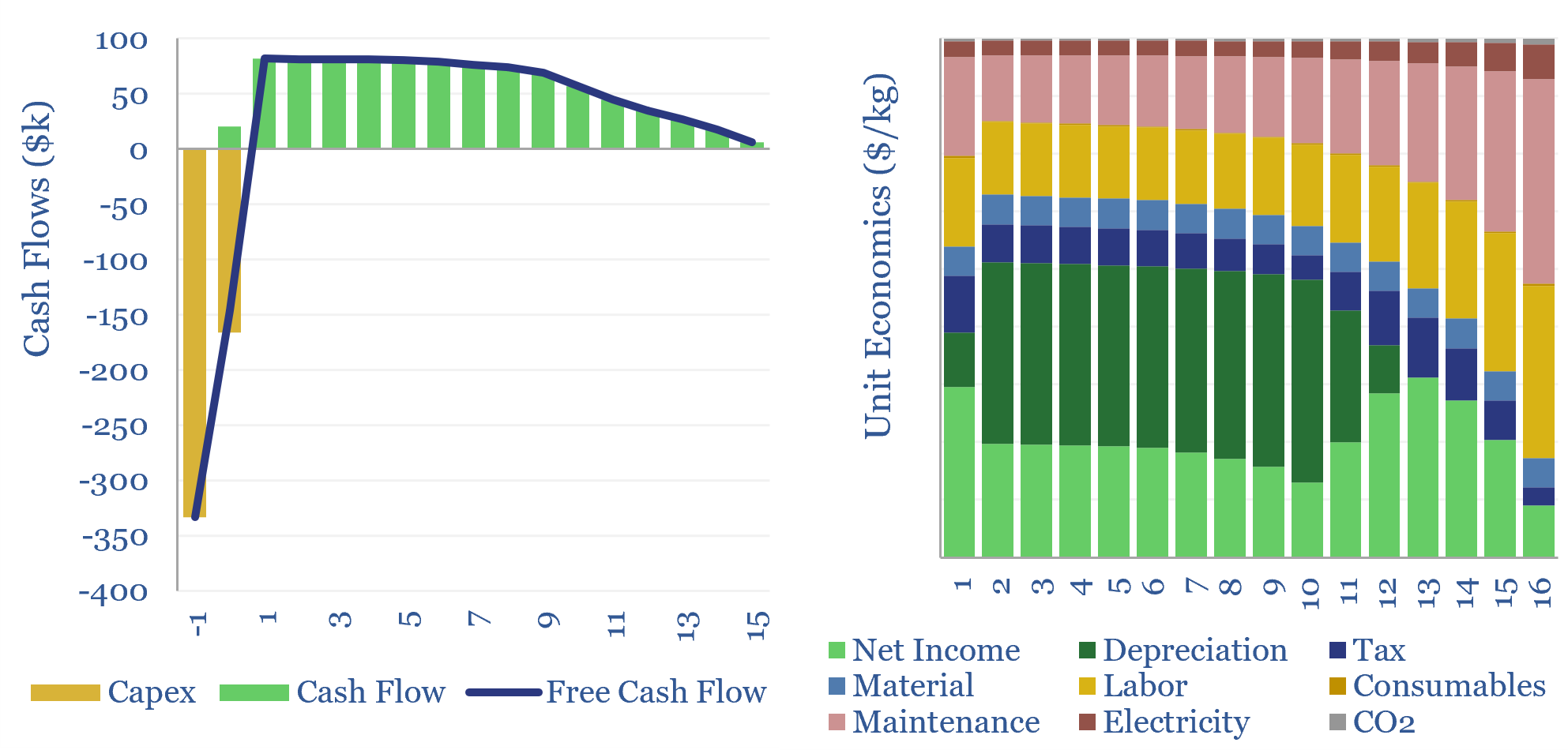
Servo motors: cost calculator?
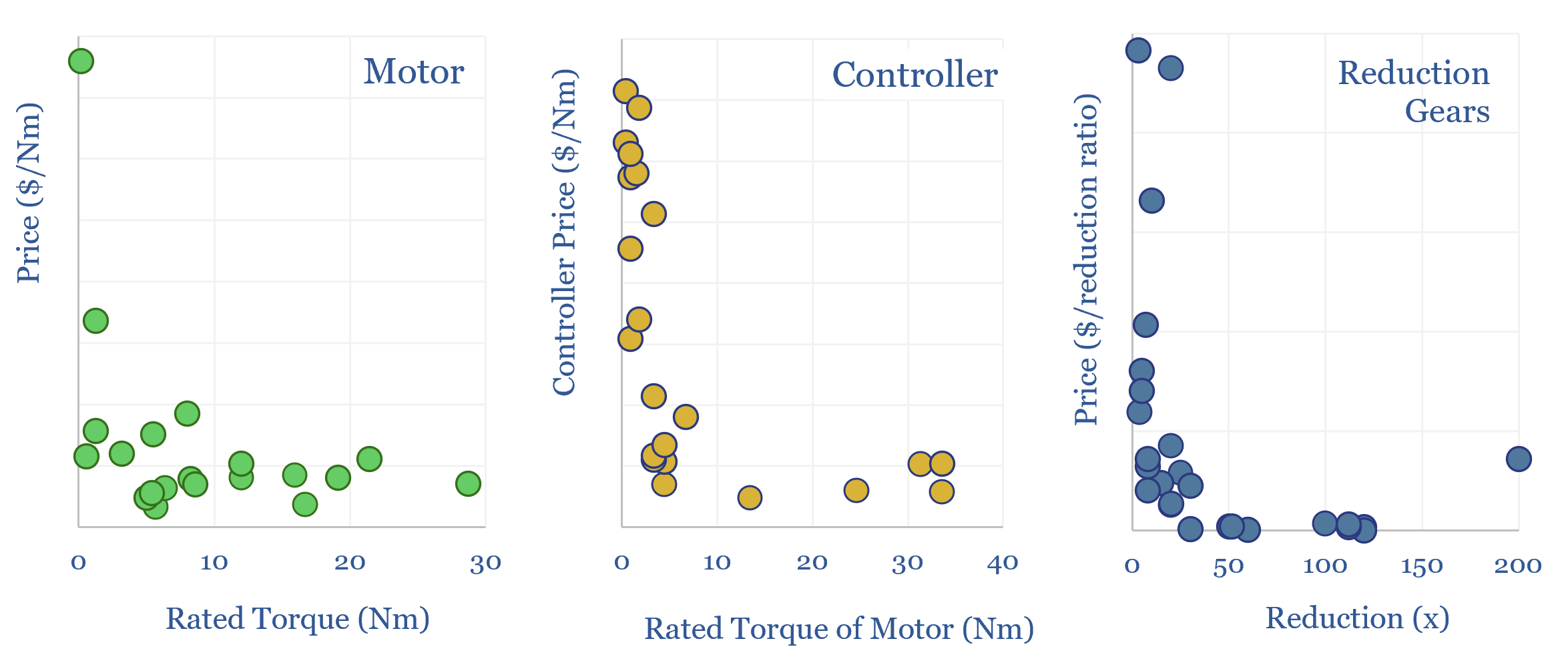
Servo motors form a $16bn pa market, used in robotics, precision manufacturing equipment, CNC machines, aerospace and med-tech. This data-file estimates the costs of servo-motors, based on underlying controller costs, motor costs and reduction gear costs. Hence we have attempted a simple servo motor cost calculator.
-
Storage tank costs: storing oil, energy, water and chemicals?
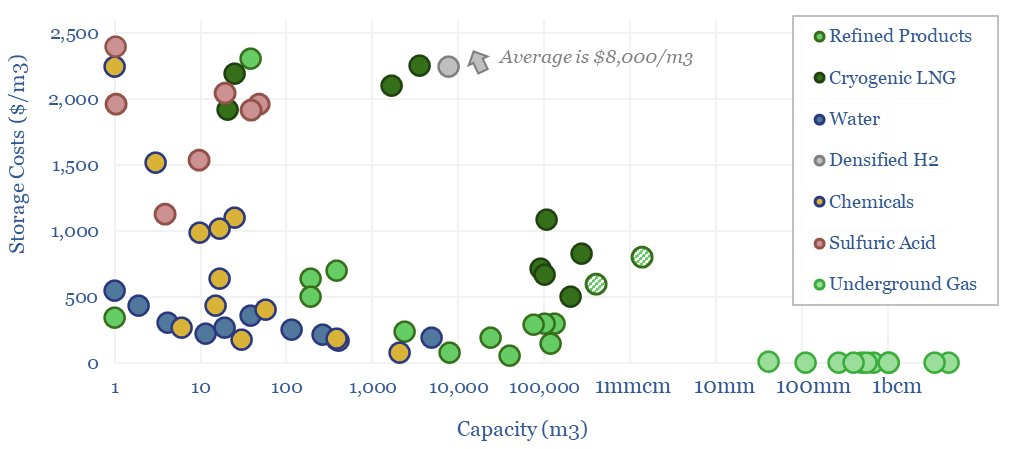
Storage tank costs are tabulated in this data-file, averaging $100-300/m3 for storage systems of 10-10,000 m3 capacity. Costs are 2-10x higher for corrosive chemicals, cryogenic storage, or very large/small storage facilities. Some rules of thumb are outlined below with underlying data available in the Excel.
-
Industrial gas separation: swing producers?
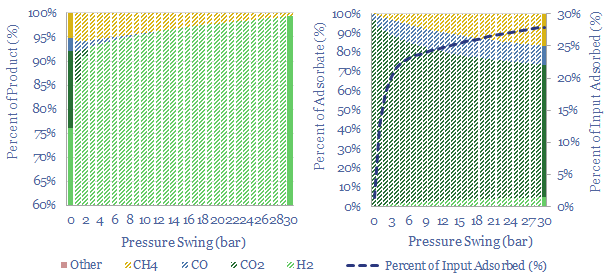
Swing Adsorption separates gases, based on their differential loading onto zeolite adsorbents at varying Pressures. The first PSA plant goes back to 1966. Today, tens of thousands of PSA plants purify hydrogen, biogas, polymers, nitrogen/oxygen and possibly in the future, can capture CO2? This 16-page note explores the technology, costs, challenges, companies.
-
Exhaust gas recirculation in gas power: the economics?
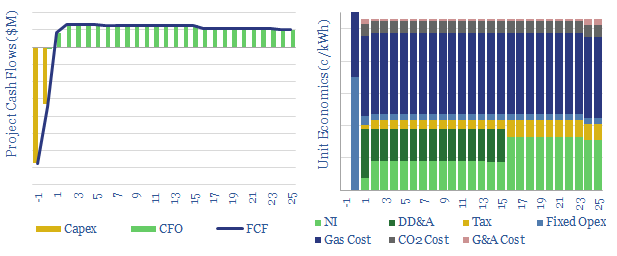
This data-file explores an alternative design for a combined cycle gas turbine, re-circulating exhaust gases after combustion, in order to facilitate CO2 capture. Costs and operating parameters are summarized from recent technical papers. Even with EGR, it will be challenging to decarbonize a gas turbine for less than $100/ton.
-
Afforesting deserts: energy economics?
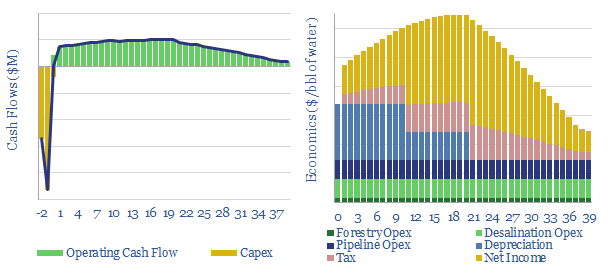
We model the economics of afforesting deserts by desalinating and distributing sufficient water for trees to grow. The best economics are achievable in the Permian, with 10% IRRs at $30/ton CO2 prices. But the energy economics cannot work to green the world’s most hyper-arid deserts, such as the Sahara.
-
Waste heat recovery: heat exchanger costs?
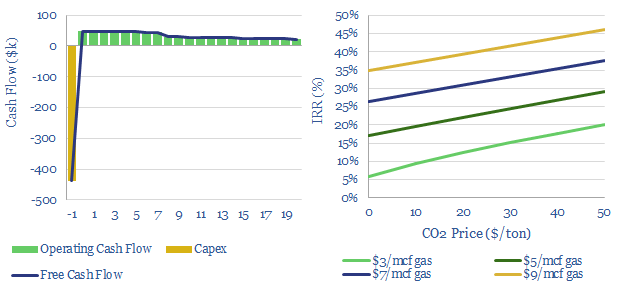
Industrial heat comprises around 20% of global CO2 emissions, but around half of all heat generated may ultimately be wasted. Hence, this model simplifies the economics of using a heat exchanger to recover waste heat. A CO2 price above $50/ton would greatly accelerate waste heat recovery projects.
-
Renewable diesel: the economics?
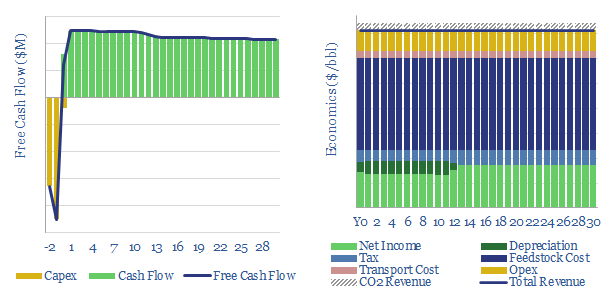
Our base case is that a US renewable diesel facility must achieve $4.6/gallon sales revenues (which is c$200/bbl) as it commercializes a product with up to 75% lower embedded emissions than conventional diesel. Similarly, a bio-diesel facility must achieve $3.6/gallon sales on a product with 60% lower embedded emissions.
-
US shale: the quick and the dead?
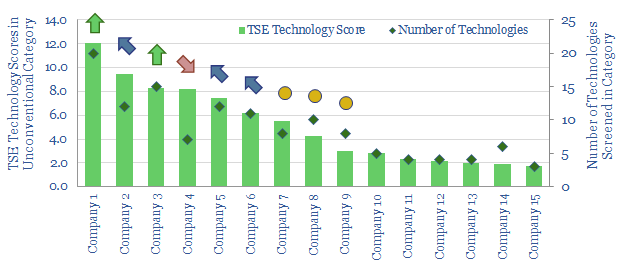
It is no longer possible to compete in the US shale industry without leading digital technologies. This 10-page note outlines best practices, process by process, based on 500 patents and 650 technical papers. Chevron, Conoco and ExxonMobil lead our screens. Falling from the leader-board is EOG, whose long-revered technical edge may have been eclipsed.
-
CO2 disposal in geologic formations: the economics?
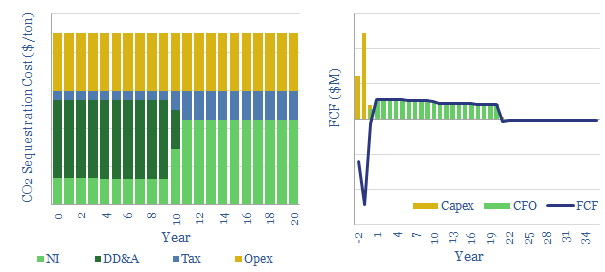
Costs of disposing of CO2 are extremely variable and project-dependent, ranging from $5-50/ton, with a base case of $22.5/ton. This is the disposal price needed to earn a 10% post-tax IRR, transporting, injecting and monitoring CO2 in the subsurface.
Content by Category
- Batteries (89)
- Biofuels (44)
- Carbon Intensity (49)
- CCS (63)
- CO2 Removals (9)
- Coal (38)
- Company Diligence (95)
- Data Models (840)
- Decarbonization (160)
- Demand (110)
- Digital (60)
- Downstream (44)
- Economic Model (205)
- Energy Efficiency (75)
- Hydrogen (63)
- Industry Data (279)
- LNG (48)
- Materials (82)
- Metals (80)
- Midstream (43)
- Natural Gas (149)
- Nature (76)
- Nuclear (23)
- Oil (164)
- Patents (38)
- Plastics (44)
- Power Grids (130)
- Renewables (149)
- Screen (117)
- Semiconductors (32)
- Shale (51)
- Solar (68)
- Supply-Demand (45)
- Vehicles (90)
- Wind (44)
- Written Research (354)