Industrial heat comprises around 20% of global CO2 emissions, but around half of all the heat generated may ultimately be wasted. Hence, this model simplifies the economics of waste heat recovery, capturing the costs of heat exchangers at industrial facilities, based on the engineering equations of heat exchange and recent technical papers.
Different estimates place the global heat exchanger market value at around $20bn per year as of 2022, as captured in our database of market sizing.
But heat exchange becomes increasingly important to accelerate efficiency gains in the energy transition. Heat exchangers are used to increase the efficiency of thermal power plants (60% of combustion heat ends up in the exhaust gas!), for thermal energy storage, or to lower the energy penalties from CCS absorbers.
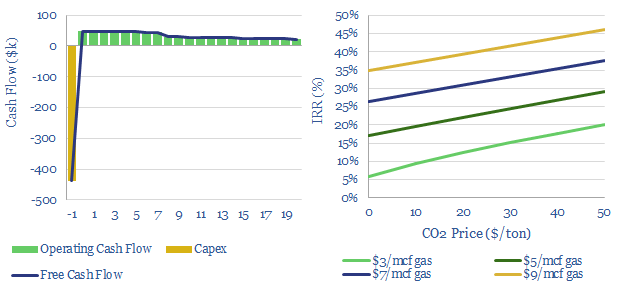
Installing a heat exchanger to capture waste heat will likely earn a 6% IRR in our base case assumptions for the US at $3/mcf natural gas.
IRRs are uplifted to above 20%, either if we assume higher gas prices ($6/mcf) or a $50/ton CO2 price. IRRs can reach 40% with both.
High IRRs may be necessary to unlock waste heat recovery. First, each project is complex, with large amounts of engineering, and implementation disrupts operations at a plant.
Second, although IRRs are high, NPVs are low, as many projects will be small-scale. For example, the NPV10 may be less than $1M on a single, small heat exchanger project, even if it achieves a 40% IRR.
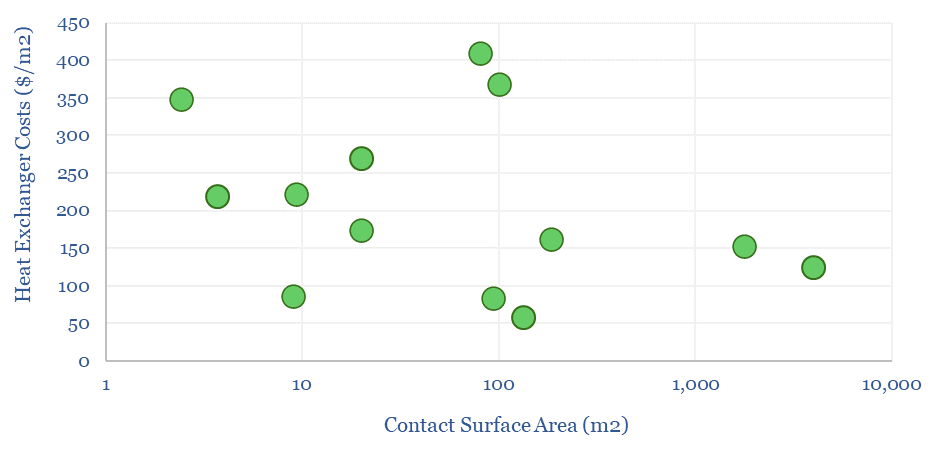
The capex costs of heat exchangers are estimated at $200/m2 on average, but this varies between $100/m2 and $500/m2 depending on the thermal swing and corrosiveness of fluid streams being heat exchanged. Some systems use stainless steel and others require high grade nickel steels. Plate-fin designs are 2x more efficient than shell-tube designs.
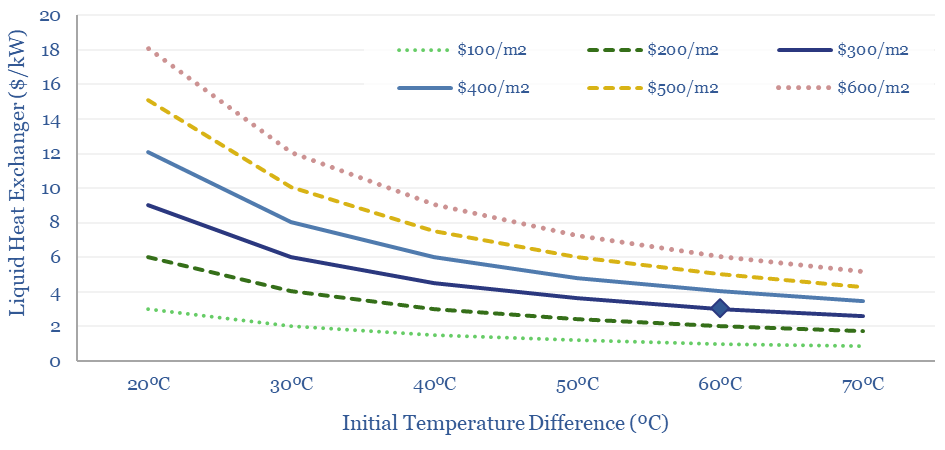
The capex costs of heat exchangers in $/kW terms are variable, and complex to calculate, but we have made an attempt in the ‘Cost Estimates’ tab. Heat exchanger cost depends on the heat transfer coefficient of the heat exchanger in kW/m2-K (which itself can vary by a factor of 200x), the size of the heat exchanger (in m2 of surface area and m3 of capacity), while the amount of heat exchange (in kW) will mostly be determined by the temperature difference of the fluids being heat-exchanged.
Other research into waste heat recovery covers Rankine Engines, Absorption Chillers and Insulation Materials.
The model contains a variation looking at waste heat recovery in gas-fired facilities, and another variation looking at waste-heat recovery in coal-fired facilities. Then there are backup tabs with tabulated costs for heat exchangers (in $/m2), translating $/m2 cost terms into $/kW terms, and notes from technical papers.