Search results for: “gas”
-
Green Hydrogen Economy: Holy Roman Empire?
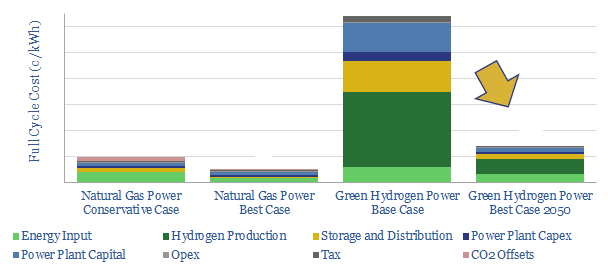
We model the green hydrogen value chain: harnessing renewable energy, electrolysing water, storing the hydrogen, then generating usable power in a fuel cell. Today’s costs are very high, at 64c/kWh. Even by 2050, our best case scenario is 14c/kWh, which elevates household electricity bills by $440-990/year compared with decarbonizing natural gas.
-
Oil: what happens when you defer or curtail production?

The aim of this data-file is to tabulate technical papers into production deferrals at oil and gas fields. The impact depends on the reservoir type, but generally we expect shut-ins during the 2020 COVID crisis will lower effective production capacity. Shale and Middle East producers could be relatively better placed.
-
Green deserts: a final frontier for forest carbon?
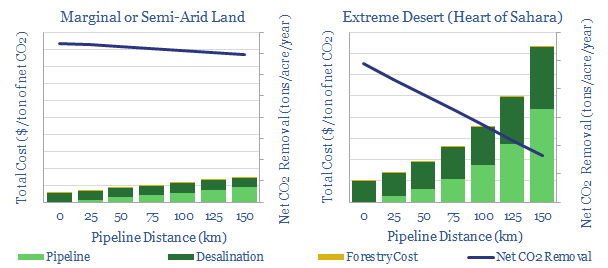
Is there potential to afforest any of the world’s 11bn acres of arid and semi-arid lands, by desalinating and distributing seawater? Energy economics do not work in the most extreme deserts (e.g., the Sahara). Buy $60-120/ton CO2 prices may suffice in semi-arid climates. The best economics of all use waste water from oil and gas,…
-
Hydrogen vehicles and fuelling stations: where’s the IP?
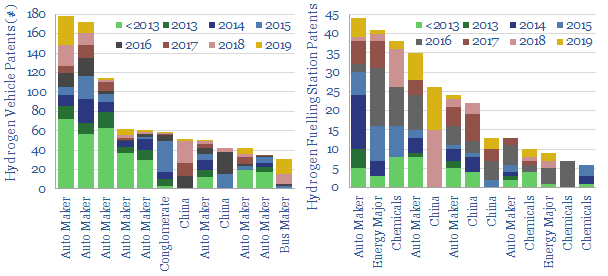
We cleaned 18,600 patents into hydrogen vehicles and vehicle fuelling stations. Technology leaders include large auto-makers, industrial gas companies, Energy Majors and hydrogen specialists. Overall, the patents indicate the array of challenges that must be solved to scale up hydrogen fuel in transport.
-
Hydrogen: lost in transportation?
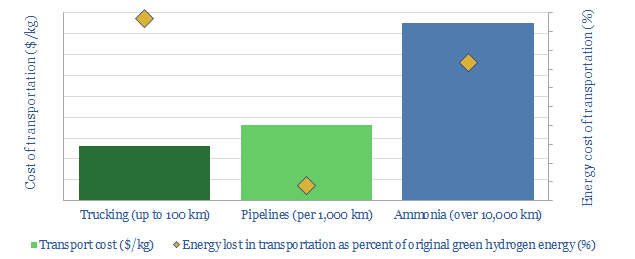
Transporting hydrogen will be more challenging than any other energy commodity ever commercialised. This 19-page note reviews the costs and complexities of cryogenic trucks, pipelines and chemical carriers (e.g., ammonia). Midstream costs will be 2-10x higher than natural gas, while up to 50% of hydrogen’s embedded energy may be lost in transit.
-
Technology transition database: what determines adoption rates?
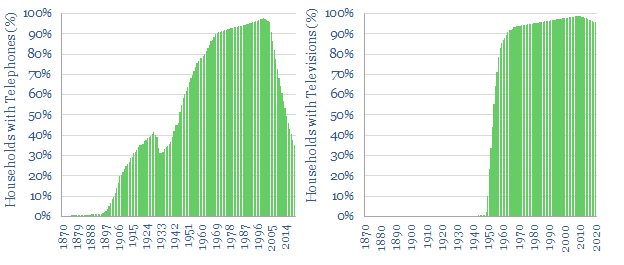
This database plots the adoption rates for twenty technologies that transformed living standards around the United States, year-by-year, from 1870 to 2020. Adoption rates are more rapid for technologies when they require less infrastructure, are more transformational, are more economic and are more recent.
-
Wind power: decline rate conclusions?
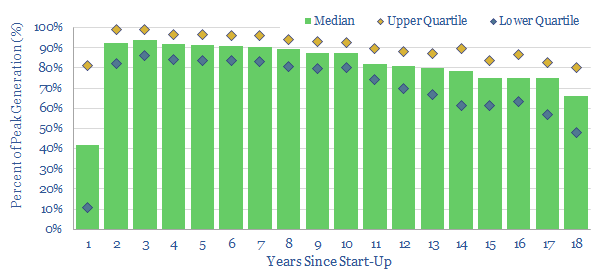
This 4-page PDF presents our conclusions from tabulating the ‘decline rates’ of 1,215 US wind power plants, which have reported data to the US EIA. US wind generation profiles are not dissimilar from well-managed oil and gas fields; some projects may suffer 2% lower IRRs versus forecasts if they have not factored in declines; and…
-
Solar power: decline rates?
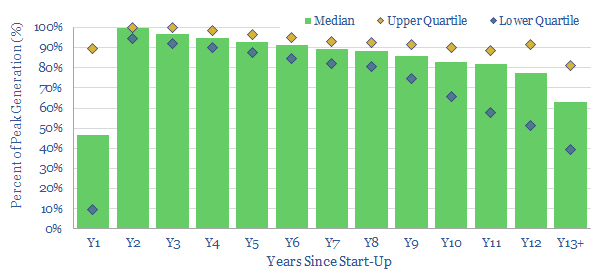
This data-file tabulates the ‘decline rates’ of 3,200 US solar power plants going back to 2001. The median YoY decline is found to run at 2.5%. However, the data are volatile and variable. Hence this data-file gives full granularity, asset by asset. Decline rates could detract c4pp from the IRRs of future solar projects and…
-
US shale: the economics?
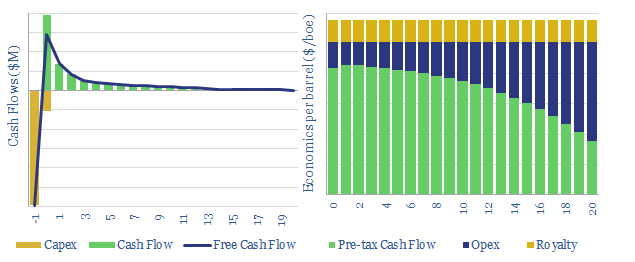
This model breaks down the economics of US shale, including a granular build-up of capex costs across 18 different categories. Our base case requires a $40/bbl oil price for a 10% IRR at a $7.0M shale well with a 1.0 kboed IP30. Economics range from $35-50/bbl. They are most sensitive to productivity.
-
Ground source heat pumps: the economics?
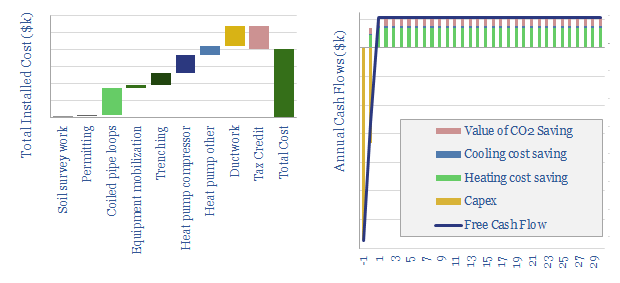
A ground source heat pump approximately doubles the efficiency of home heating and cooling, through heat-exchange with the shallow earth, which remains at 10-15°C temperatures year-round. This data-file captures the cost and CO2 savings.
Content by Category
- Batteries (89)
- Biofuels (44)
- Carbon Intensity (49)
- CCS (63)
- CO2 Removals (9)
- Coal (38)
- Company Diligence (95)
- Data Models (840)
- Decarbonization (160)
- Demand (110)
- Digital (60)
- Downstream (44)
- Economic Model (205)
- Energy Efficiency (75)
- Hydrogen (63)
- Industry Data (279)
- LNG (48)
- Materials (82)
- Metals (80)
- Midstream (43)
- Natural Gas (149)
- Nature (76)
- Nuclear (23)
- Oil (164)
- Patents (38)
- Plastics (44)
- Power Grids (130)
- Renewables (149)
- Screen (117)
- Semiconductors (32)
- Shale (51)
- Solar (68)
- Supply-Demand (45)
- Vehicles (90)
- Wind (44)
- Written Research (355)