Search results for: “small scale LNG”
-
The Ascent of Small Scale LNG?
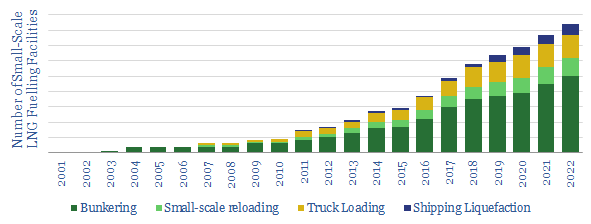
Large LNG projects make large headlines. But we are excited by the ascent of small-scale LNG facilities. At less than 1MTpa each, these facilities can be harder to track, which is the objective of this data-file. We find small LNG liquefaction capacity is set to double, to 25MTpa. Liquefaction facilities for shipping will rise 8x…
-
Small-Scale LNG liquefaction Costs: New Opportunities?
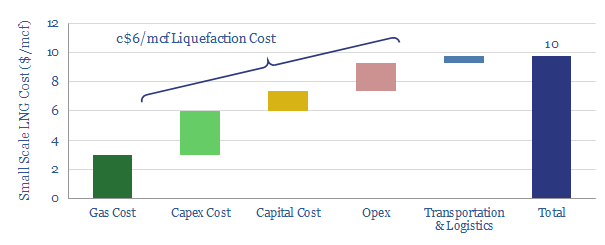
Small-scale LNG technologies can be economic at $10/mcf, generating 15% pre-tax IRRs, off $3/mcf input gas. This data-file tabulates the line-by-line costs of typical small-scale LNG technologies (SMRs, N2 expansion). Against this baseline, we model a more cutting-edge technology, which preserves strong economics at c25x smaller scale.
-
LNG: top conclusions in the energy transition?
Thunder Said Energy is a research firm focused on economic opportunities that drive the energy transition. Our top ten conclusions into LNG are summarized below, looking across all of our research.
-
LNG liquefaction technologies: an overview?
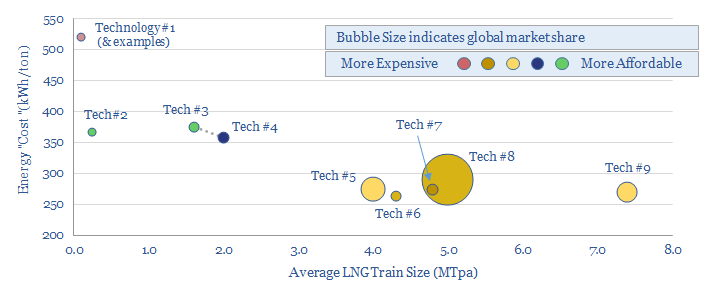
This data-file is an overview of different LNG liquefaction technologies: APCI, APX, Optimised Cascade, Fluid Cascade, DMR, SMR, PRICO and MMLS. A typical LNG liquefaction plant has energy intensity of 280kWh/ton, consuming 5% of the input gas entering the plant, with 20kg/boe of Scope 1&2 CO2 intensity. But efficient and electric-drive compression can lower these…
-
How do LNG costs vary with plant size?
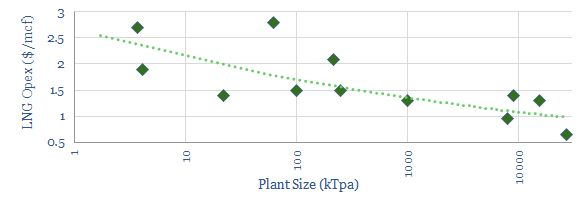
This data-file tabulates a dozen data-points on LNG plant opex, from company disclosures, the technical literature and academic papers. Opex is a function of plant size, and tends to fall by $0.3/mcf for each 10x change in plant capacity.
-
Global LNG supply model: by project and by country?

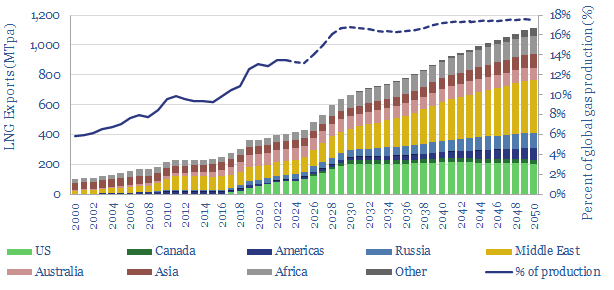
Global LNG output ran at 406MTpa in 2024. This model estimates global LNG production by facility across 150 LNG facilities. Our latest forecasts are that global LNG demand will rise at a 6% CAGR, to reach 710MTpa by 2035, for an absolute growth rate of +30MTpa per year, but there is a supply-crunch in 2024-26,…
-
LNG plant compression: gas drives vs electric motors?
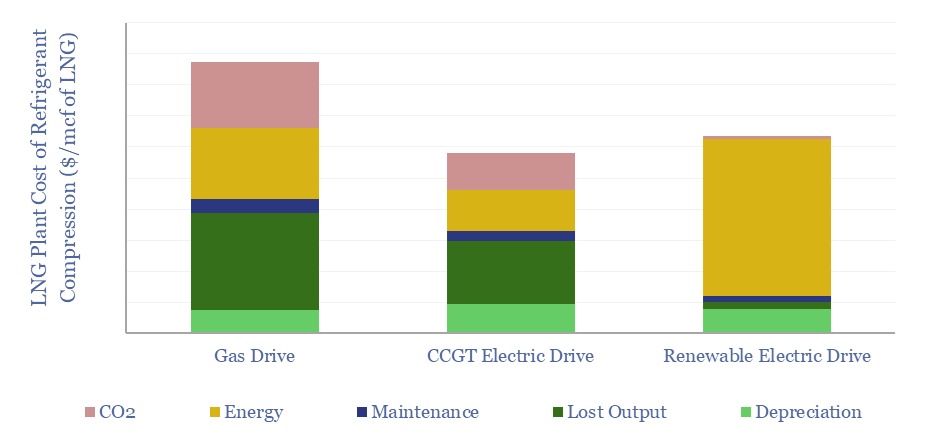
This data-file compares the costs of refrigerant compression at LNG plants, using gas turbines, electric motors powered by on-site CCGTs, or electric motors powered by renewable electricity. eLNG has higher capex costs, but higher efficiency, lower opex, and short payback times. Numbers in $/mcf and $/MTpa can be stress-tested in the data-file.
-
Global LNG: offtake contracts and spot market development?
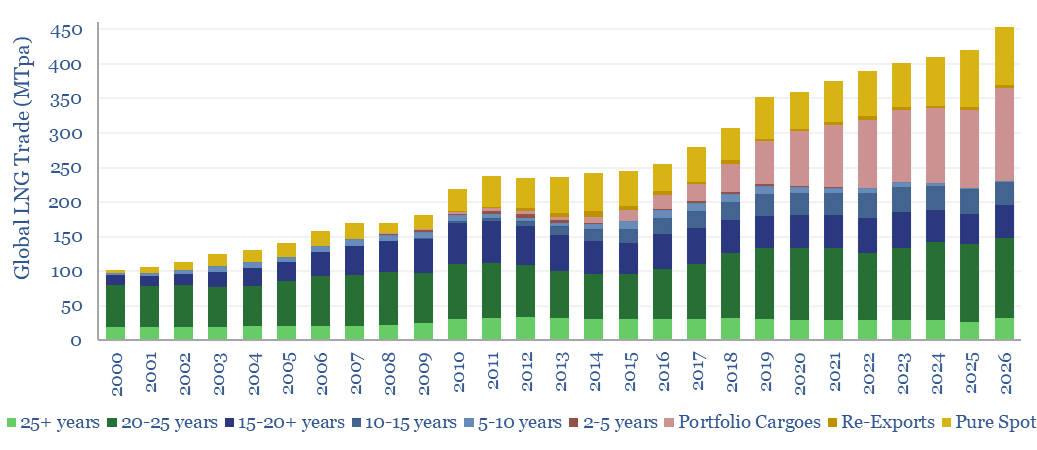
This database of global LNG contracts tabulates the details for 450 LNG offtake contracts, tracking buyers, sellers, facilities, contract durations and destination flexibility. The total market has grown by 3x in the past 20-years to 400MTpa in 2023, while the spot and short-term market has increased by 10x to 150MTpa.
-
LNG as a Shipping Fuel: the Economics
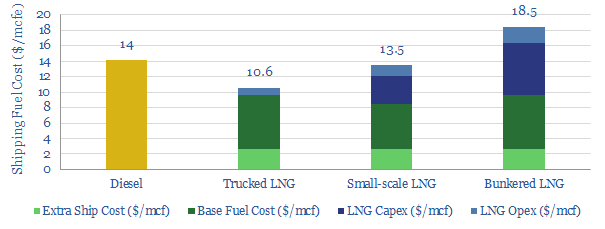
This data-file provides line-by-line cost estimates for LNG as a shipping fuel, for trucked LNG, small-scale LNG and bunkered LNG. After IMO 2020 regulations buoy diesel pricing, it should be economical to fuel newbuild ships with small-scale LNG; and in the US it should be economical to convert pre-existing ships to LNG.
-
LNG liquefaction: the economics?
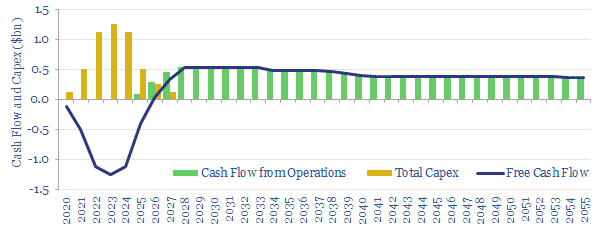
This model captures the economics for a typical LNG liquefaction project, breaking down IRRs and NPVs as a function of key input-variables. In our base case, a new LNG project costing $750/Tpa must charge a $3.6/mcf liquefaction spred for a 10% IRR.
Content by Category
- Batteries (89)
- Biofuels (44)
- Carbon Intensity (49)
- CCS (63)
- CO2 Removals (9)
- Coal (38)
- Company Diligence (95)
- Data Models (840)
- Decarbonization (160)
- Demand (110)
- Digital (60)
- Downstream (44)
- Economic Model (205)
- Energy Efficiency (75)
- Hydrogen (63)
- Industry Data (279)
- LNG (48)
- Materials (82)
- Metals (80)
- Midstream (43)
- Natural Gas (149)
- Nature (76)
- Nuclear (23)
- Oil (164)
- Patents (38)
- Plastics (44)
- Power Grids (130)
- Renewables (149)
- Screen (117)
- Semiconductors (32)
- Shale (51)
- Solar (68)
- Supply-Demand (45)
- Vehicles (90)
- Wind (44)
- Written Research (354)