Search results for: “climate model”
-
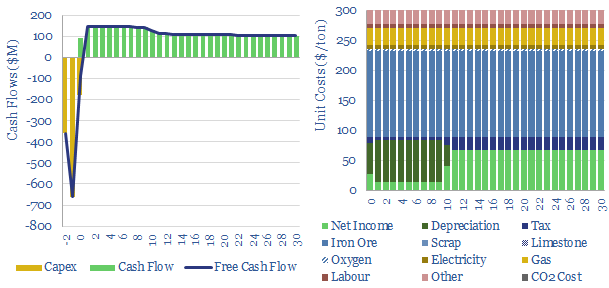
Aluminium producers: company screen?
Leading aluminium producers are reviewed in this data-file, across ten companies, producing half of the world’s global output. Scale ranges 1MTpa to 7MTpa. CO2 intensity of primary aluminium production ranges from 3 tons/ton to 17 tons/ton, in aggregate across these companies.
-
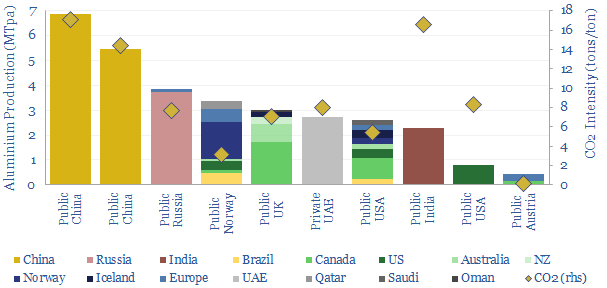
Cement costs and energy economics?
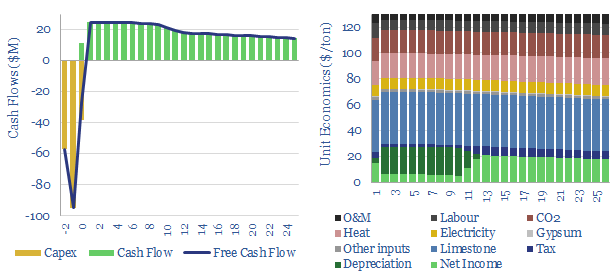
This data-file captures cement costs, based on inputs, capex and energy economics. A typical cement plant requires a cement price of $130/ton for a 10% IRR, on capex costs of $200/Tpa, energy intensity of 1,000 kWh/ton and CO2 intensity of 0.9 tons/ton. Cement costs can be stress tested in the data-file.
-
US hydrogen production: by facility and by company?
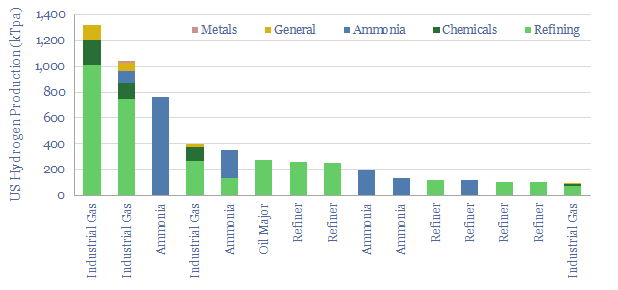
10MTpa of hydrogen is produced in the US, of which 40% is sold by industrial gas companies, 20-25% is generated on site at refineries, 20% at ammonia plants and 15-20% in chemicals/methanol. This datafile breaks down US hydrogen production by facility. Owners of existing steam methane reforming units may readily be able to capture CO2…
-
MHI CCS technology: performance, costs and emissions?
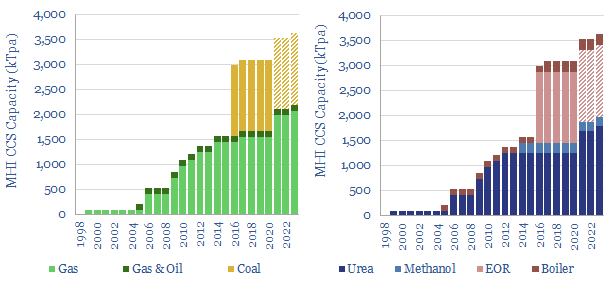
MHI has deployed an amine-based CO2 capture technology, in 15 plants globally, going back to 1999. Reboiler duties are around 2.6 GJ/ton on a 10% CO2 feed. Capture rates and capture purity are high. Degradation and amine emissions are controlled, and c80-90% below MEA. CCS costs and complexities remain high. In our view, this is…
-
Naphtha cracking: costs of ethylene, propylene and aromatics?
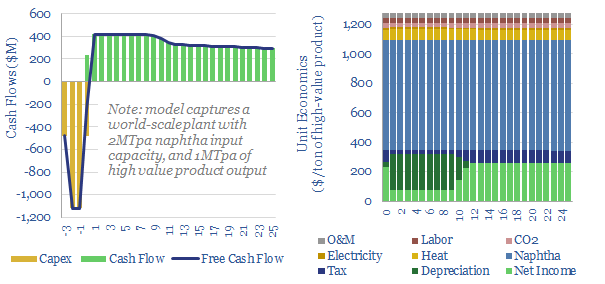
Naphtha cracking costs $1,300/ton for high value products, such as ethylene, propylene, butadiene and BTX aromatics, to derive a 10% IRR constructing a greenfield naphtha cracker, with $1,600/Tpa capex. CO2 intensity averages 1 ton of CO2 per ton of high value products. This data-file captures the economics for naphtha cracking, a cornerstone of the modern…
-
MIRALON: turquoise hydrogen breakthrough?
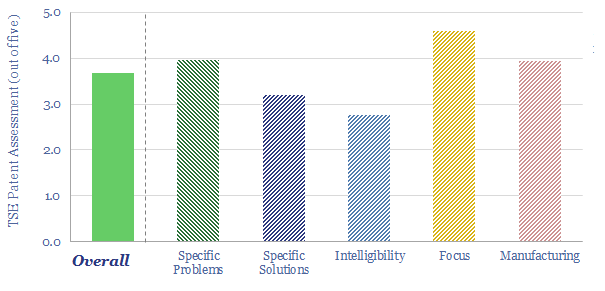
MIRALON is an advanced material, being commercialized by Huntsman, purifying carbon nanotubes from the pyrolysis of methane and also yielding turquoise hydrogen. This data-file reviews MIRALON technology, patents, and a strong moat. Our model sees 15% IRRs if Huntsman reaches a medium-term cost target of $10/kg MIRALON and $1/kg H2.
-
Global hydrogen supply-demand: by region, by use & over time?
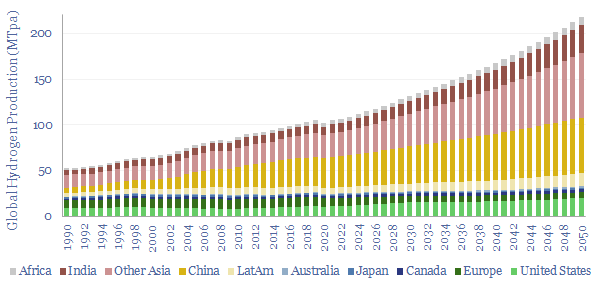
Global production of hydrogen is around 110MTpa in 2023, of which c30% is for ammonia, 25% is for refining, c20% for methanol and c25% for other metals and materials. This data-file estimates global hydrogen supply and demand, by use, by region, and over time, with projections through 2050.
-
Hot potassium carbonate CCS: energy economics?
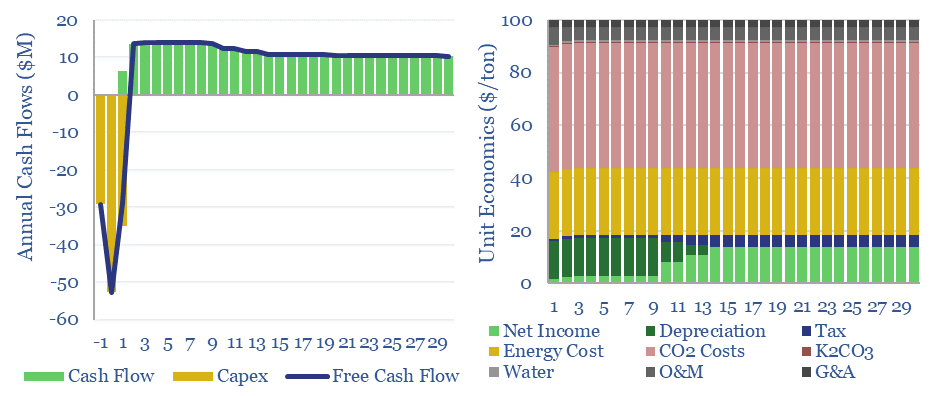
Hot potassium carbonate is a post-combustion CCS technology that bypasses the degradation issues of amines, and can help to decarbonize power, BECCS and cement plants. We think costs are around $100/ton and energy penalties are 30-50%. Potassium carbonate CCS can be stress-tested in this data-file, across 50 inputs.
-
Redox flow batteries: costs and capex?
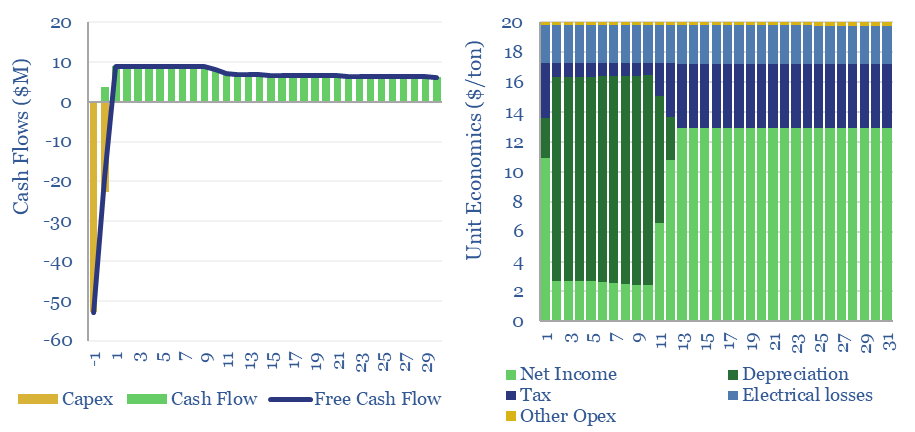
Redox flow battery costs are built up in this data-file, especially for Vanadium redox flow. In our base case, a 6-hour battery that charges and discharges daily needs a storage spread of 20c/kWh to earn a 10% IRR on $3,000/kW of up-front capex. Longer-duration redox flow batteries start to out-compete lithium ion batteries for grid-scale…
Content by Category
- Batteries (89)
- Biofuels (44)
- Carbon Intensity (49)
- CCS (63)
- CO2 Removals (9)
- Coal (38)
- Company Diligence (95)
- Data Models (840)
- Decarbonization (160)
- Demand (110)
- Digital (60)
- Downstream (44)
- Economic Model (205)
- Energy Efficiency (75)
- Hydrogen (63)
- Industry Data (279)
- LNG (48)
- Materials (82)
- Metals (80)
- Midstream (43)
- Natural Gas (149)
- Nature (76)
- Nuclear (23)
- Oil (164)
- Patents (38)
- Plastics (44)
- Power Grids (130)
- Renewables (149)
- Screen (117)
- Semiconductors (32)
- Shale (51)
- Solar (68)
- Supply-Demand (45)
- Vehicles (90)
- Wind (44)
- Written Research (354)