Search results for: “heat pumps”
-
Pumped hydro: generation profile?
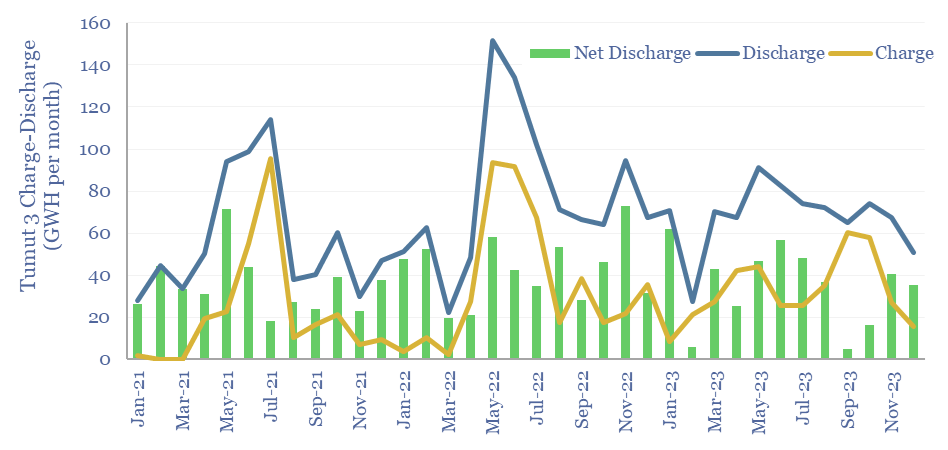
Pumped hydro facilities can provide long-duration storage, but the utilization rate is low, and thus the costs are high, according to today’s case study within the Snowy hydro complex in Australia. Tumut-3 can store energy for weeks-months, then generate 1.8 GW for 40+ hours, but it is only charging/dischaging at 12% of its nameplate capacity.
-
Midstream opportunities in the energy transition?
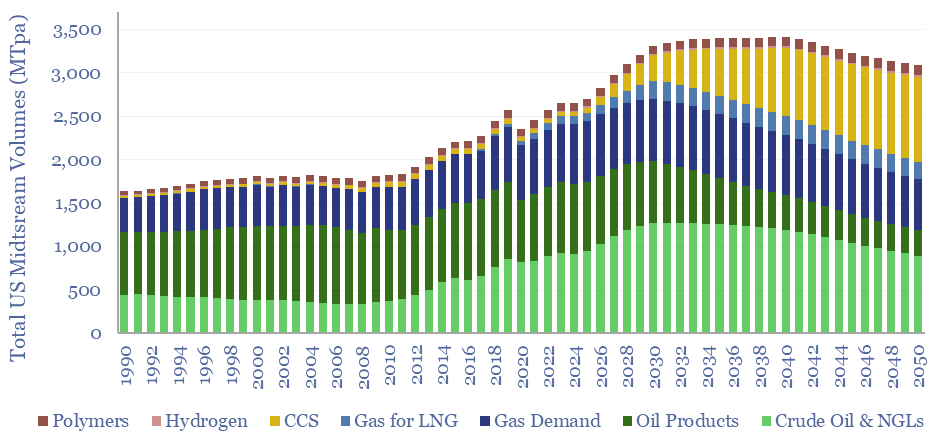
The midstream industry moves molecules, especially energy-molecules, and especially in pipelines. Despite the mega-trend of electrification, there are still strong midstream opportunities in the energy transition, backstopping volatility and moving new molecules. This short note captures our top ten conclusions. (1) Our overall outlook on the US midstream industry sees the total tonnage of molecules…
-
Market concentration by industry in the energy transition?
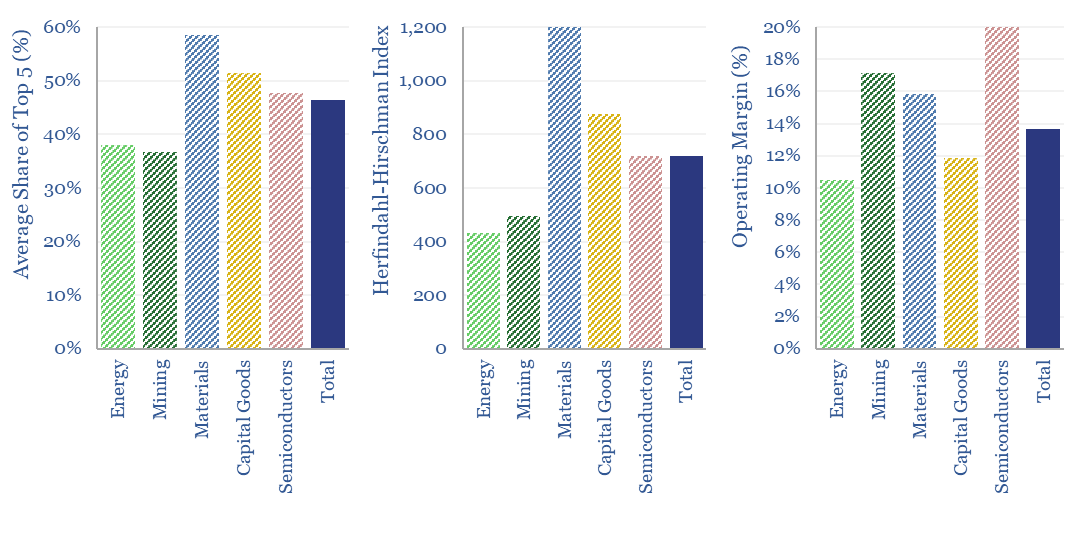
What is the market concentration by industry in energy, mining, materials, semiconductors, capital goods and other sectors that matter in the energy transition? The top five firms tend to control 45% of their respective markets, yielding a ‘Herfindahl Hirschman Index’ (HHI) of 700.
-
Storage tank costs: storing oil, energy, water and chemicals?
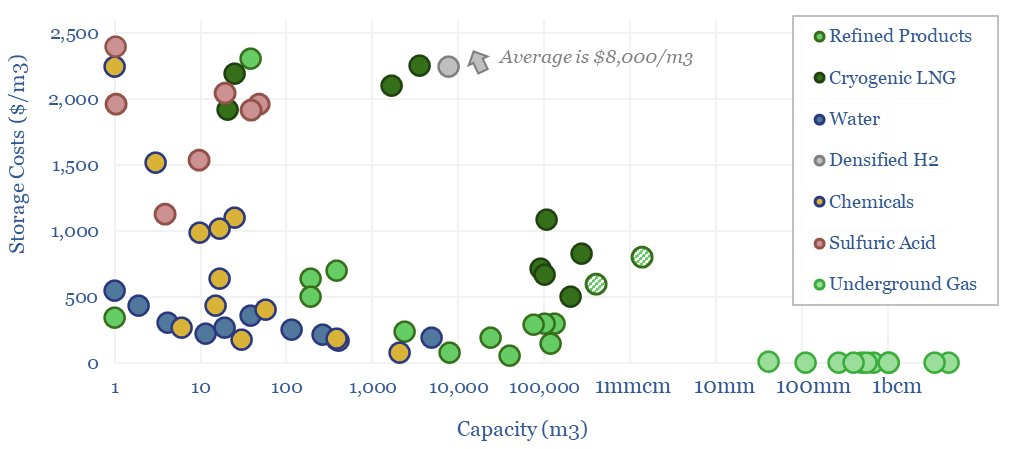
Storage tank costs are tabulated in this data-file, averaging $100-300/m3 for storage systems of 10-10,000 m3 capacity. Costs are 2-10x higher for corrosive chemicals, cryogenic storage, or very large/small storage facilities. Some rules of thumb are outlined below with underlying data available in the Excel.
-
Desalination by reverse osmosis: the economics?
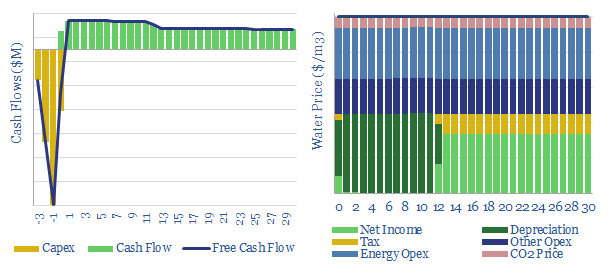
35bn tons of desalinated water are produced each year, absorbing 250 TWH of energy, or 0.4% of total global energy consumption. These numbers will likely rise, due to demographic trends, and due to climate change. Desalination costs average $1.0/m3, use 3.5kWh/m3 of electricity and can demand shift.
-
Flaring reduction: screen of service and equipment companies?
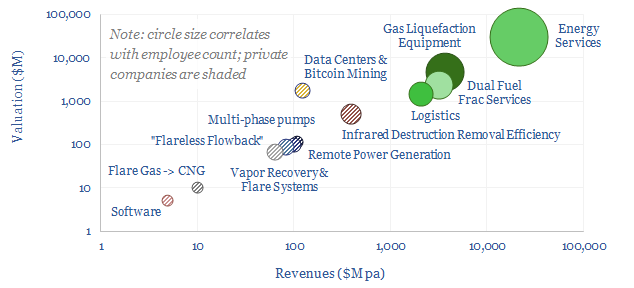
This data-file is a screen of companies that can reduce routine flaring and reduce the ESG impacts of unavoidable residual flaring. The landscape is broad, ranging from large, listed and diversified oil service companies with $30bn market cap to small private analytics companies with
-
Global CO2 emissions breakdown?
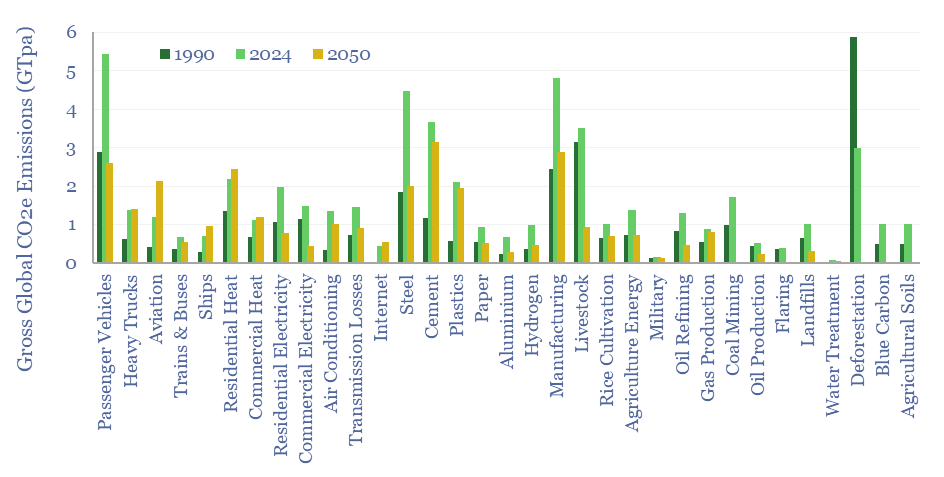
Global CO2 emissions rose from 32GTpa of CO2-equivalents in 1990 to 54GTpa in 2024, and are seen optimistically declining to 30GTpa by 2050, on a gross basis. This global CO2 emisisons breakdown covers 33 sources that each explain over 0.5% of global CO2e emissions, as a way of tracking emissions by source, by year, and…
-
Coal-to-gas switching: what CO2 abatement cost?
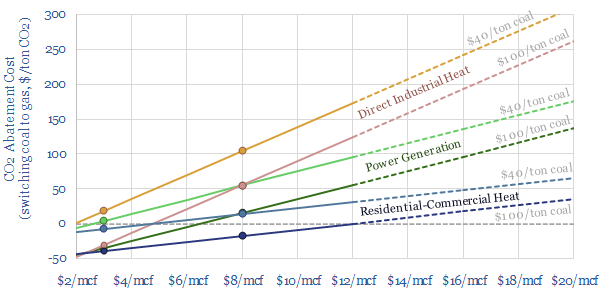
Coal-to-gas switching halves the CO2 emissions per unit of primary energy. This data-file estimates the CO2 abatement costs. Gas is often more expensive than coal. But as a rule of thumb, a $30-60/ton CO2 price makes $6-8/mcf gas competitive with $60-80/ton coal. CO2 abatement costs are materially lower in the US and after reflecting efficiency.…
-
Gas turbines and CHP: technology leaders?
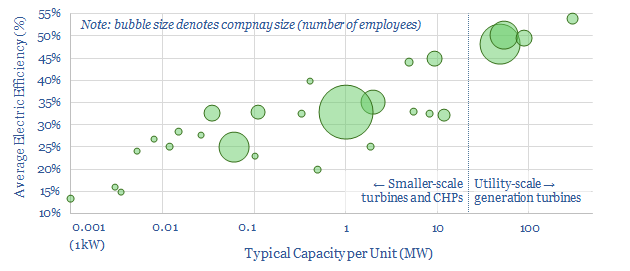
This data-file profiles 30 leading companies in gas turbines and CHPs, from mega-caps such as GE, Siemens and Mitsubishi, down to small-caps and private companies with exciting new technologies. Case studies are also presented, with details on turbine installations.
-
A new case for gas: what if renewables get overbuilt?
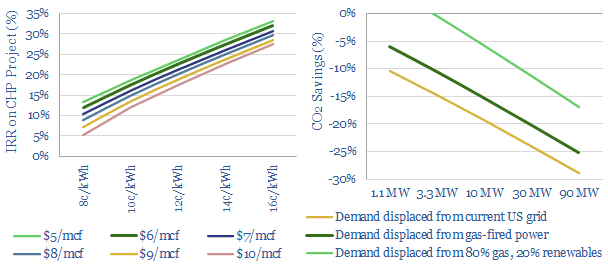
Overbuilding renewables may make power grids more expensive and less reliable. Hence more businesses may choose to generate their own power behind the meter, installing combined heat and power systems fuelled by natural gas. IRRs reach 20-30%. Efficiency is 70-80%. Total CO2 falls by 6-30%. This 17-page note outlines the opportunity.
Content by Category
- Batteries (88)
- Biofuels (44)
- Carbon Intensity (49)
- CCS (63)
- CO2 Removals (9)
- Coal (38)
- Company Diligence (93)
- Data Models (831)
- Decarbonization (159)
- Demand (110)
- Digital (58)
- Downstream (44)
- Economic Model (203)
- Energy Efficiency (75)
- Hydrogen (63)
- Industry Data (278)
- LNG (48)
- Materials (82)
- Metals (77)
- Midstream (43)
- Natural Gas (148)
- Nature (76)
- Nuclear (23)
- Oil (164)
- Patents (38)
- Plastics (44)
- Power Grids (127)
- Renewables (149)
- Screen (114)
- Semiconductors (30)
- Shale (51)
- Solar (67)
- Supply-Demand (45)
- Vehicles (90)
- Wind (43)
- Written Research (351)