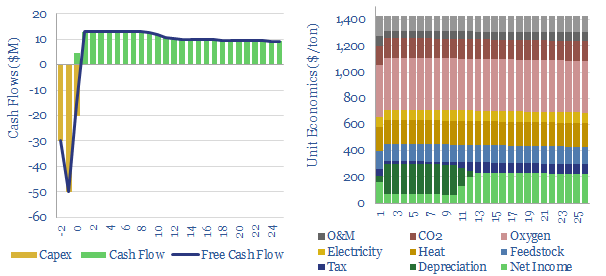
Acetylene production costs are broken down in this data-file, estimated at $1,425/ton for a 10% IRR on a petrochemical facility that partially oxidizes the methane molecule. CO2 intensity is over 3 kg/kg. Up to 12MTpa of acetylene is produced globally for welding and in petrochemicals.
Acetylene is a gas with the composition C2H4 (H-C≡C-H), formed via three main production pathways, used mostly as a petrochemical feedstock, but also in welding and metal-working. The gas was discovered by Edmund Davy in 1836. However, Walter Reppe (1892-1969) of BASF is considered the founder of modern acetylene chemistry, creating a safe process to handle acetylene at 25 bar pressures..
Market sizing data on the global acetylene market is highly variable, with different commentators reaching starkly different numbers. One reason is that many integrated petrochemical facilities produce their own acetylene on site, and only a small share of production is sold onwards. Upper estimates that have crossed our screen imply around 12MTpa of acetylene production in 2022.
Acetylene use in the petrochemical industry consumes around 70-80% of global market volumes. It is an important gas because the C≡C triple bond can easily be vinylated to produce H-X compounds. This pathway yields vinyl acetate, acrylonitrile, acetaldehyde and butane-1,4-diol for polyurethanes such as ‘spandex’. BASF discloses that up to 20 processes at Ludwigshafen use acetylene as an input.
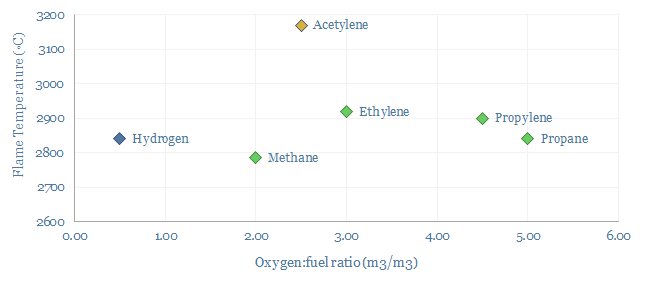
Acetylene use in the welding and metal-working industry consume around 20-30% of global market volumes. This is because of acetylene’s combustion properties, forming a very high flame temperature around 3,000◦C, high enthalpy of combustion of 50 MJ/kg, a fast flame speed of 10-12 m/s versus 2-6 m/s for other gases and a low moisture content in the exhaust gas. Oxy-acetylene flames cut quickly, saving cost. And ferrous metals are often flame hardened, to improve their longevity, which requires a hot and low moisture flame. Although we wonder whether electric arc welding will increasingly displace acetylene.
Production of acetylene occurs via three main pathways. We think the dominant process in the West is partial oxidation of methane, at very hot temperatures, around 2,000-3,000◦C. Another method purifies acetylene by-products from ethane cracking. A third pathway uses a reaction between calcium carbide and water to form C2H2 and calcium hydroxide.
Acetylene production costs are estimated at $1,425/ton in this data-file, in order to earn a 10% IRR on a large production facility, and after reflecting capex costs, feedstock gas prices, heat, electricity, cryogenic oxygen, opex costs and CO2 prices. Production costs are most sensitive to input gas prices, and recent gas prices from 2022 can result in cash costs around $2,500/ton in Europe, almost 2x normal levels.
Energy intensity is high, as the partial oxidation reaction of methane forms large quantities of CO and water vapor. 3 CH4 + 3 O2 → C2H2 + CO + 5 H2O, in order to generate high reaction temperatures that yield acetylene. We estimate the CO2 intensity of acetylene production is over 3 tons/ton (Scope 1+2 basis), which flows through to the embedded CO2 intensity of products in downstream value chains.
Companies producing acetylene include many of the usual suspects in chemicals and industrial gases, such as BASF, Linde, Air Products, Air Liquide, Praxair, LyondellBasell, Asia Technical Gas and many Chinese producers. All of our petrochemicals research is summarized here.