Search results for: “ammonia”
-
Absorption chillers: the economics?
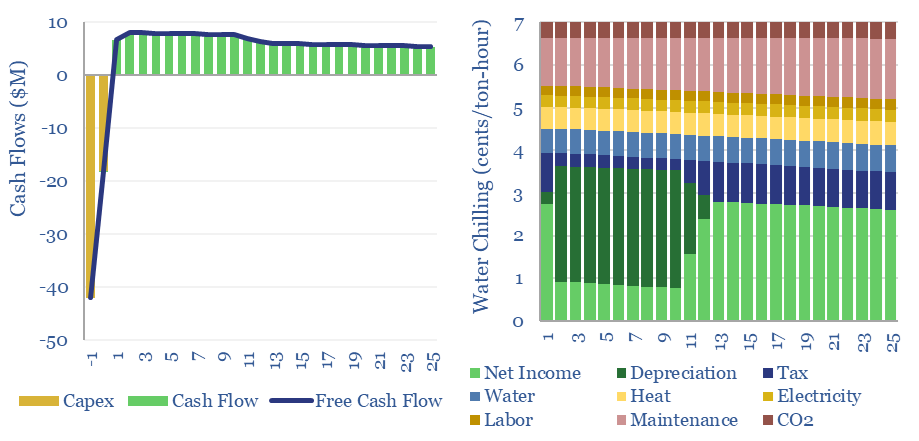
Absorption chillers perform the thermodynamic alchemy of converting waste heat into coolness. Capex costs of absorption chillers average $600/kW-th and all-in absorption chiller costs run to 6-7 cents/ton-hour, depending on the price of incoming waste heat. This data-file captures the economics of absorption chillers from first principles.
-
Nitric acid: production costs?
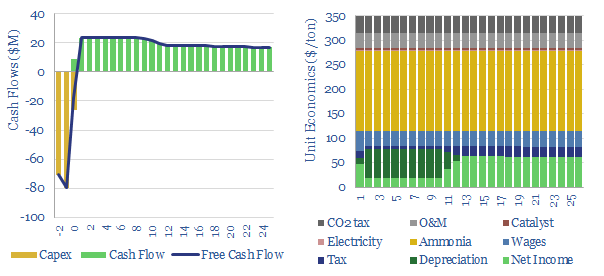
Global production of nitric acid is 60MTpa, in a $25bn pa market, spanning c500 production facilities. This data-file estimates a marginal cost of $350/ton HNO3 and a CO2 intensity averaging 1.8 tons/ton. There are feedback loops where gas shortages could result in fertilizer and metal shortages.
-
Global hydrogen supply-demand: by region, by use & over time?
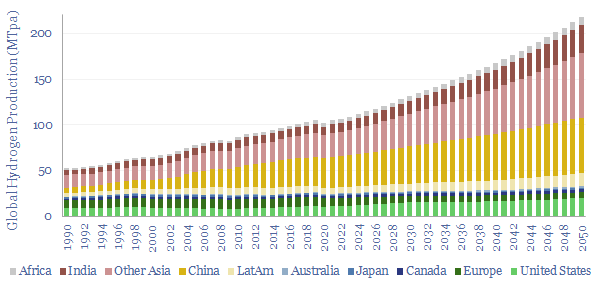
Global production of hydrogen is around 110MTpa in 2023, of which c30% is for ammonia, 25% is for refining, c20% for methanol and c25% for other metals and materials. This data-file estimates global hydrogen supply and demand, by use, by region, and over time, with projections through 2050.
-
Topsoe: autothermal reforming technology?
Topsoe autothermal reforming technology aims to maximize the uptime and reliability of blue hydrogen production, despite ultra-high combustion temperatures from the partial oxidation reaction, while achieving high energy efficiency, 90-97% CO2 capture and
-
Selective catalytic reduction: costs of NOx removal?
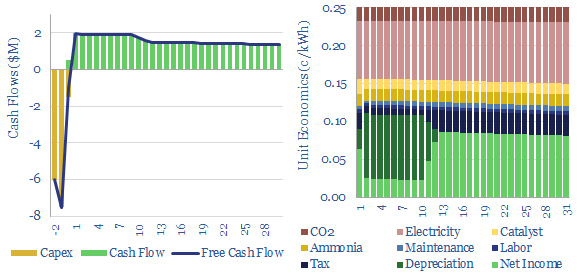
This data-file captures selective catalytic reduction costs to remove NOx from the exhaust gas of combustion boilers and burners. Our base case estimate is 0.25 c/kWh at a combined cycle gas plant, which equates to $4,000/ton of NOx removed. Capex costs, operating costs, coal plants and marine fuels can be stress-tested in the model.
-
Hydrogen: overview and conclusions?
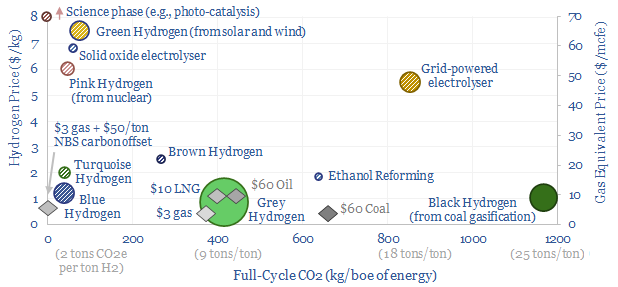
We think the best opportunities in hydrogen will be to decarbonize gas at source via blue and turquoise hydrogen, displacing ‘black hydrogen’ that currently comes from coal, and to produce small-scale feedstock on site via electrolysis for select industries. Others see green hydrogen as a cornerstone of the future energy system. We think there may…
-
Cryogenic air separation: costs and energy economics?
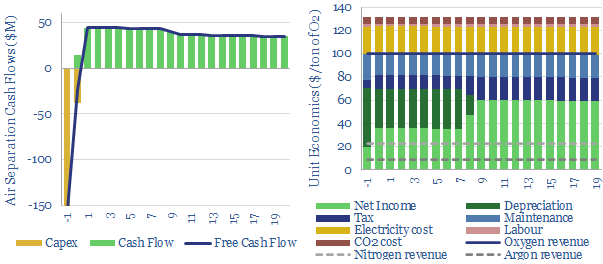
This data-file calculates the costs of cryogenic air separation units, which are important in the production of industrial gases, ammonia, metals, materials, medical applications and new energy technologies such as blue hydrogen. Good base cases are $100/ton oxygen, $20/ton nitrogen, $200/Tpa capex and 60kWh/ton of electricity (on an input air basis).
-
Energy economics: energy content of combustion fuels?
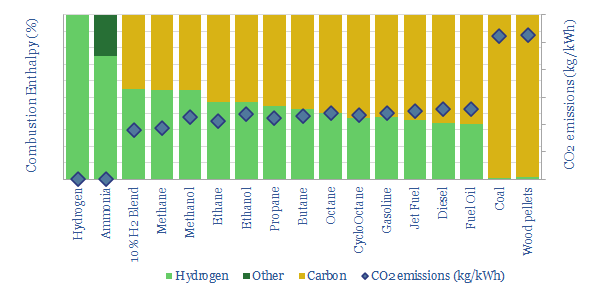
The purpose of this data-file is to disaggregate the energy economics of combusting different fuels, including natural gas, different oil products, NGLs, coal, hydrogen, methanol, ammonia et al. The most effective way to blend more hydrogen into the energy mix is coal-to-gas switching, followed by using lighter oil products.
-
Industrial gases: air separation units?
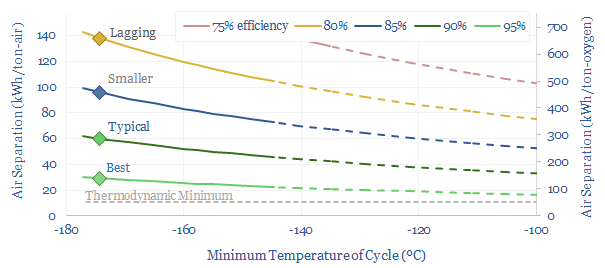
Cryogenic air separation is used to produce 400MTpa of oxygen, plus pure nitrogen and argon; for steel, metals, ammonia, wind-solar inputs, semiconductor, blue hydrogen and Allam cycle oxy-combustion. Hence this 16-page report is an overview of industrial gases. How does air separation work? What costs, energy use and CO2 intensity? Who benefits amidst the energy…
-
Commodity demand: how sensitive to GDP growth?
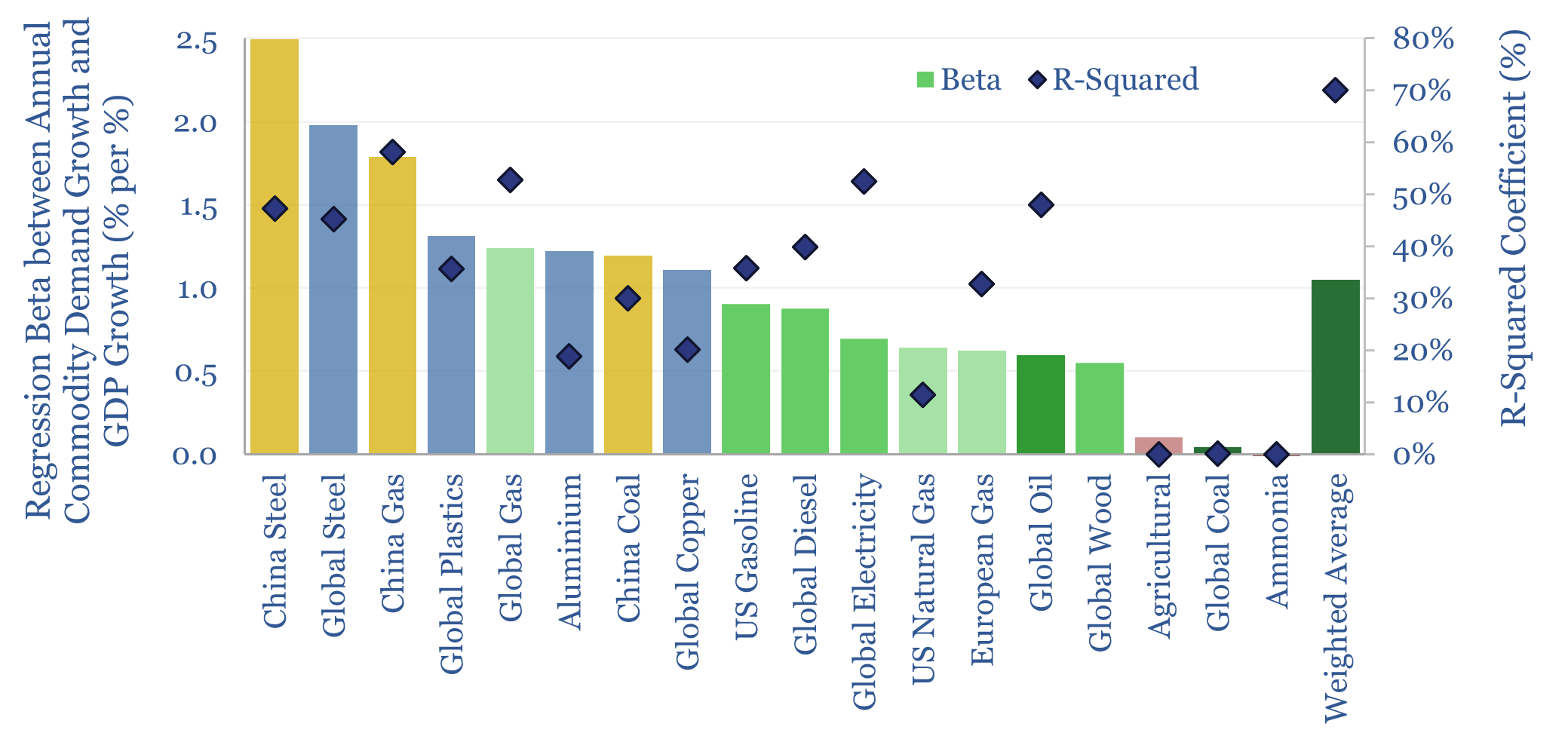
How sensitive is global commodity demand to GDP growth? This 15-page report runs regressions for 25 commodities. Slower GDP growth matters most for oil markets, which are entering a new, more competitive, era. China is also slowing. But we still see bright spots in gas, metals, materials in our 2025 commodity outlook.
Content by Category
- Batteries (89)
- Biofuels (44)
- Carbon Intensity (49)
- CCS (63)
- CO2 Removals (9)
- Coal (38)
- Company Diligence (94)
- Data Models (838)
- Decarbonization (160)
- Demand (110)
- Digital (59)
- Downstream (44)
- Economic Model (204)
- Energy Efficiency (75)
- Hydrogen (63)
- Industry Data (279)
- LNG (48)
- Materials (82)
- Metals (80)
- Midstream (43)
- Natural Gas (148)
- Nature (76)
- Nuclear (23)
- Oil (164)
- Patents (38)
- Plastics (44)
- Power Grids (130)
- Renewables (149)
- Screen (117)
- Semiconductors (32)
- Shale (51)
- Solar (68)
- Supply-Demand (45)
- Vehicles (90)
- Wind (44)
- Written Research (354)