Search results for: “climate model”
-
Fully subsea offshore projects: the economics?
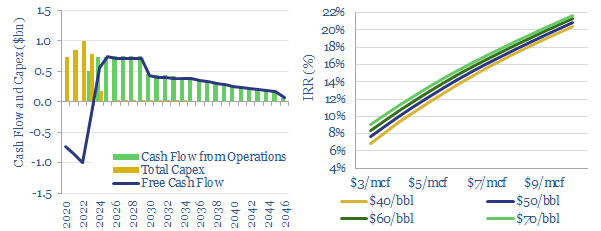
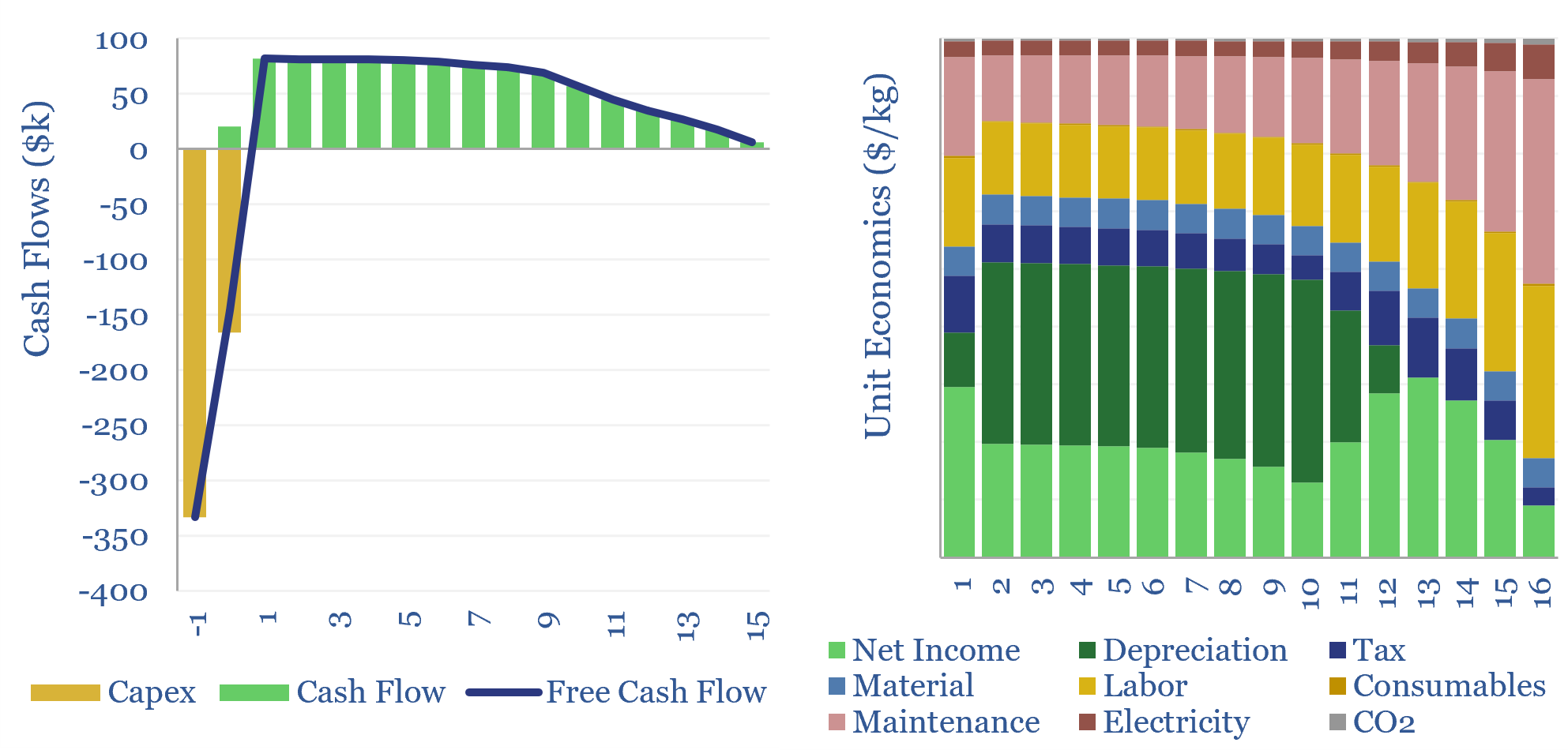
The model presents the economic impacts of developing a typical, 625Mboe offshore gas condensate field using a fully subsea solution, compared against installing a new production facility. The result is a c4% uplift in IRRs, a 50% uplift in NPV6 and a 33% reduction in the project’s gas-breakeven price. The economics are attractive.
-
COVID-19 Impacts on Global Oil Demand?
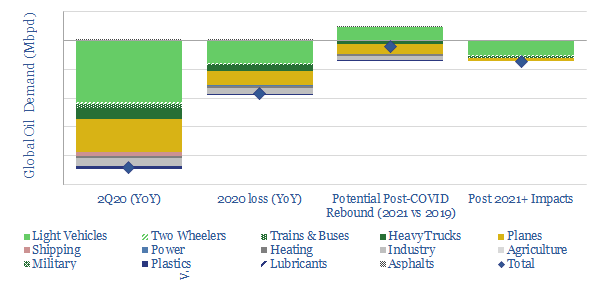
Global oil demand could decline -22Mbpd YoY in 2Q20, due to COVID-19, with losses averaging 9-12 Mbpd across 2020. Our model looks line-by-line around the global oil market, to help you stress-test your own scenarios under different input assumptions.
-
Restoring soil carbon: the economics?
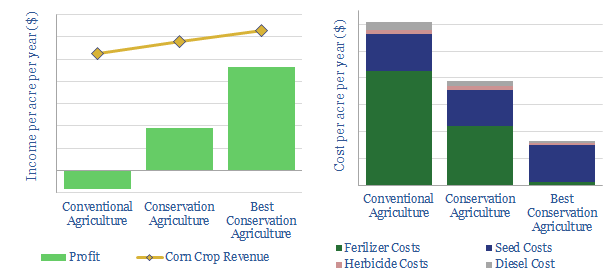
We model the economics for conservation agriculture to restore soil carbon. 5-30T of CO2 can be sequestered per acre per year, while deflating farm costs by 36-73% and raising yields 10-20%. This would transform crop-growing economics from marginal to material.
-
Jet fuel demand: by region and forecasts to 2050?
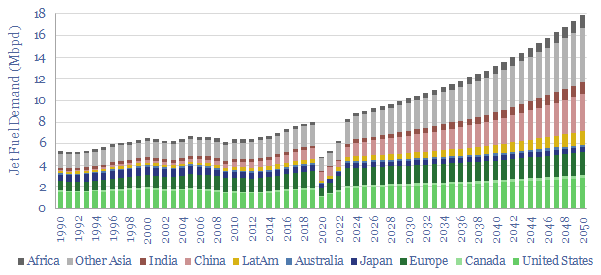
Jet fuel demand ran at 8Mbpd in 2019, the last year before COVID, and could rise to 18Mbpd by 2050, as global population rises 25%, jet fuel demand per capita doubles and fuel economy per aviation mile rises by 20%. This data file breaks down jet fuel demand by region, including our forecasts through 2050,…
-
Renewable diesel: the economics?
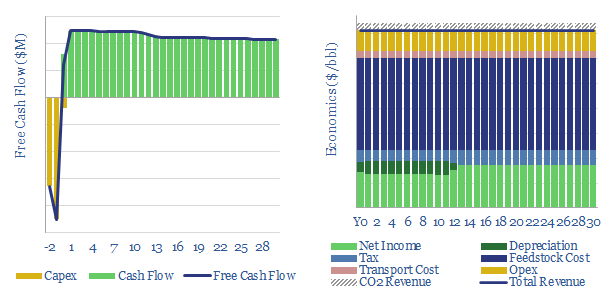
Our base case is that a US renewable diesel facility must achieve $4.6/gallon sales revenues (which is c$200/bbl) as it commercializes a product with up to 75% lower embedded emissions than conventional diesel. Similarly, a bio-diesel facility must achieve $3.6/gallon sales on a product with 60% lower embedded emissions.
-
Waste heat recovery: heat exchanger costs?
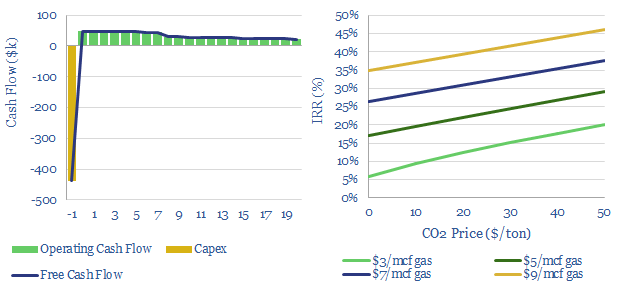
Industrial heat comprises around 20% of global CO2 emissions, but around half of all heat generated may ultimately be wasted. Hence, this model simplifies the economics of using a heat exchanger to recover waste heat. A CO2 price above $50/ton would greatly accelerate waste heat recovery projects.
-
Transporting green hydrogen as ammonia or toluene?
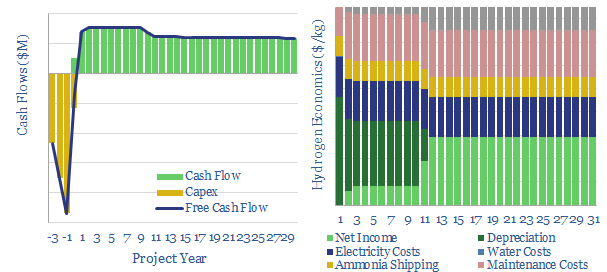
Green hydrogen could be converted into ammonia, shipped like LPGs, then cracked back into green hydrogen in a developed world country. The best case costs are around $10/kg, while generating an IRR of 10%, with full, round-trip energy efficiency of c60%.
-
Exhaust gas recirculation in gas power: the economics?
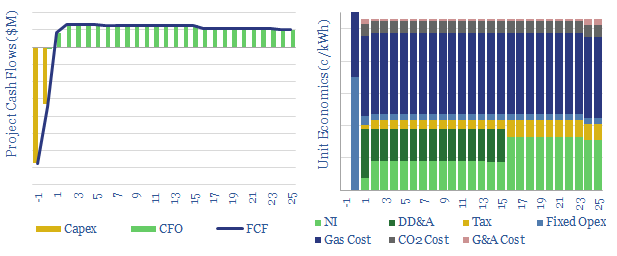
This data-file explores an alternative design for a combined cycle gas turbine, re-circulating exhaust gases after combustion, in order to facilitate CO2 capture. Costs and operating parameters are summarized from recent technical papers. Even with EGR, it will be challenging to decarbonize a gas turbine for less than $100/ton.
-
Turbo-charge gas turbines: the economics?
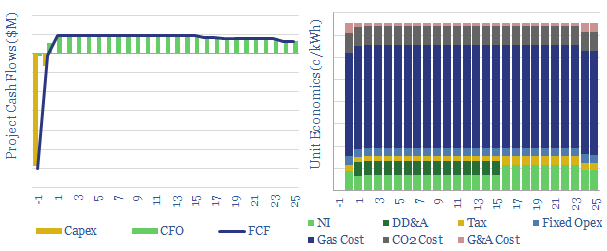
This data-file models the economics of turbo-charging gas turbines, which increases the mass flow of combustion air, to improve their power ratings by c10-20%. IRRs are solid. Turbo-charged gas turbines could thus gain greater share as grids become saturated with renewables
Content by Category
- Batteries (87)
- Biofuels (42)
- Carbon Intensity (49)
- CCS (63)
- CO2 Removals (9)
- Coal (38)
- Company Diligence (92)
- Data Models (824)
- Decarbonization (159)
- Demand (110)
- Digital (58)
- Downstream (44)
- Economic Model (201)
- Energy Efficiency (75)
- Hydrogen (63)
- Industry Data (276)
- LNG (48)
- Materials (81)
- Metals (76)
- Midstream (43)
- Natural Gas (146)
- Nature (76)
- Nuclear (23)
- Oil (164)
- Patents (38)
- Plastics (44)
- Power Grids (124)
- Renewables (149)
- Screen (112)
- Semiconductors (30)
- Shale (51)
- Solar (67)
- Supply-Demand (45)
- Vehicles (90)
- Wind (43)
- Written Research (348)