Search results for: “heat pumps”
-
Grid connection sizes: residential, commercial and industrial?
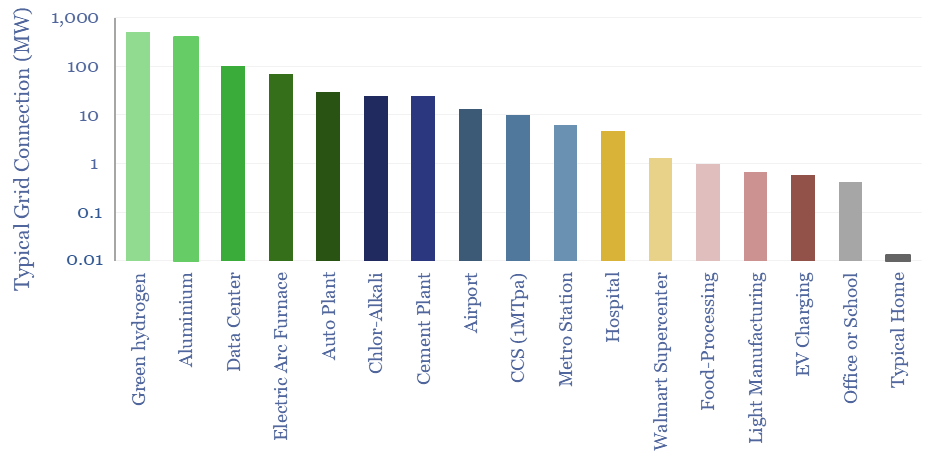
What are the typical sizes of grid connections at different residential, commercial and industrial facilities? This data-file derives aggregates estimates, from the 10kW grid connections of smaller homes to the GW-scale grid connections of large data-centers, proposed green hydrogen projects and aluminium plants.
-
CO2 intensity: Scope 1, 2 & 3 and Scope 4 emissions?
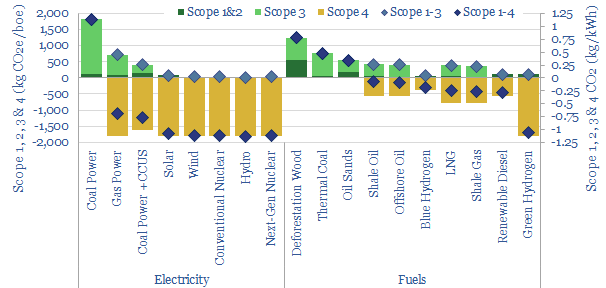
Scope 4 CO2 emissions capture the CO2 that is avoided by use of a product. Many energy investments with positive Scope 1-3 emissions have deeply negative Scope 1-4 emissions. Numbers are quantified and may offer a more constructive approach to decarbonization investments.
-
Residential energy consumption over time?
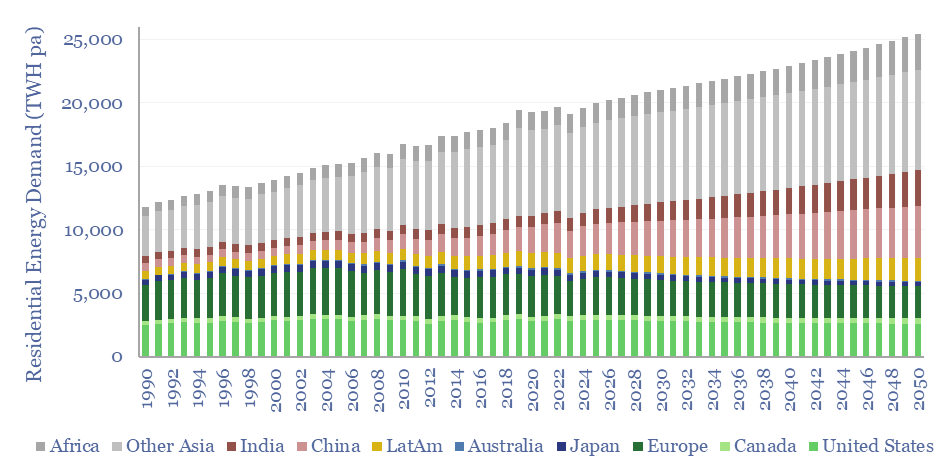
Global residential energy demand runs at 2.5 MWH pp pa, of which c40% is from electricity, 40% is gas, c13% is biomass and c7% is oil. In our gas and power models, electrification rises to 65% by 2050, to help renewables reach 50% of global electricity. Heat pumps improve efficiency and lower primary demand in the developed world.
-
Power capacity of a typical home?
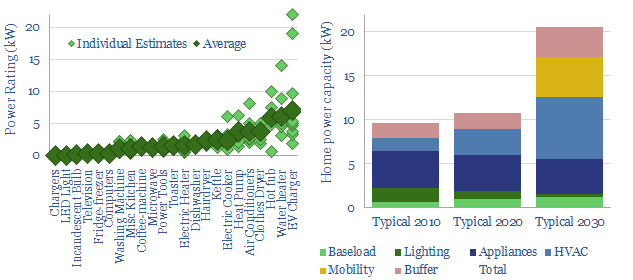
A typical home in the developed world currently has a 10kW maximum power capacity before tripping its circuit-breaker (although it varies). This could easily double in the energy transition, due to phasing back gas heating, gas cooking and the addition of home charging stations for electric vehicles.
-
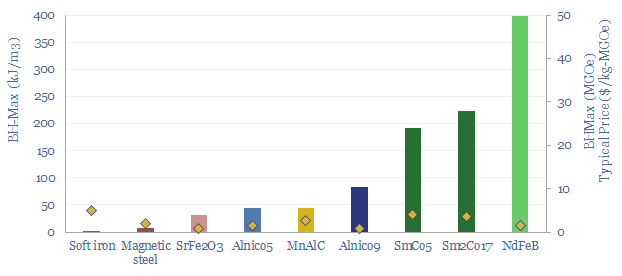
Magnets and permanent magnets: company screen?
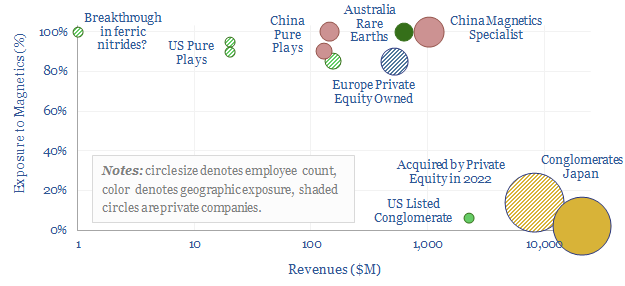
The global magnet industry is fragmented across hundreds of suppliers, including 800 in Asia-Pacific. The total market is worth $20bn pa. The purpose of this data-file is to highlight a dozen leading magnet companies, including producers of permanent magnets, Rare Earth magnets (e.g., NdFeB), ferrites and other magnetic components.
-
Hydrofluoric acid: the economics?
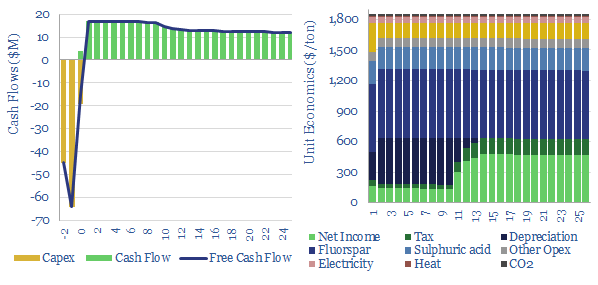
Hydrogen fluoride is a crucial commodity chemical. This model captures its production from acid-grade fluorspar and sulfuric acid. We think marginal costs are around $1,850/ton, in order to earn a 10% IRR on a production facility costing $4,000/Tpa, while the fully loaded CO2 intensity is around 0.75 tons/ton.
-
Organic Rankine Cycles: the energy economics?
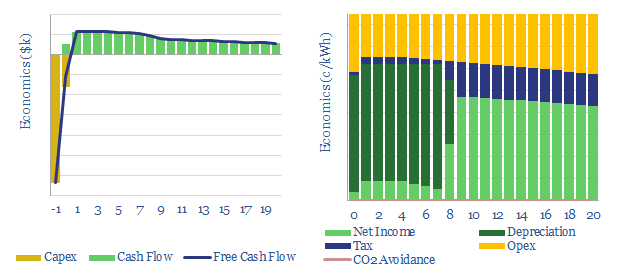
This data-file captures the energy economics of an Organic Rankine Cycle to recover low-grade waste heat (at 70-200C) from an industrial facility, or in the geothermal industry. A CO2 price of $50-75/ton could greatly accelerate adoption and improve the efficiency of industrial facilities.
-
Combined heat and power turbines: market sizing?
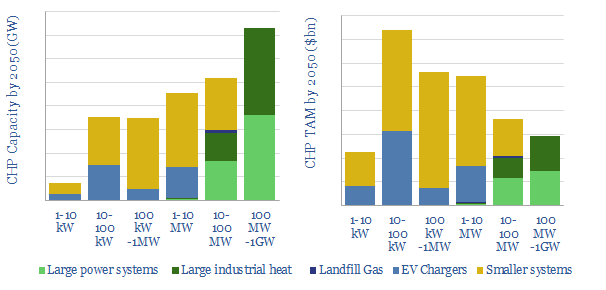
The purpose of this data-file is to ballpark the ultimate potential market size for combined heat and power systems in the US (CHPs). Our build-up looks across five main categories: large power facilities, large industrial heating facilities, landfill gas, electric vehicle charging and smaller-scale commercial and multi-family usage.
-
Absorption chillers: the economics?
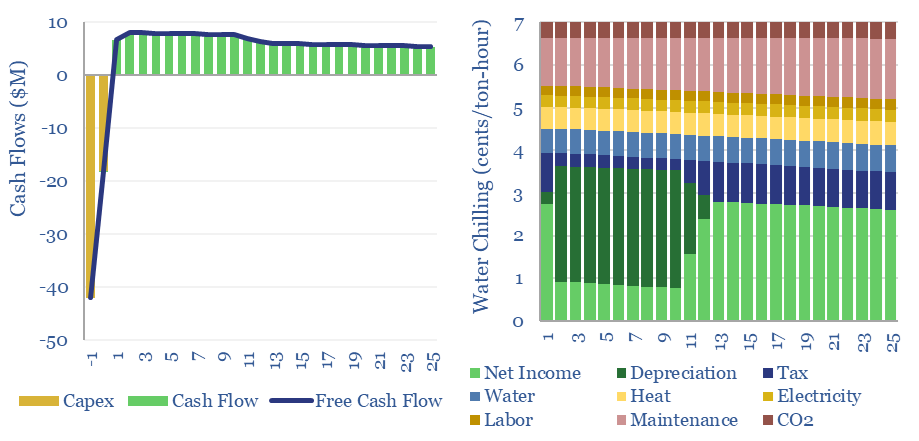
Absorption chillers perform the thermodynamic alchemy of converting waste heat into coolness. Capex costs of absorption chillers average $600/kW-th and all-in absorption chiller costs run to 6-7 cents/ton-hour, depending on the price of incoming waste heat. This data-file captures the economics of absorption chillers from first principles.
Content by Category
- Batteries (88)
- Biofuels (44)
- Carbon Intensity (49)
- CCS (63)
- CO2 Removals (9)
- Coal (38)
- Company Diligence (92)
- Data Models (830)
- Decarbonization (159)
- Demand (110)
- Digital (58)
- Downstream (44)
- Economic Model (203)
- Energy Efficiency (75)
- Hydrogen (63)
- Industry Data (278)
- LNG (48)
- Materials (82)
- Metals (77)
- Midstream (43)
- Natural Gas (146)
- Nature (76)
- Nuclear (23)
- Oil (164)
- Patents (38)
- Plastics (44)
- Power Grids (126)
- Renewables (149)
- Screen (114)
- Semiconductors (30)
- Shale (51)
- Solar (67)
- Supply-Demand (45)
- Vehicles (90)
- Wind (43)
- Written Research (350)