Search results for: “renewables”
-
Enhanced geothermal: technology challenges?
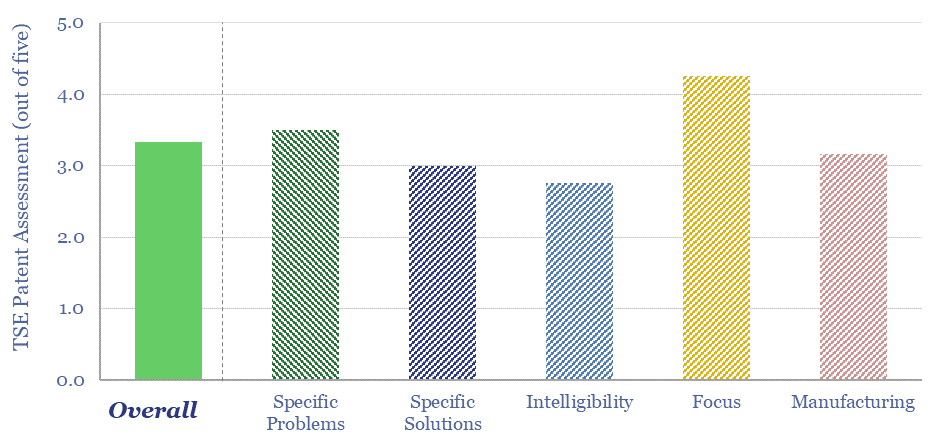
This data-file tabulates the greatest challenges and focus areas for harnessing deep geothermal energy, based on reviewing 30 recent patents from 20 companies in the space. We conclude that recent advances from the unconventional oil and gas industry are going to be a crucial enabler.
-
Hydro electric power: the economics?
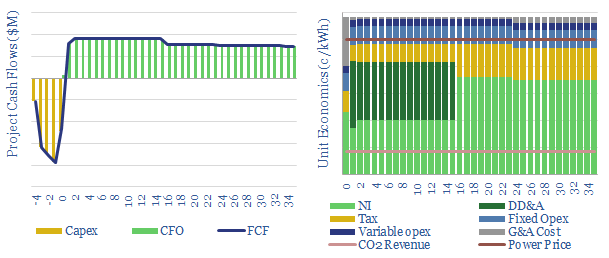
A typical hydro project requires a 10c/kWh power price and a $50/ton CO2 price to generate an unlevered IRR of 10%. 80% of the cost is capex. Hence at a 6% hurdle rate, the incentive price falls to 6c/kWh. Cash opex is 2c/kWh. CO2 intensity is effectively nil, even after reflecting the construction energy.
-
Onshore wind: the economics?
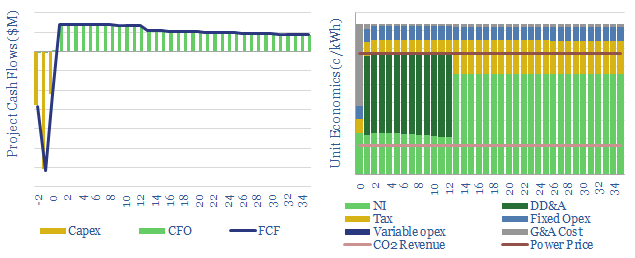
The levelized cost of onshore wind is estimated in this economic model, at 5-7c/kWh to generate 5-10% levered IRRs on new wind project costing $1,000-3,000/kW. The model also contains a granular breakdown of wind capex costs, operating costs, and other economic assumptions for wind projects.
-
Uranium mining: the economics?
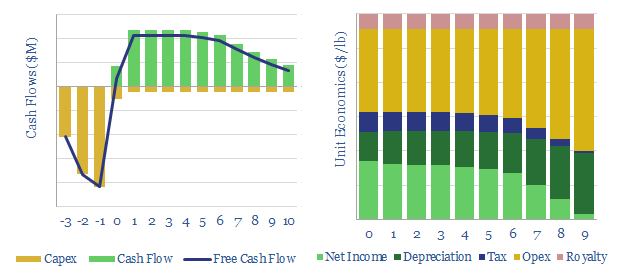
This data-file disaggregates the marginal costs of a new uranium mine, as a simple function of uranium prices, ore grade, capex and opex. Our base case is a marginal cost of $60/lb for a 10% IRR. Cash costs range from $7-40/lb. But lower ore grades can easily require $90/lb uranium to justify investment.
-
Power-to-liquids: the economics?
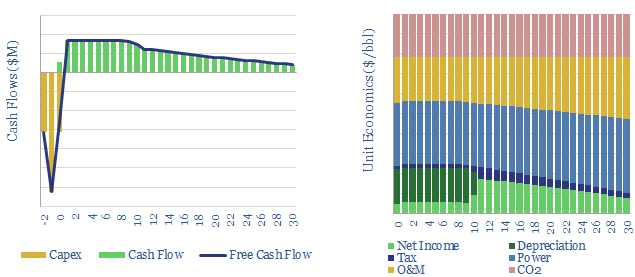
Liquid transport fuels with almost no CO2 emissions could be created from renewable energy, by electrolysing water and CO2, then combining the hydrogen and CO, e.g., via Fischer Tropsch. This simple models stress tests the economics. Our base case estimates are for costs between $400-600/bbl ($10-14/gallon).
-
Ethanol from corn: the economics?
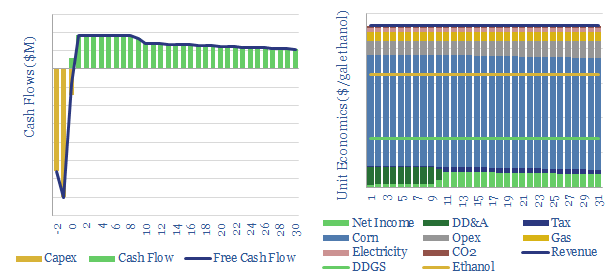
This data-file captures the economics of producing ethanol from corn. Our base case requires a price of $1.6/gallon of ethanol for a 10% IRR on a new greenfield plant, equivalent to $2.4/gallon gasoline. 40% of the US corn crop is diverted into biofuels, but the rationale is marginal.
-
Power-to-liquids: companies commercializing electro-fuels?
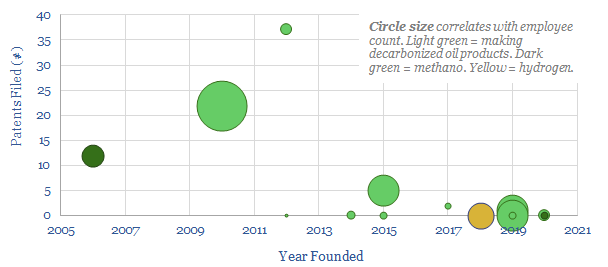
This data-file summarizes the details of c15 companies aiming to commercialise low-carbon electro-fuels, using power-to-liquids technologies, and their progress to-date. The average company was founded in 2015, with 5 patents and 15 employees. Although this is skewed towards 3-4 leaders.
-
Photovoltaic silicon: the economics?
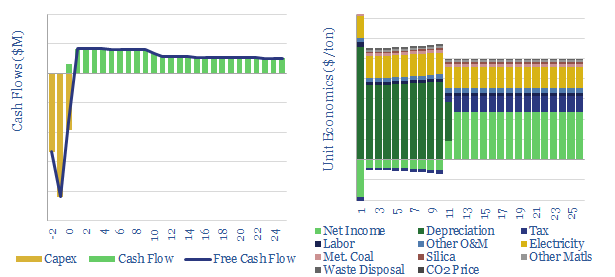
This model breaks down the costs of photovoltaic silicon, which explains $0.1/W of a $0.3/W solar panel. There is no way silicon producers are making economic returns below $12.5/kg mono-crystalline polysilicon prices. The average kg of PV silicon in a solar panel is also most likely associated with 140kg of direct CO2.
-
Solar costs: four horsemen?
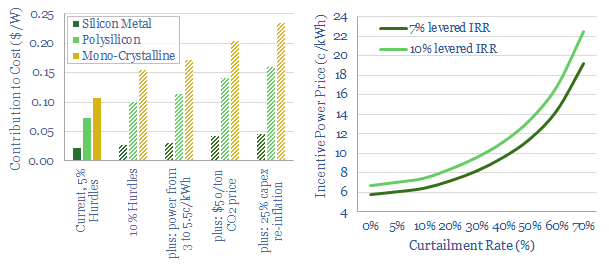
Solar costs have deflated by an incredible 90% in the past decade to 4-7c/kWh. Some commentators now hope for 2c/kWh by 2050. Further innovations are doubtless. But there are four challenges, which could stifle future deflation or even re-inflate solar. Most debilitating would be a re-doubling of CO2-intensive PV-silicon?
-
Array Technologies: solar tracking breakthrough?
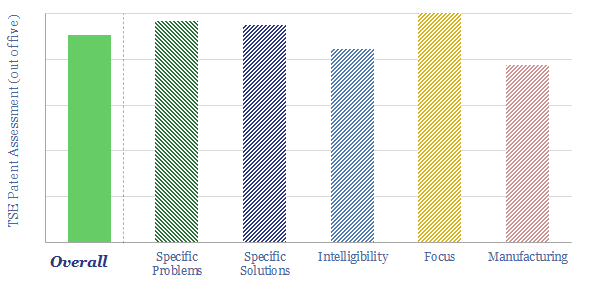
Array Technologies IPO-ed in October-2020. It manufactures solar tracking systems, supporting 25% of US solar modules installed to date. Its systems can uplift solar generation by 5-25%. we found clear, specific, intelligible patents, back-stopping six out of seven key strengths that have been cited by the company.
Content by Category
- Batteries (88)
- Biofuels (44)
- Carbon Intensity (49)
- CCS (63)
- CO2 Removals (9)
- Coal (38)
- Company Diligence (93)
- Data Models (831)
- Decarbonization (159)
- Demand (110)
- Digital (58)
- Downstream (44)
- Economic Model (203)
- Energy Efficiency (75)
- Hydrogen (63)
- Industry Data (278)
- LNG (48)
- Materials (82)
- Metals (77)
- Midstream (43)
- Natural Gas (148)
- Nature (76)
- Nuclear (23)
- Oil (164)
- Patents (38)
- Plastics (44)
- Power Grids (127)
- Renewables (149)
- Screen (114)
- Semiconductors (30)
- Shale (51)
- Solar (67)
- Supply-Demand (45)
- Vehicles (90)
- Wind (43)
- Written Research (351)