Search results for: “climate model”
-
CO2-Cured Concrete: Solidia vs traditional cement?
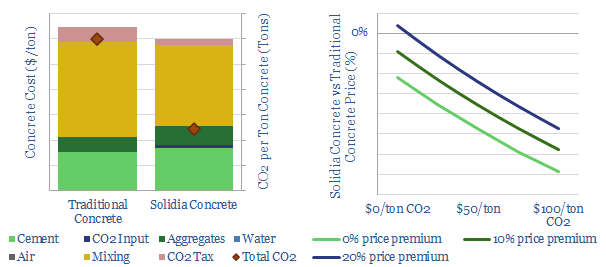
CO2-cured concrete has c60% lower emissions than traditional concrete, which is the most widely used construction material on the planet, comprising 4bn tons of annual CO2 emissions, or 8% of the global total. This data-file profiles the CO2 and economic costs of Solidia versus traditional cement, to size the opportunity.
-
Nuclear Power Project Economics
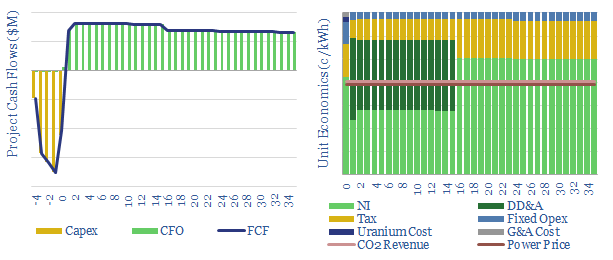
This data-file models the costs of nuclear power project, based on technical papers and past projects around the industry. An up-front capex cost of $6,000/kW might yield a levelized cost of 15c/kWh. But 6-10c/kWh is achievable via a renaissnace in next-generation nuclear.
-
Land intensity of energy transition: acres per MW and per ton?
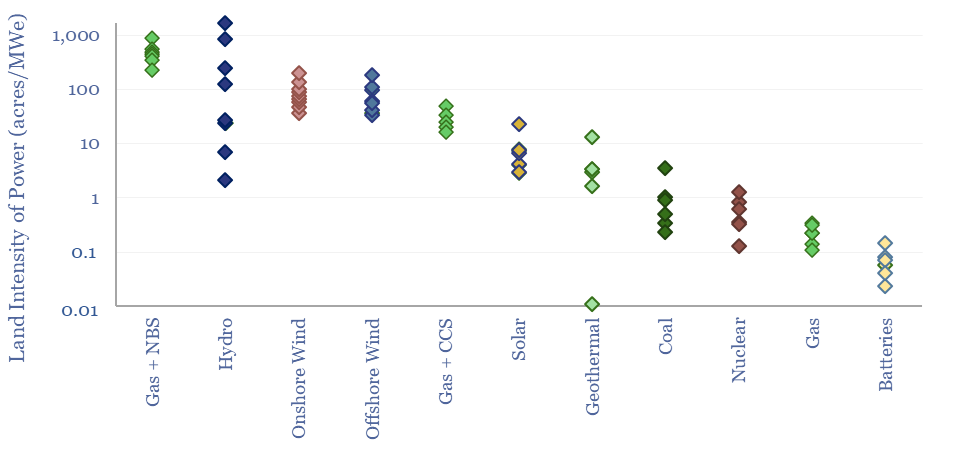
This data-file compares the land intensity of energy technologies and energy transition technologies. Land use is estimated in acres per MW of power generation, or in tons of CO2-equivalents abated per acre per year. Numbers vary by an order of magnitude. Data are sourced from technical papers and our broader work.
-
Refrigeration and phase change materials: energy economics?
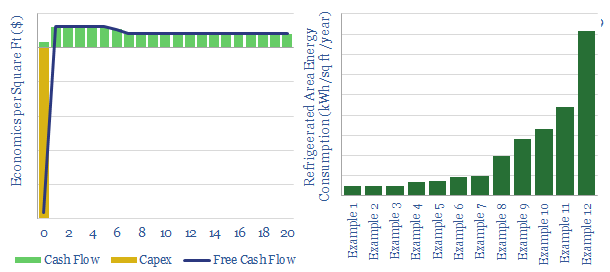
This data-file contains our numbers and analysis into the energy economics of phase change materials: an emerging class of materials, which can store and release heat by changing from solid to liquid phases. We quantify costs, IRRs and energy consumption of typical cold storage facilities.
-
US gas power: generation by facility over time?
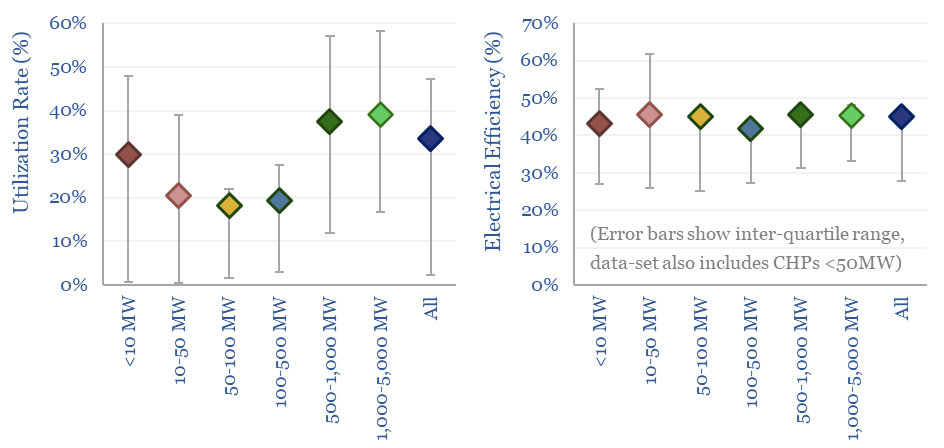
US gas power generation by facility is broken down in this data-file, across 1,850 active gas-power plants, supplying 40% of all US electricity. Descriptive statistics are available in the summary tab, a state-by-state breakdown follows in the PlantsByState tab and underlying data on all 3,000 historical facilities are provided in the AllGasPlants tab.
-
Fuel cells: performance, efficiency and decline rates?
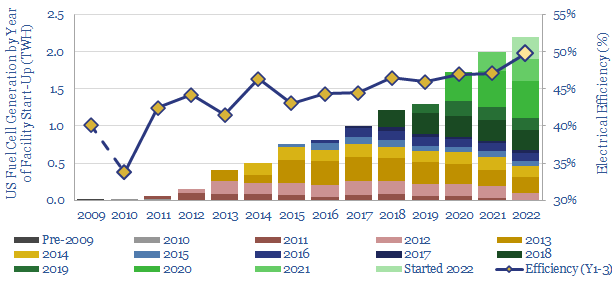
This data-file captures the performance of c160 fuel cell power plants, installed to-date in the US, generating over 2TWH of electricity, looking facility-by-facility, year-by-year. How has the performance, efficiency and longevity of US fuel cell power plants been trending over time?
-
Floating offshore wind: what challenges?
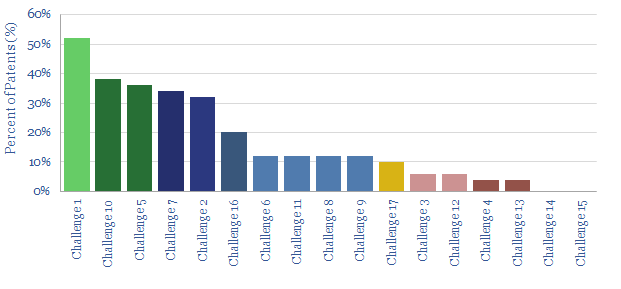
A dozen challenges for floating offshore wind projects are ranked in this 4-page note, by reviewing 50 recent patents across the industry. We model these challenges are likely to double capex and levelized costs, compared with traditional offshore wind. The potential for floating offshore wind is also location dependent.
-
Solid oxide fuel cells: what challenges?
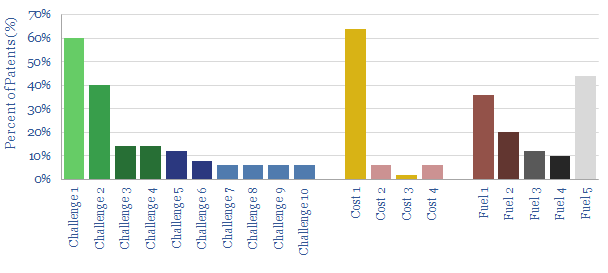
This data-file reviews fifty patents into solid oxide fuel cells, filed by leading companies in 2020. The key focus areas are improving the longevity and efficiency of SOFCs. But unfortunately, we find many of the proposed solutions are likely to increase end costs. Potential is interesting, but deflation may take longer.
-
CO2 electrolysis: the economics?
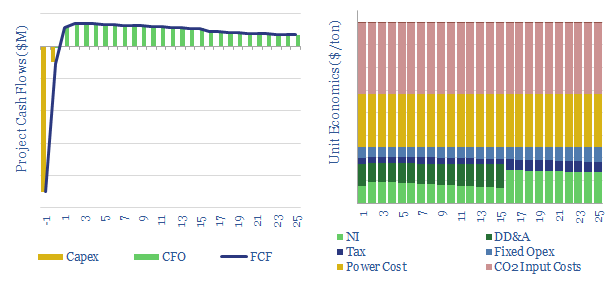
Carbon monoxide is an important chemical input for metals, materials and fuels. Could it be produced by capturing CO2 from the atmosphere or using the amine process, then electrolysing the CO2 into CO and oxygen? We find 10% IRRs could be achievable at $800/ton, competitive with conventional syngas.
Content by Category
- Batteries (89)
- Biofuels (44)
- Carbon Intensity (49)
- CCS (63)
- CO2 Removals (9)
- Coal (38)
- Company Diligence (95)
- Data Models (839)
- Decarbonization (160)
- Demand (110)
- Digital (60)
- Downstream (44)
- Economic Model (204)
- Energy Efficiency (75)
- Hydrogen (63)
- Industry Data (279)
- LNG (48)
- Materials (82)
- Metals (80)
- Midstream (43)
- Natural Gas (148)
- Nature (76)
- Nuclear (23)
- Oil (164)
- Patents (38)
- Plastics (44)
- Power Grids (130)
- Renewables (149)
- Screen (117)
- Semiconductors (32)
- Shale (51)
- Solar (68)
- Supply-Demand (45)
- Vehicles (90)
- Wind (44)
- Written Research (354)